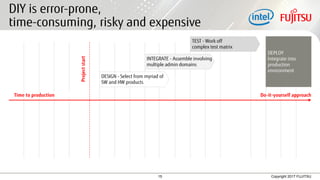
The document discusses hyper-converged infrastructures and their benefits and use cases compared to traditional data center architectures. Hyper-converged infrastructures integrate compute, storage, networking and virtualization resources into commodity x86 servers to improve scalability, flexibility and efficiency. However, use cases matter and both hyper-converged and traditional architectures may be suitable depending on the workload requirements. Fujitsu's PRIMEFLEX integrated systems provide hyper-converged and converged solutions to help customers select the optimal approach for their needs.