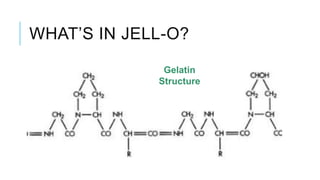
A hydrogel is a solid material that absorbs water and swells to form a network. It consists of polymer chains that are cross-linked to form a three-dimensional structure. When dry, the polymer chains are collapsed, but when placed in water, the chains hydrate and expand to create a gel-like swollen network. Common examples of hydrogels include the superabsorbent polymers used in diapers to absorb moisture and gelatin, which forms a solid gel when cooled from a liquid state due to the cross-linking of gelatin molecules.