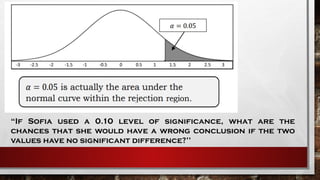
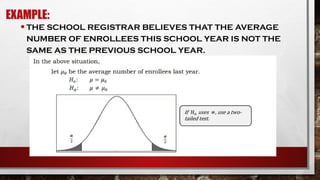
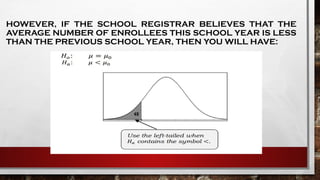
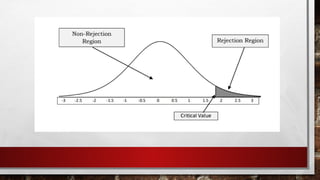
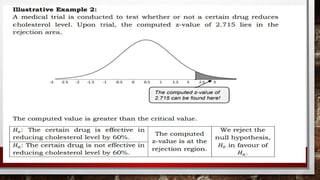
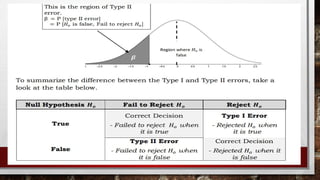
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method for making decisions based on experimental data, involving the evaluation of an assumption about a population. It consists of a null hypothesis (no significant difference) and an alternative hypothesis (indicating a real effect), with a four-step process for testing. Statistical significance is influenced by a level of significance (alpha), determining the likelihood of incorrect conclusions when the null hypothesis is true.