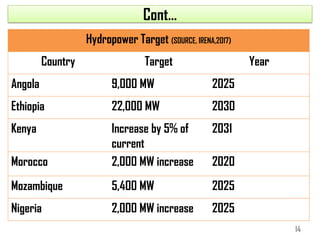
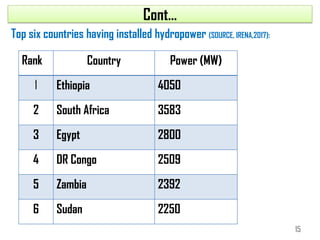
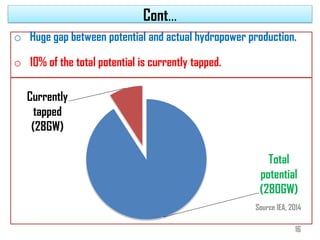
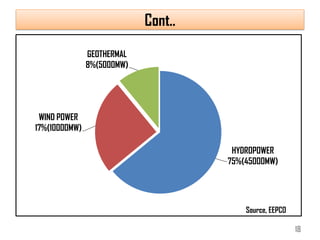
1) Africa has significant untapped hydropower potential, with only 10% of its estimated 280GW capacity currently developed. Ethiopia in particular has 45,000MW potential from its water resources.
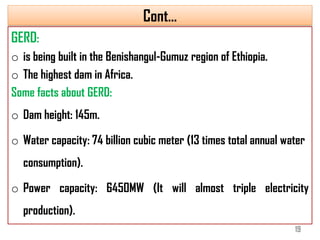
2) The Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD) is a major hydropower project under construction in Ethiopia. At 145m tall, it will be the highest dam in Africa and triple Ethiopia's electricity production to 6,450MW.
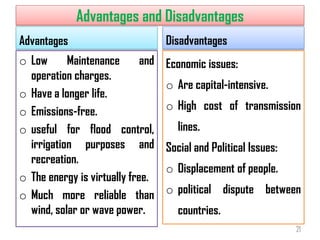
3) Hydropower has advantages of being renewable, emissions-free, and providing flood control and irrigation. However, hydropower projects require large upfront costs and transmission infrastructure, and can cause displacement of local populations.