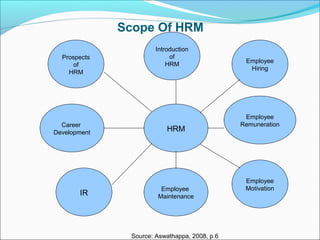
This document discusses the meaning and objectives of human resource management (HRM). It defines HRM as managing people at work to help both the organization and individuals achieve their goals. The objectives of HRM include procuring the right personnel, ensuring training and development, utilizing human resources effectively, motivating employees, and maintaining harmonious employee relations. HRM aims to coordinate organizational and individual needs and measure productivity through factors such as employee skills, motivation, creativity, and initiatives. The functions of HRM include planning, organizing, staffing, leading, and controlling as management processes, as well as job analysis, recruitment, orientation, performance appraisal, and building employee commitment as operational processes.