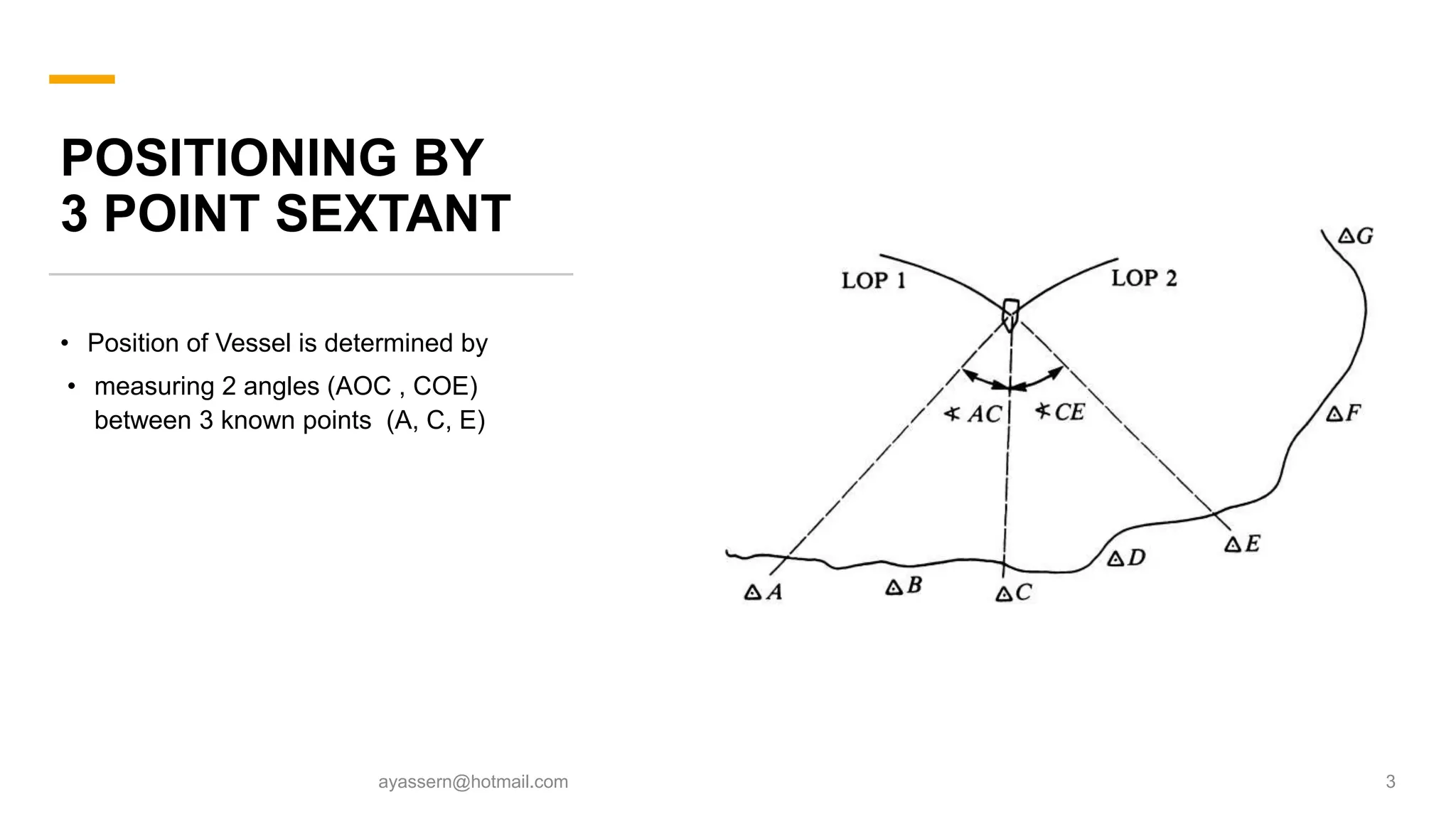
This document discusses various methods for hydrographic surveying control and positioning, including conventional visual methods like triangulation and sextant resection, as well as electronic methods. It covers topics like positioning using a sextant to measure angles between three known points, baseline range alignment by setting stakes along a shoreline baseline to form an offshore grid, and electronic distance measurement techniques including short, medium, and long range. Differential GPS is introduced as a system that uses a fixed reference point to provide real-time corrections to GPS signals and eliminate errors.