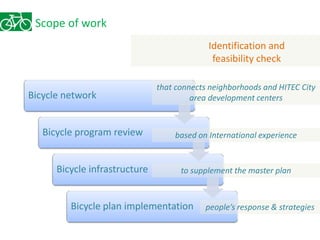
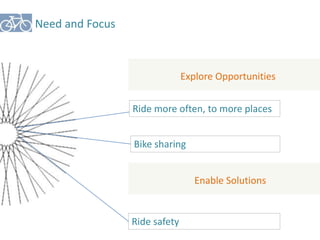
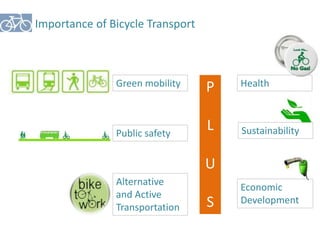
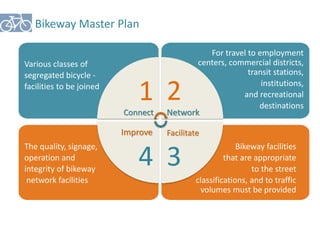
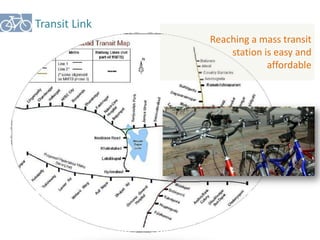
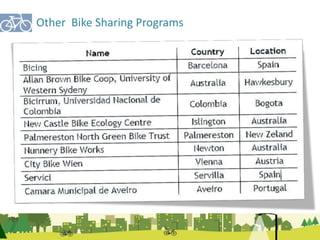
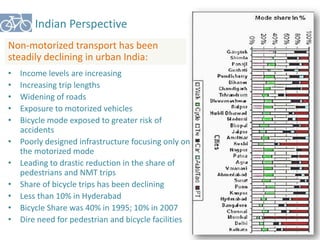
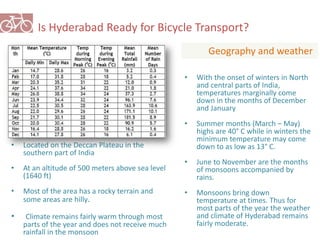
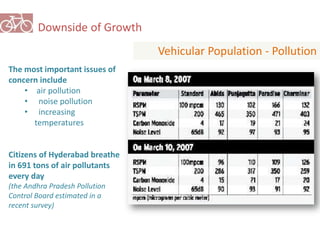
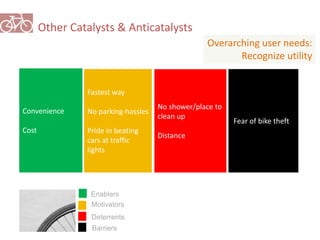
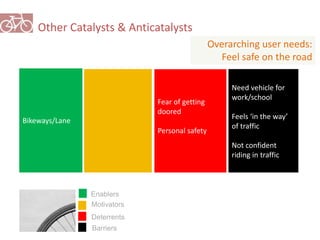
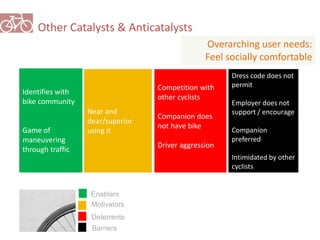
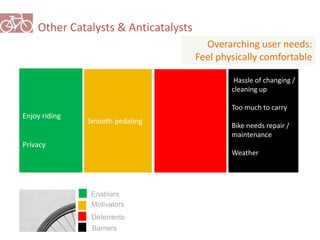
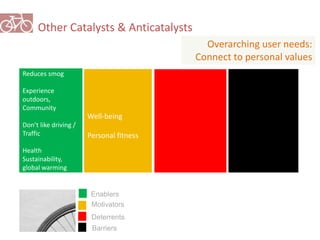
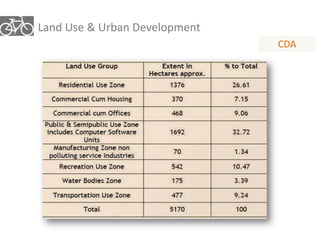
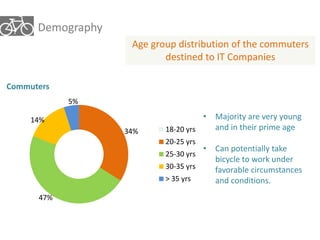
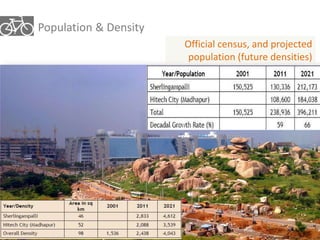
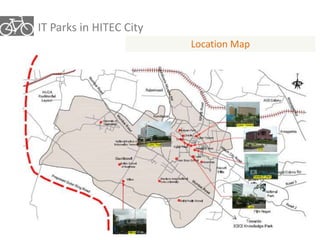
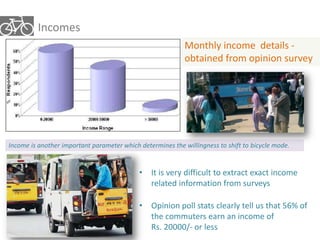
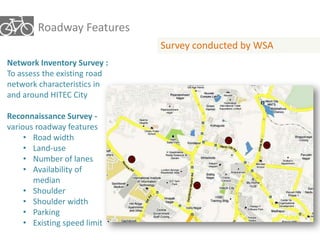
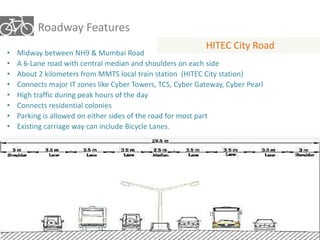
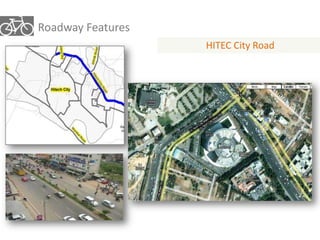
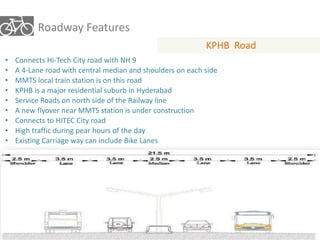
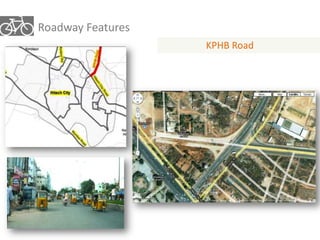
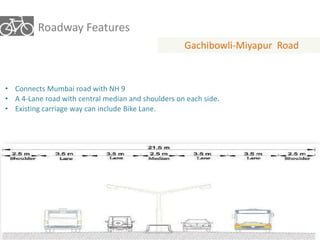
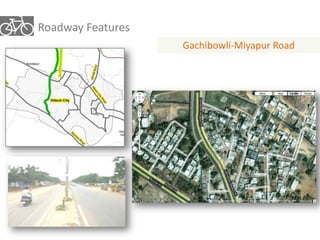
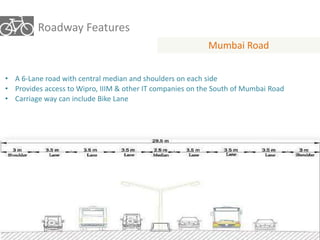
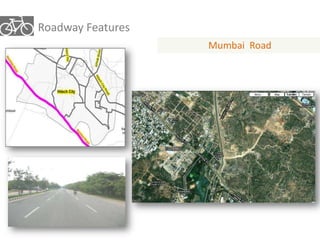
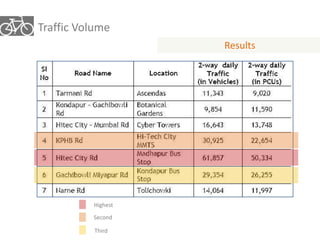
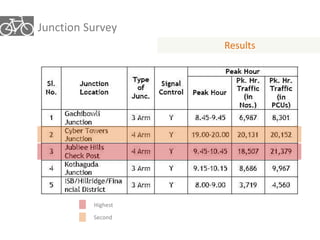
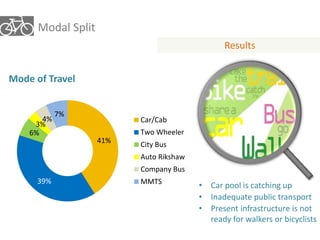
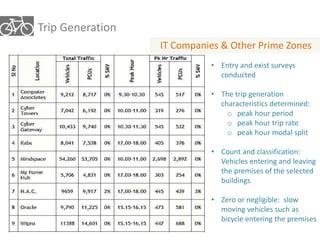
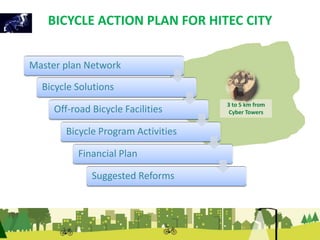
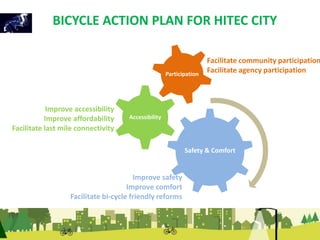
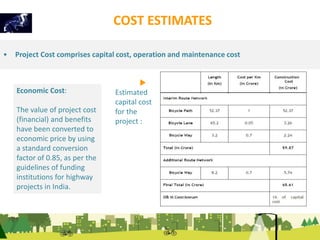
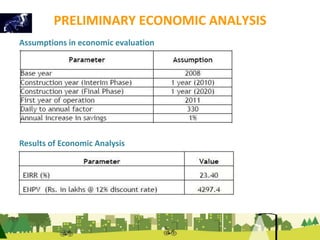
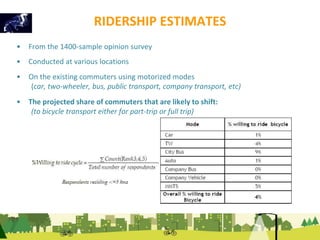
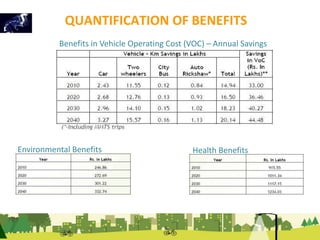
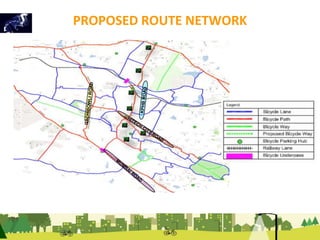
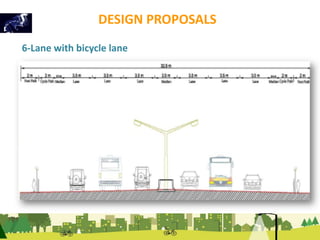
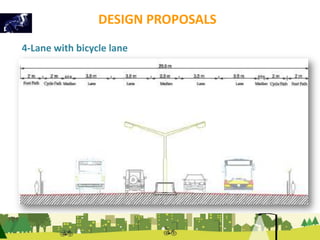
The document outlines a plan for creating India's first bicycle-friendly city in Hyderabad, focusing on a pilot project in the Hitec City area. It aims to promote cycling as a preferred mode of transport, enhance infrastructure, and reduce carbon emissions while addressing issues like safety and community engagement. The initiative draws on successful international cycling programs to inspire local policies and improvements in urban mobility.