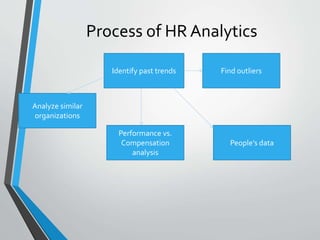
The document outlines the significance of human resource analytics, including its definition and evolution, highlighting its role in transforming raw data into actionable insights for HR managers. It details the process of HR analytics, its benefits such as optimizing ROI on human capital, and lists available software tools like IBM HR Analytics and SAP Human Capital Analytics. The conclusion emphasizes the growing importance of HR analytics in enabling better decision-making for both workforce management and core business strategies.