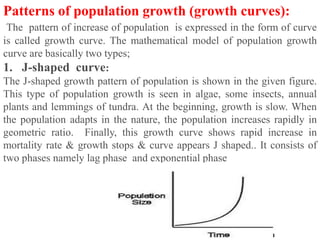
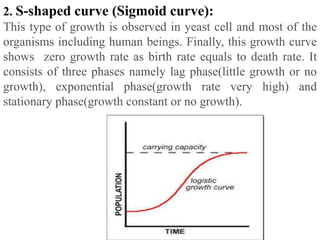
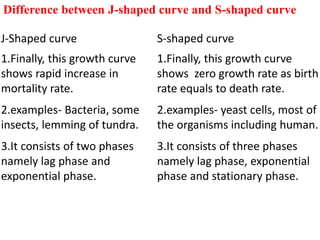
The document discusses several topics related to human population growth including:
1. The global human population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to 7 billion in 2012 and is expected to continue growing to 8.4 billion by 2030 and 9.6 billion by 2050 due to increasing birth rates and life expectancy.
2. Population growth rates depend on birth rates, death rates, immigration rates, and population doubling times which for Nepal is estimated to be every 33 years.
3. Issues caused by overpopulation include lack of resources, pollution, and socioeconomic problems like unemployment, poverty, and decreased quality of education.
4. Controlling overpopulation requires strategies like education, family planning, and increasing the