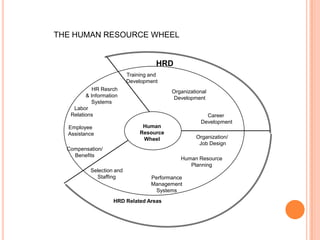
This document provides an introduction to human resource development (HRD). It discusses the primary functions of human resource management, including human resource planning, equal employment opportunity, staffing, compensation and benefits, employee relations, health and safety, and HRD. Secondary HRM functions include organization and job design, performance management, and research systems. HRD specifically involves training and development, organizational development, and career development. Training and development aims to improve employee skills and knowledge for short-term goals, while development prepares employees for future roles. Organizational development focuses on improving organizational effectiveness. Career development involves assisting employees' career progression. The document outlines critical HRD issues such as aligning HRD with strategic management goals and defining the supervisor