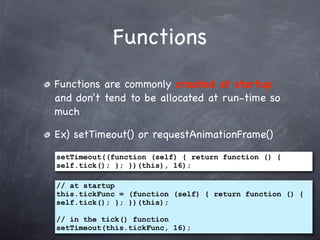
This document summarizes techniques for writing low-garbage real-time JavaScript code. It discusses how to avoid object allocation using syntax like {} and [] instead of the new keyword. It also recommends reusing objects by wiping their properties instead of creating new ones. Functions should be created at startup instead of during runtime. Vector objects should be returned as individual values instead of vector objects. While avoiding garbage entirely is difficult, these techniques can help craft responsive real-time JavaScript with minimal garbage collector overhead.



![Simple techniques
Allocation
the new keyword - e.g. new Foo().
three syntax shortcuts for common uses of new:
{} (creates a new object)
[] (creates a new array)
function () { ... } (creates a new function,
which are also garbage-collected!)
Try to create the object on startup, and re-use the
same object](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/html5kig-howtowritelowgarbagereal-timejavascript-120515001809-phpapp02/85/W3C-HTML5-KIG-How-to-write-low-garbage-real-time-javascript-4-320.jpg)

![re-cycle an existing
object
Re-cycle an existing object (providing it has no prototype
chain) by deleting all of its properties, restoring it to an
empty object like {}
Use the cr.wipe(obj) function, defined as:
! : slow than using {}
// remove all own properties on obj,
effectively reverting it to a new object
cr.wipe = function (obj)
{
for (var p in obj)
{
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(p))
delete obj[p];
}
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/html5kig-howtowritelowgarbagereal-timejavascript-120515001809-phpapp02/85/W3C-HTML5-KIG-How-to-write-low-garbage-real-time-javascript-6-320.jpg)
![Assigning [] to an array
this creates a new empty array and
garbages the old one!
To write arr.length = 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/html5kig-howtowritelowgarbagereal-timejavascript-120515001809-phpapp02/85/W3C-HTML5-KIG-How-to-write-low-garbage-real-time-javascript-7-320.jpg)

![Code Example
To delete the element at an index from an
array.
var sliced = arr.slice(index + 1);
arr.length = index;
arr.push.apply(arr, sliced);
for (var i = index, len = arr.length - 1; i < len; i++)
arr[i] = arr[i + 1];
arr.length = len;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/html5kig-howtowritelowgarbagereal-timejavascript-120515001809-phpapp02/85/W3C-HTML5-KIG-How-to-write-low-garbage-real-time-javascript-10-320.jpg)




