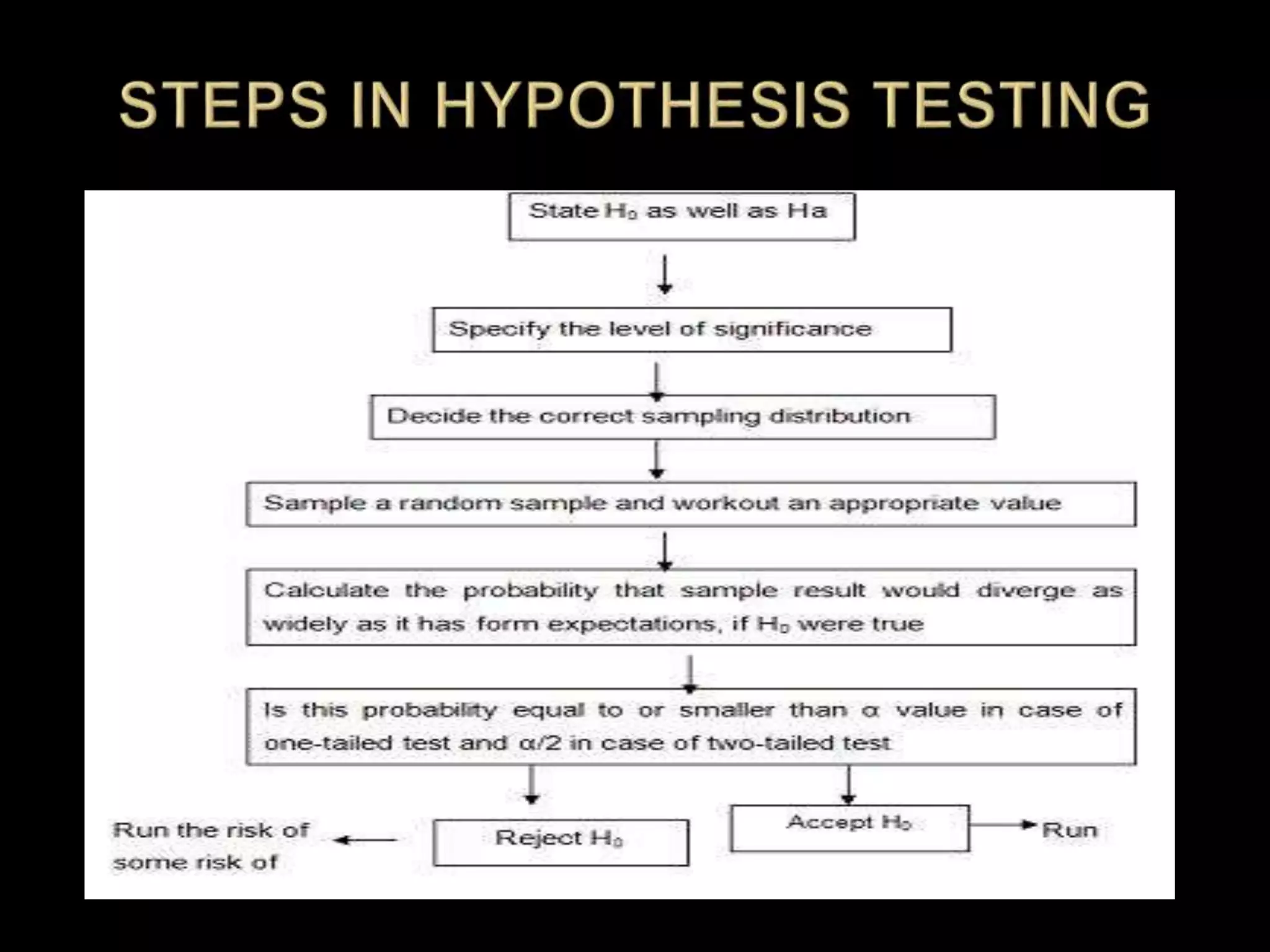
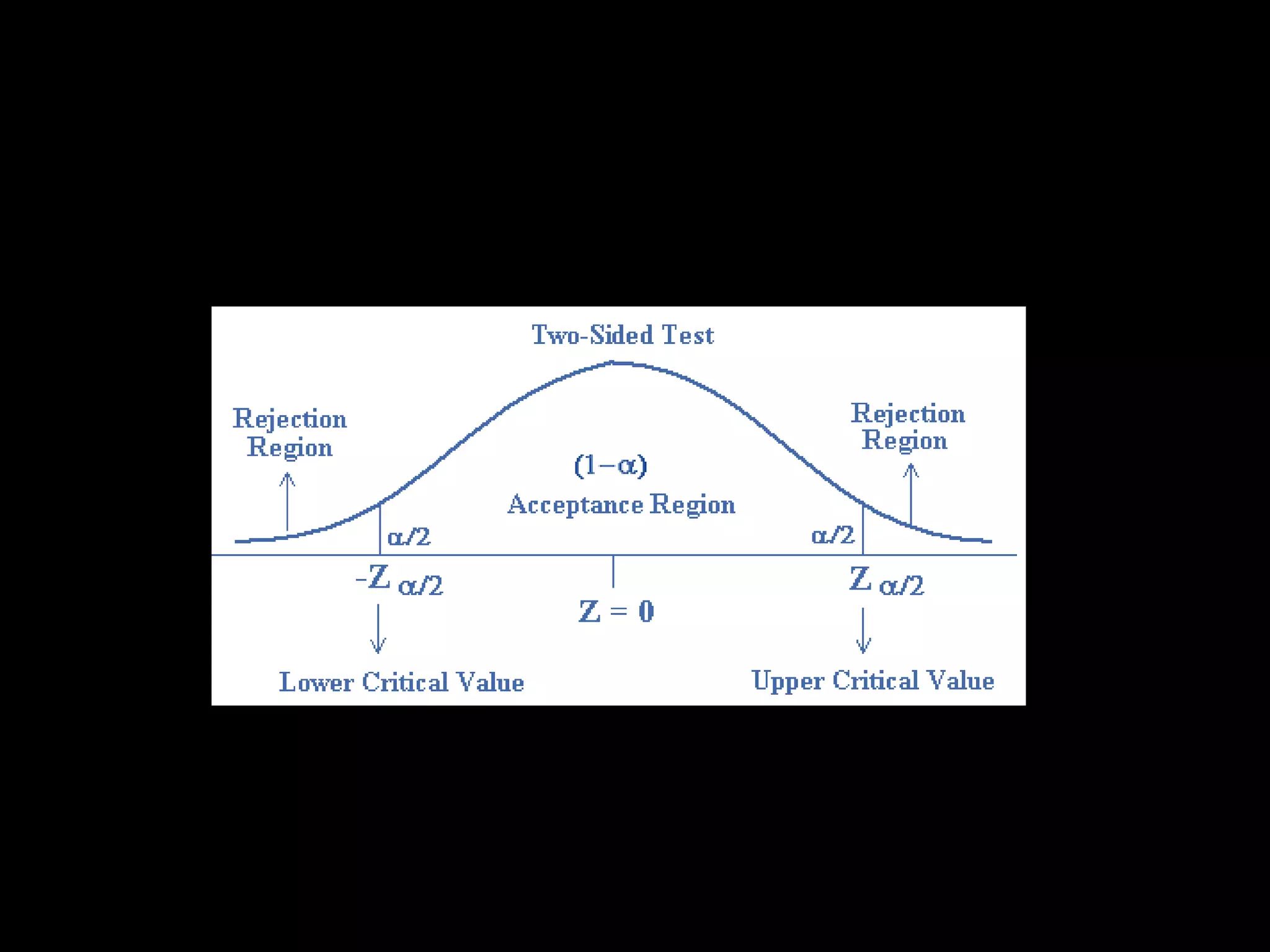
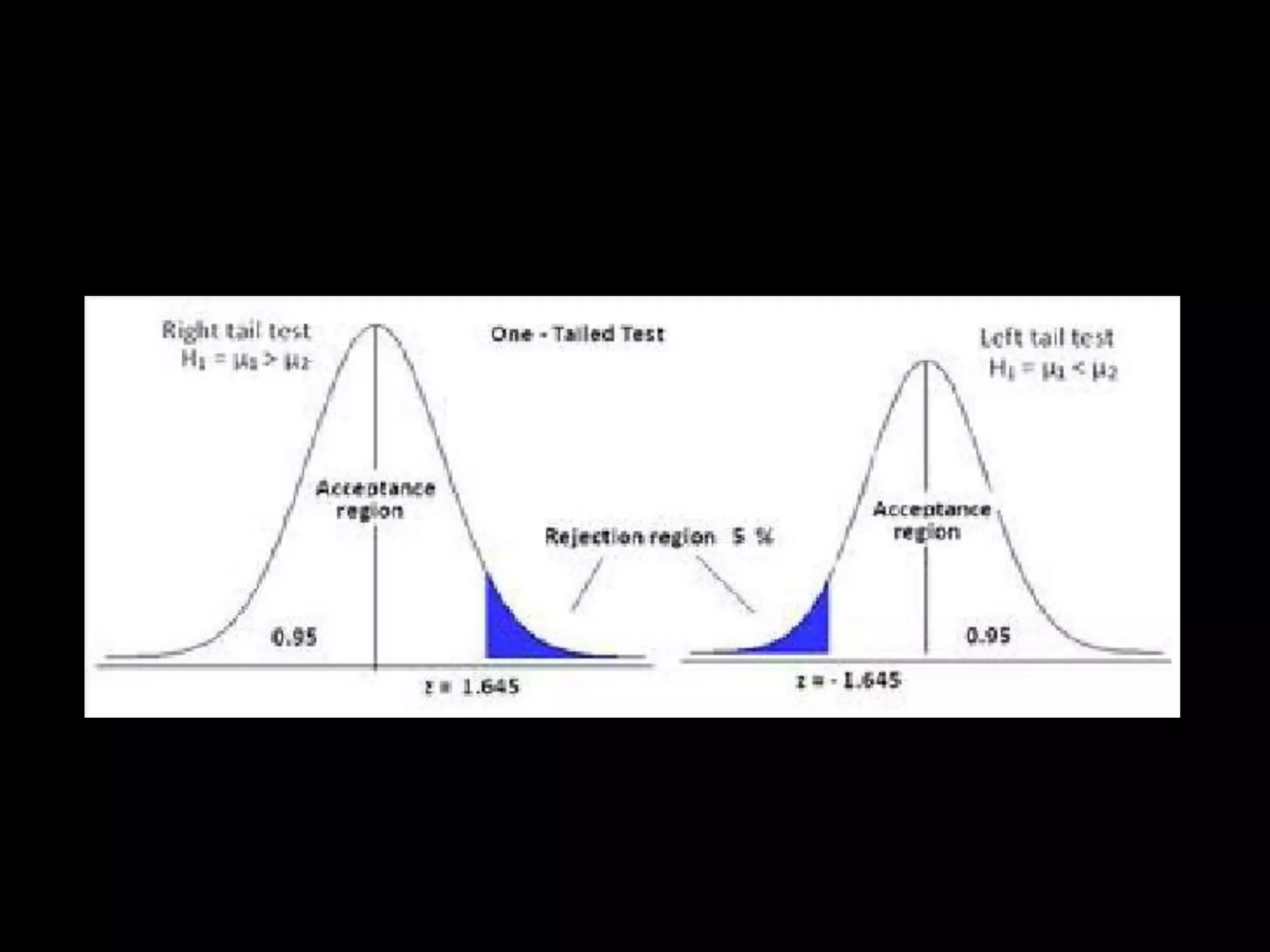
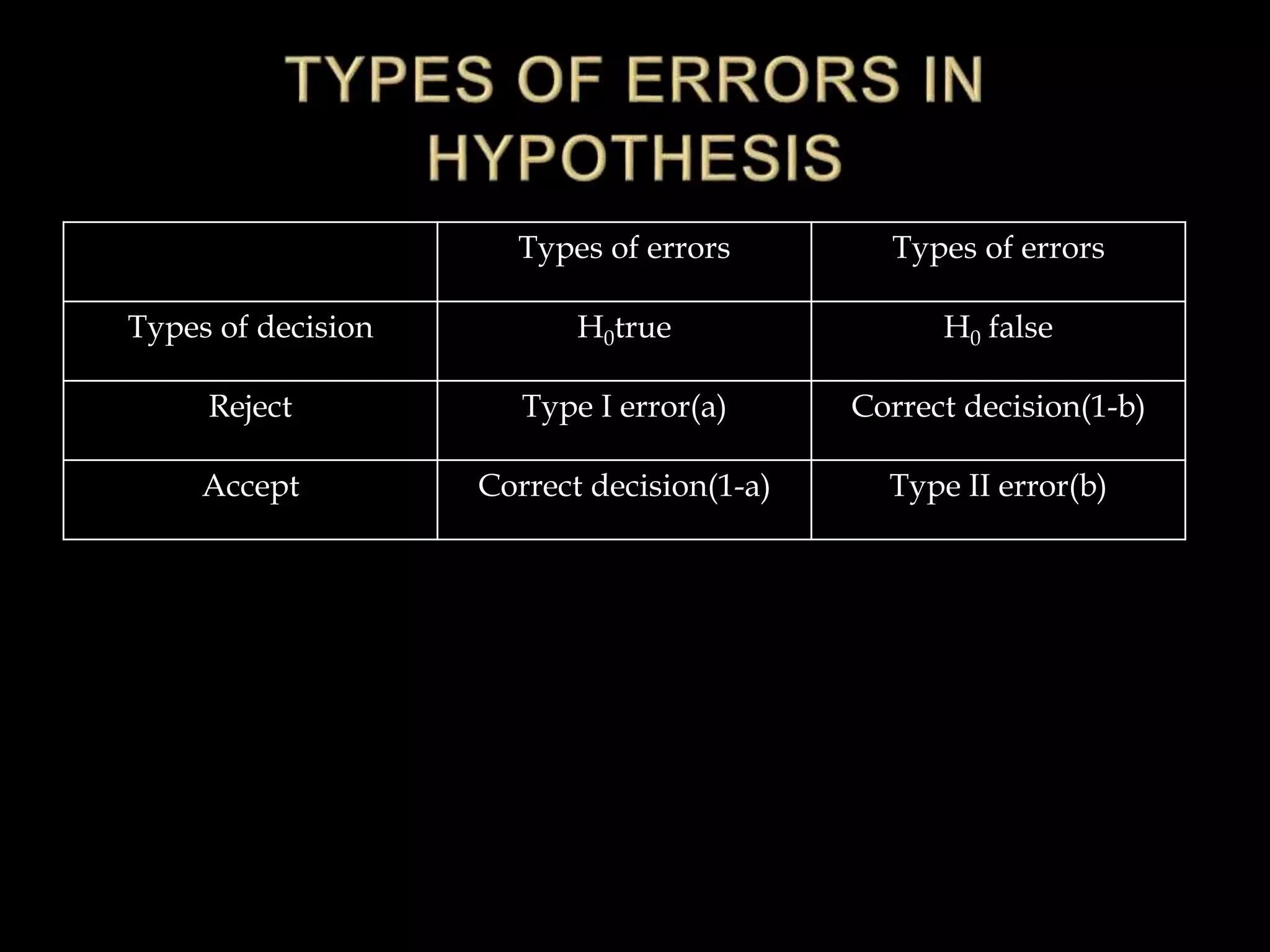
The document discusses hypotheses, including defining a hypothesis, the characteristics of a good hypothesis, and the steps involved in hypothesis testing. It notes that a hypothesis is a tentative explanation that can be tested, and outlines criteria for constructing strong hypotheses, such as being clear, precise, and testable. The document also covers the sources of hypotheses, approaches to testing hypotheses like classical and Bayesian statistics, and the types of errors that can occur in hypothesis testing like type 1 and type 2 errors.