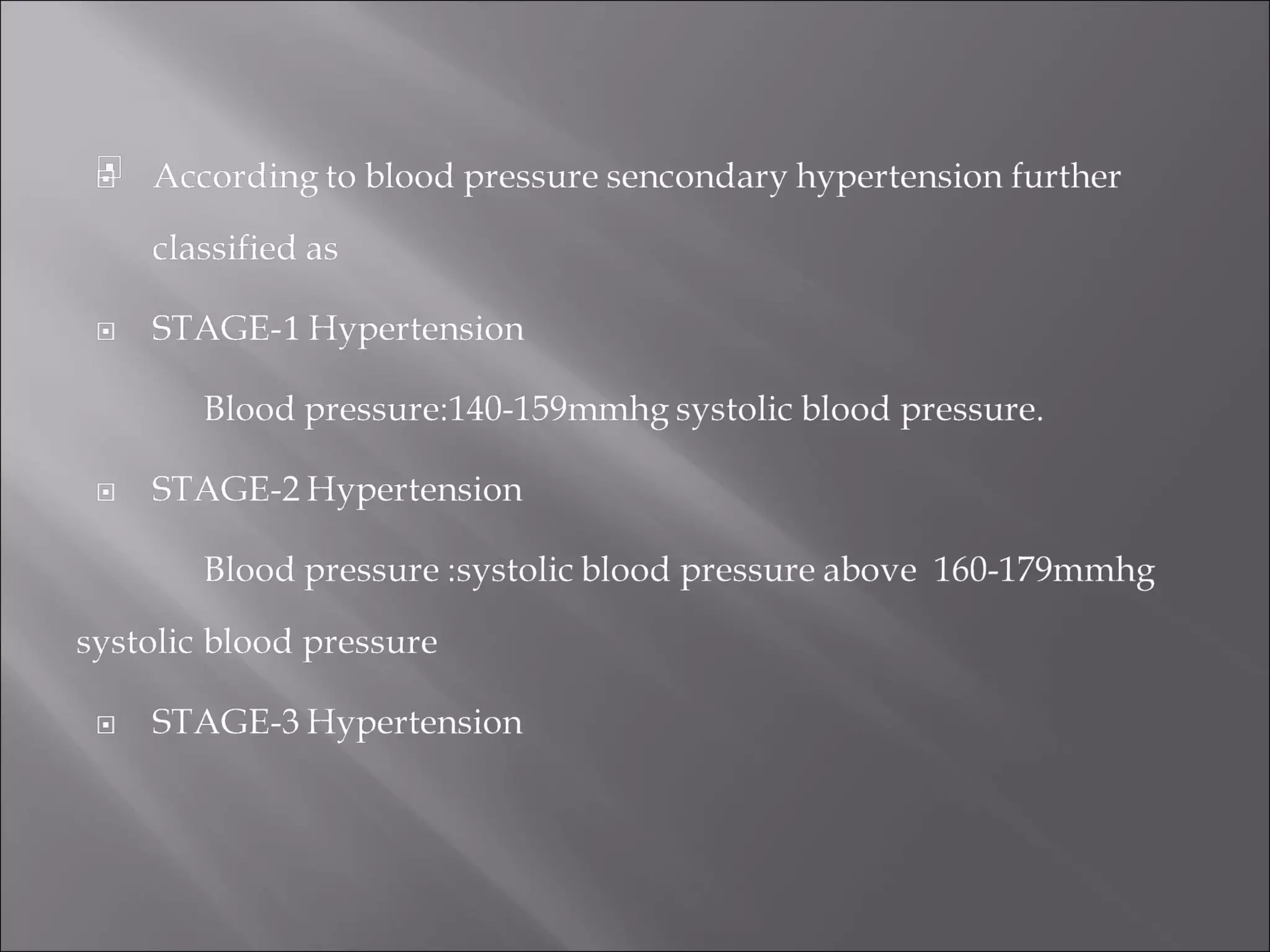
This document discusses hypertension (high blood pressure), including definitions, types, causes, complications, treatment options, and ICD-10 coding guidelines. It defines normal blood pressure and the two main types of hypertension: primary (essential) and secondary, which has an identifiable cause such as kidney disease or obesity. Treatment options include lifestyle modifications and several classes of pharmacological treatments that act on blood pressure in different ways. The document concludes by explaining the new ICD-10 codes for hypertensive urgency and emergency, and providing definitions to guide accurate use of these codes.