Introduction to HRM (Human Resource Management)
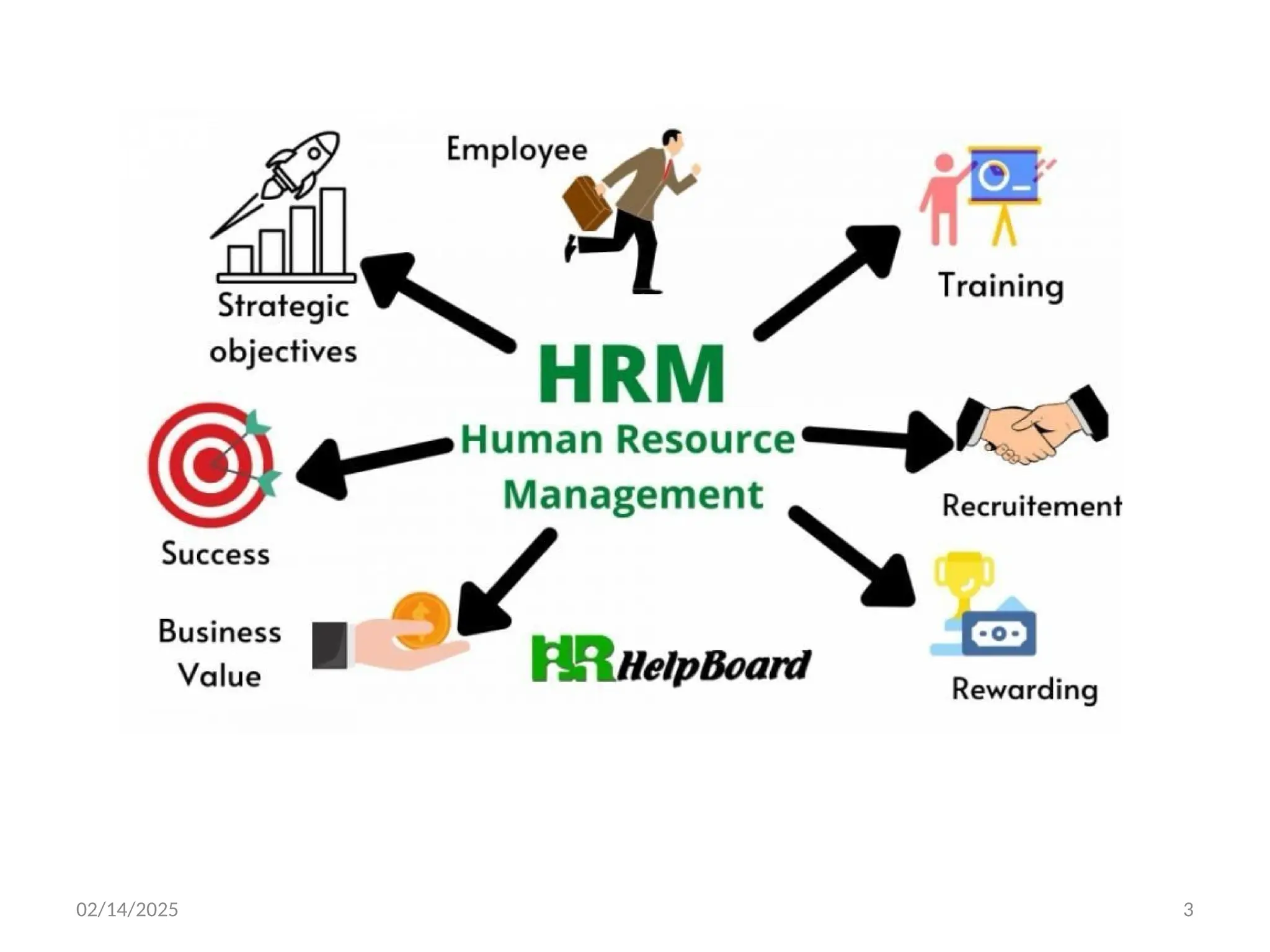
Human Resource Management (HRM) is the strategic approach to managing an organization's workforce, focusing on maximizing employee performance and ensuring a conducive work environment. It deals with recruitment, development, and well-being of employees, aligning them with the organization’s goals.
Objective of HRM
The primary objective of HRM is to effectively utilize human resources, ensuring they are motivated, skilled, and aligned with organizational objectives. It aims to foster a productive work environment, enhance employee satisfaction, and contribute to the company's success.
Functions of HRM
HRM functions include recruitment, employee training and development, performance management, compensation, employee relations, and labor law compliance. These functions help create an efficient, motivated, and well-managed workforce.
Job Analysis
Job analysis involves identifying and detailing the responsibilities, skills, qualifications, and requirements for each job within an organization. This helps in the recruitment process, performance evaluation, and setting appropriate compensation.
Human Resource Selection Process
The HR selection process includes several stages, such as job posting, screening, interviews, testing, and final selection. This ensures that the most suitable candidate is chosen for the job based on skills, experience, and organizational fit.
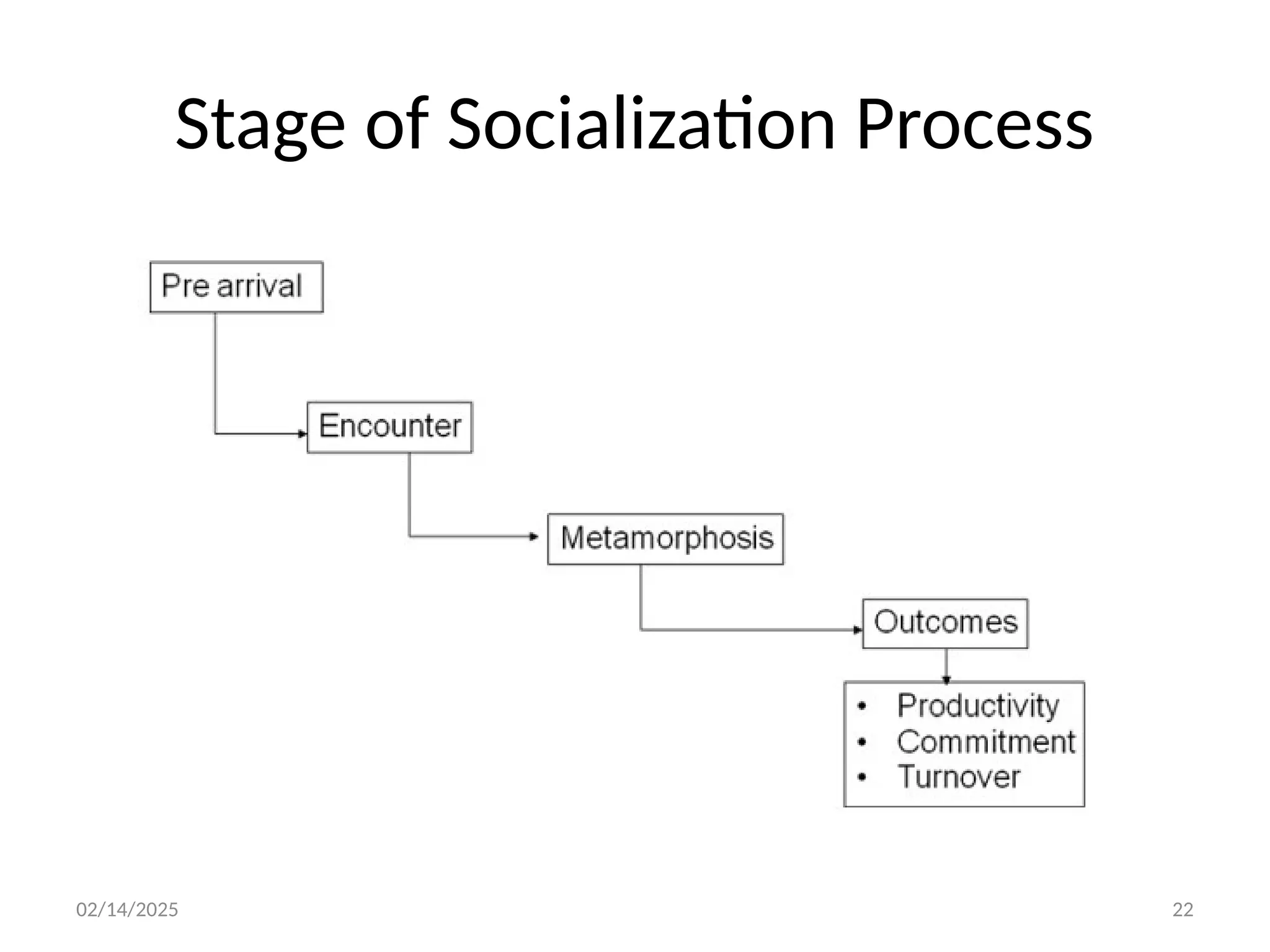
Socializing the New Employees
Employee socialization refers to the process by which new hires adjust to the organizational culture and environment. This includes orientation programs, mentoring, and fostering relationships to help them settle into their new roles.
Labor Welfare Schemes
Labor welfare schemes are initiatives designed to improve workers' well-being, including health benefits, financial security, and social support. These schemes are essential for fostering job satisfaction and ensuring a healthy work-life balance for employees.
Accidents and Safety Measures
Accident prevention and safety measures involve identifying potential risks in the workplace and implementing practices to minimize accidents. It includes regular training, safety protocols, hazard assessments, and ensuring compliance with occupational safety regulations to protect employees.