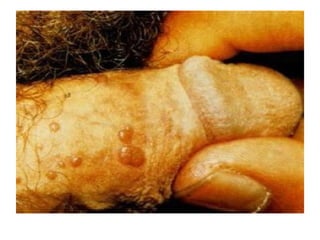
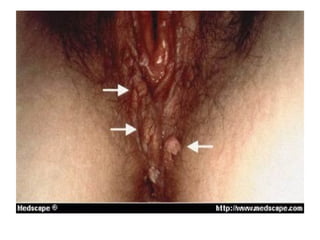
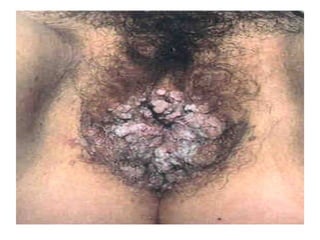
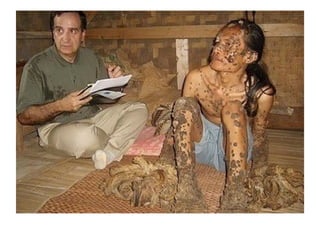
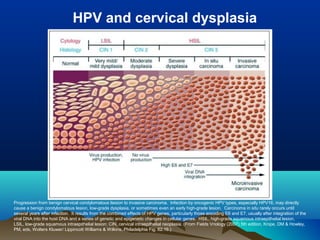
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a small non-enveloped DNA virus that infects squamous epithelia and mucous membranes, producing different types of warts or papillomas. Over 70 types of HPV exist.
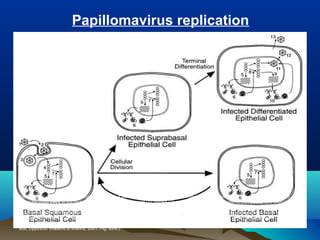
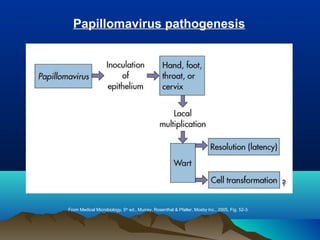
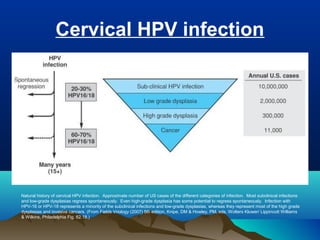
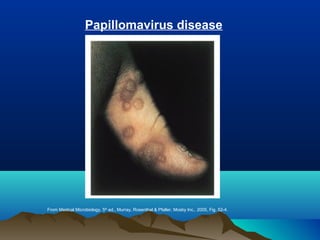
- HPV replicates in basal epithelial cells and causes lesions depending on the virus type, such as common warts or genital warts. HPV types 16 and 18 can cause invasive cancers like cervical cancer.
- HPV is transmitted through direct skin or mucosa contact and shows tissue specificity. Diagnosis involves pathology, cytology, or nucleic acid tests to identify the HPV type. Prevention includes vaccines and Pap smears, while treatment consists of surgery.