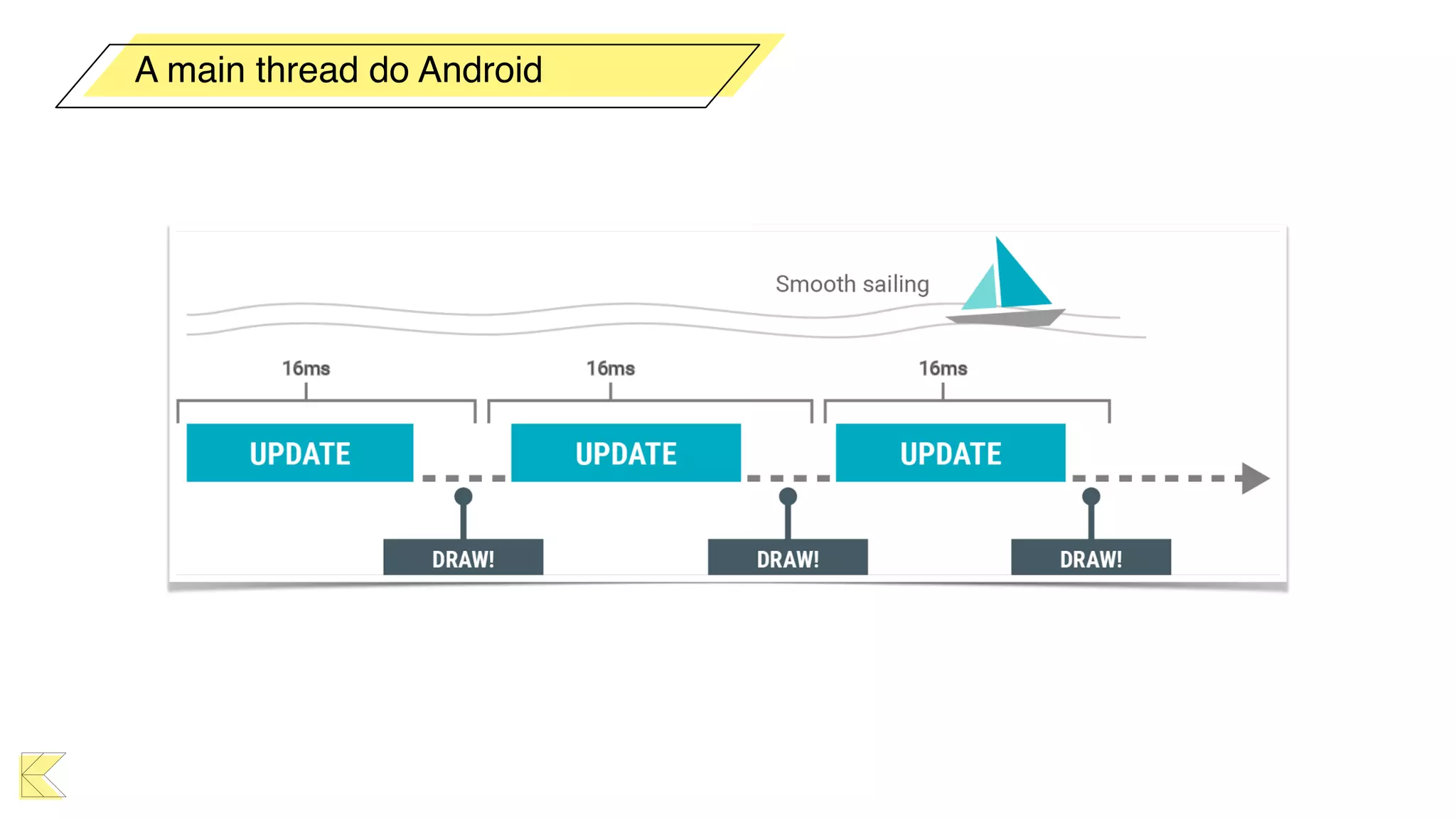
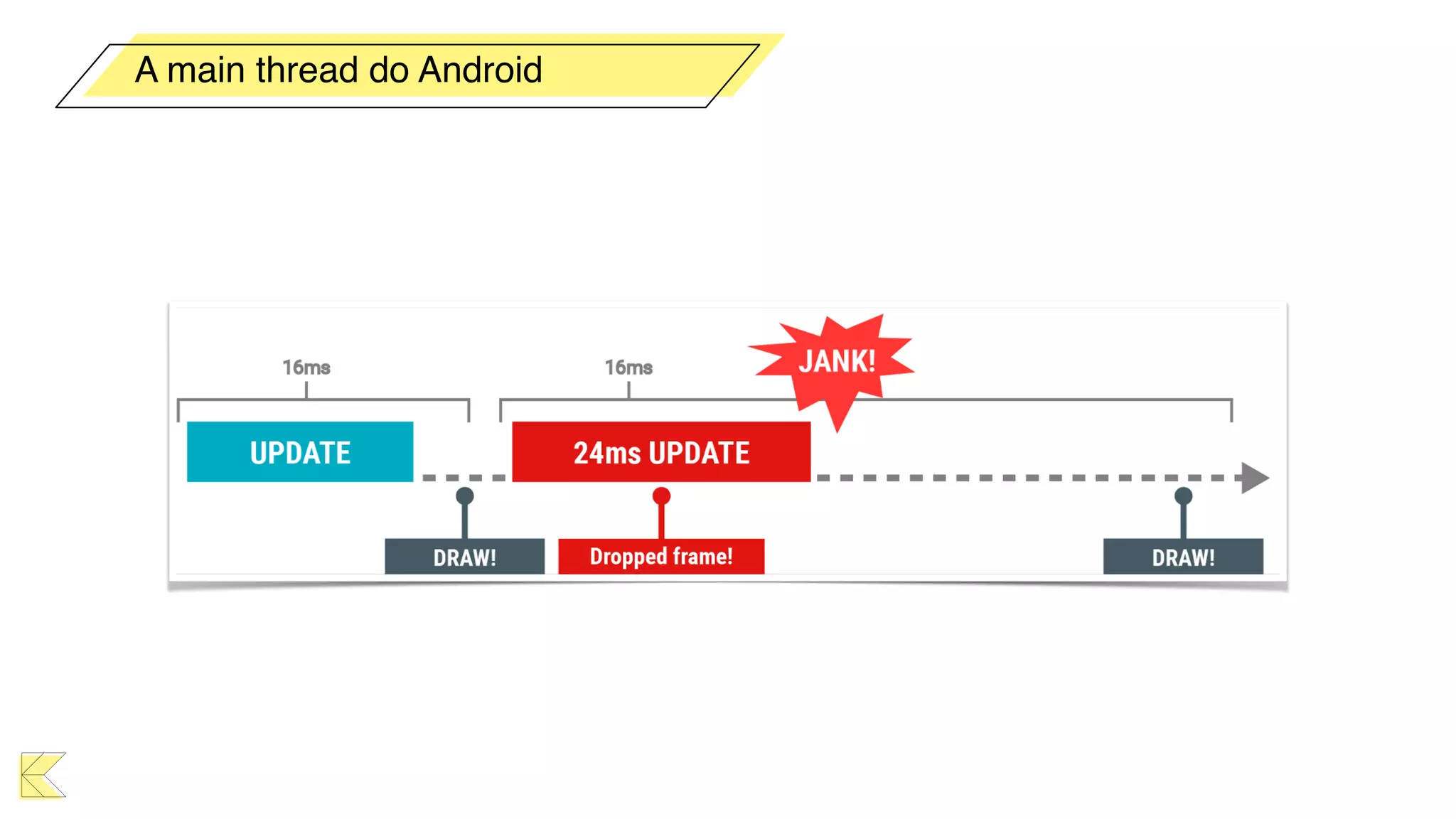
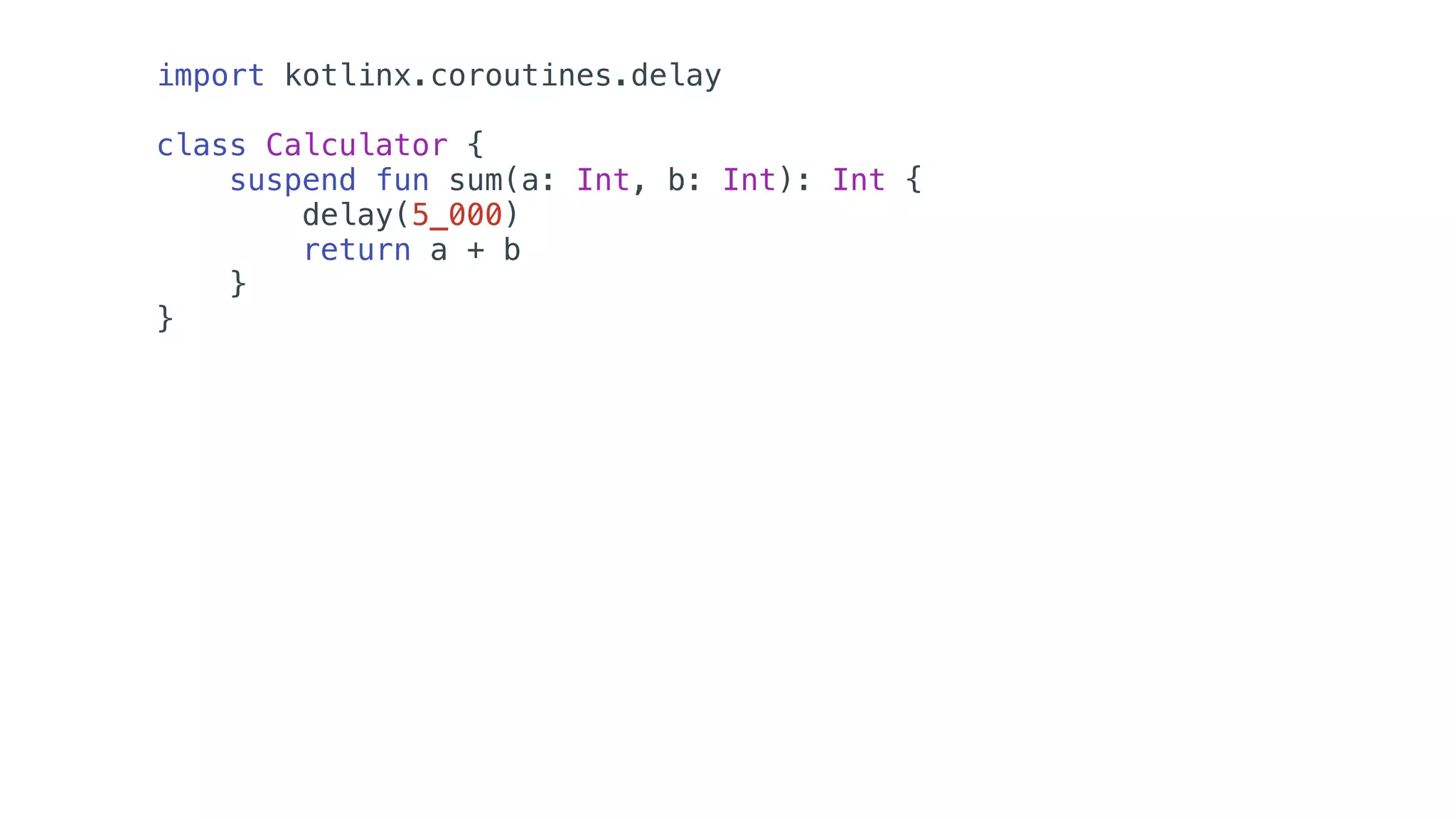
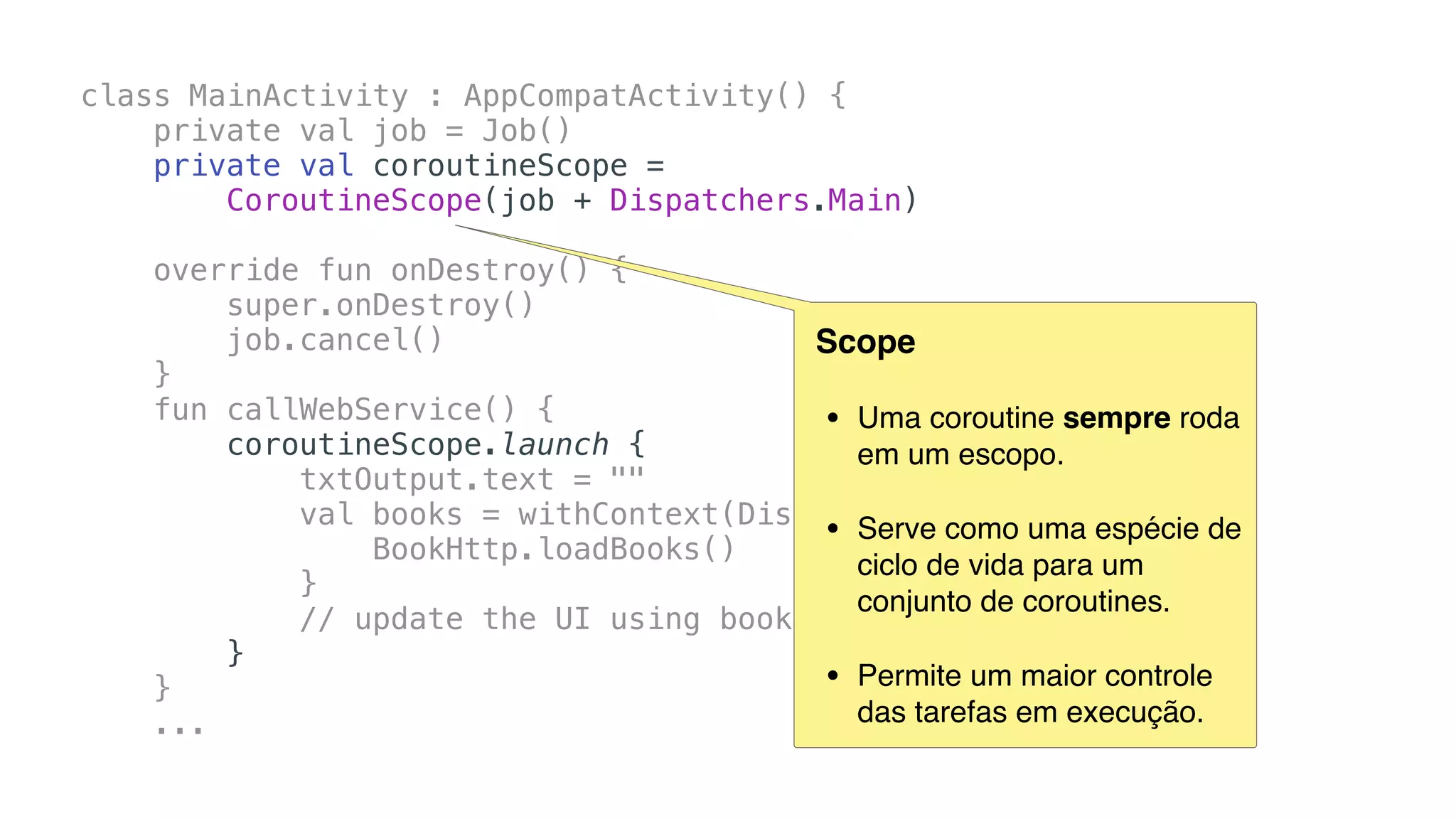
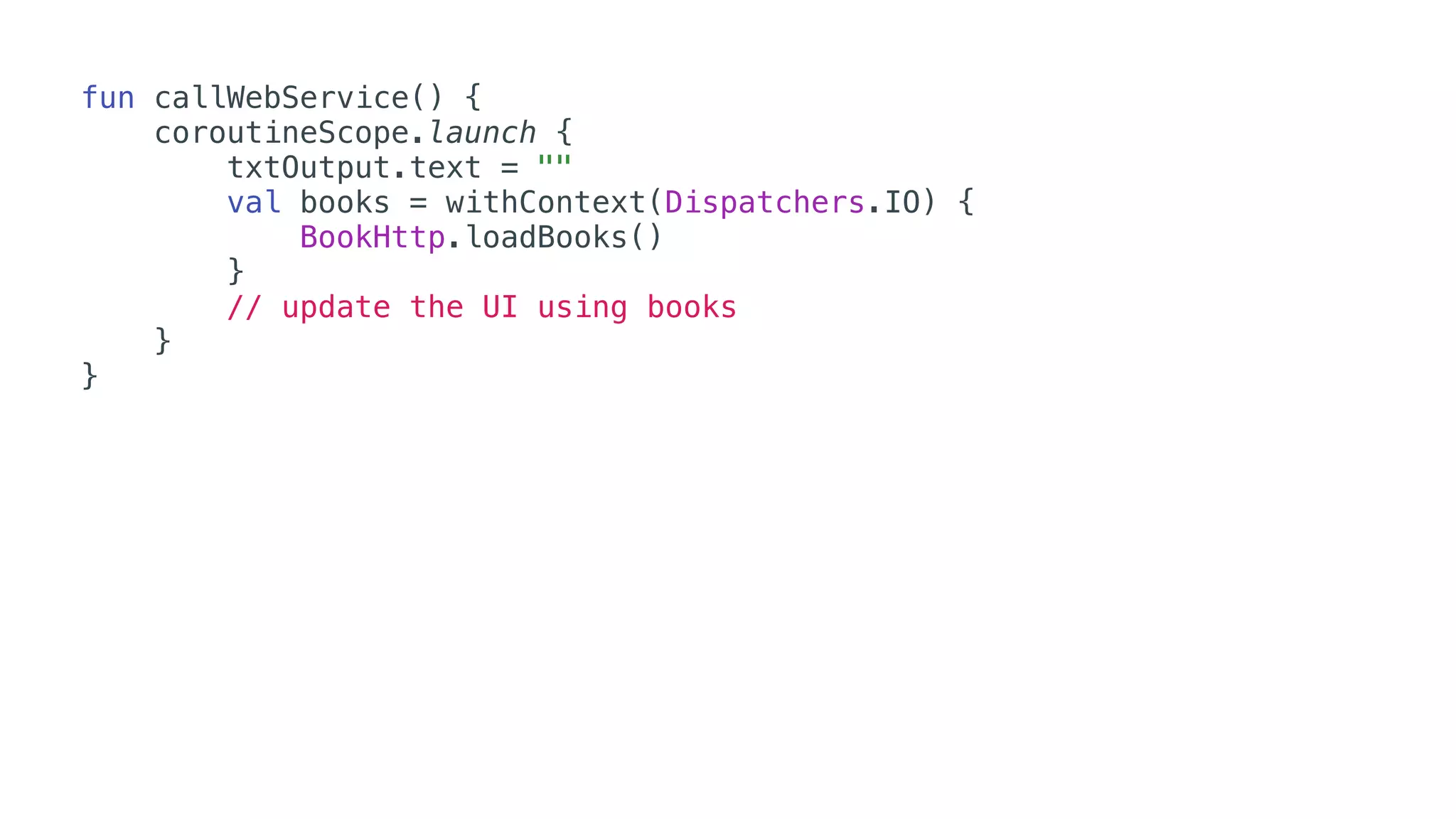
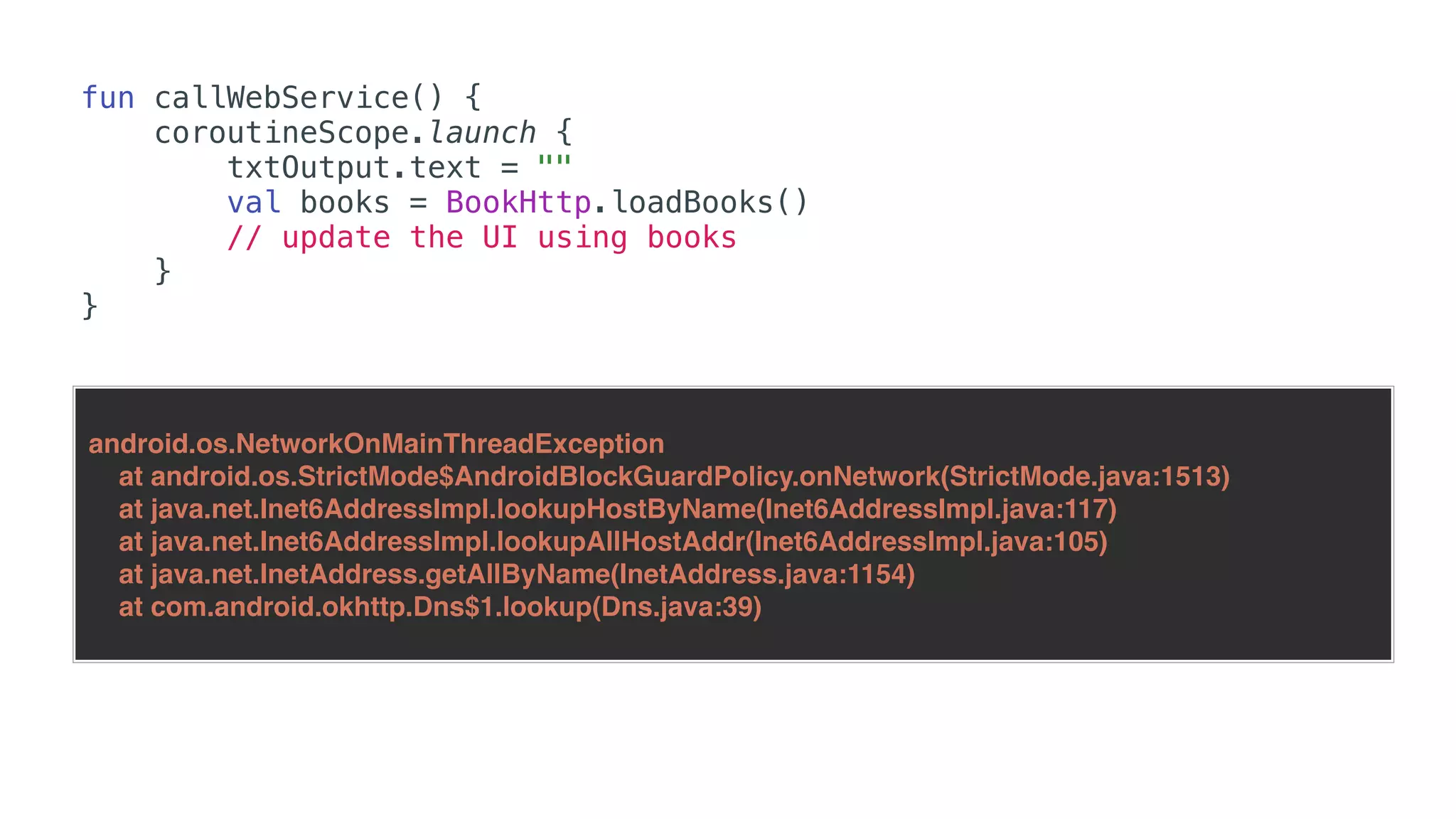
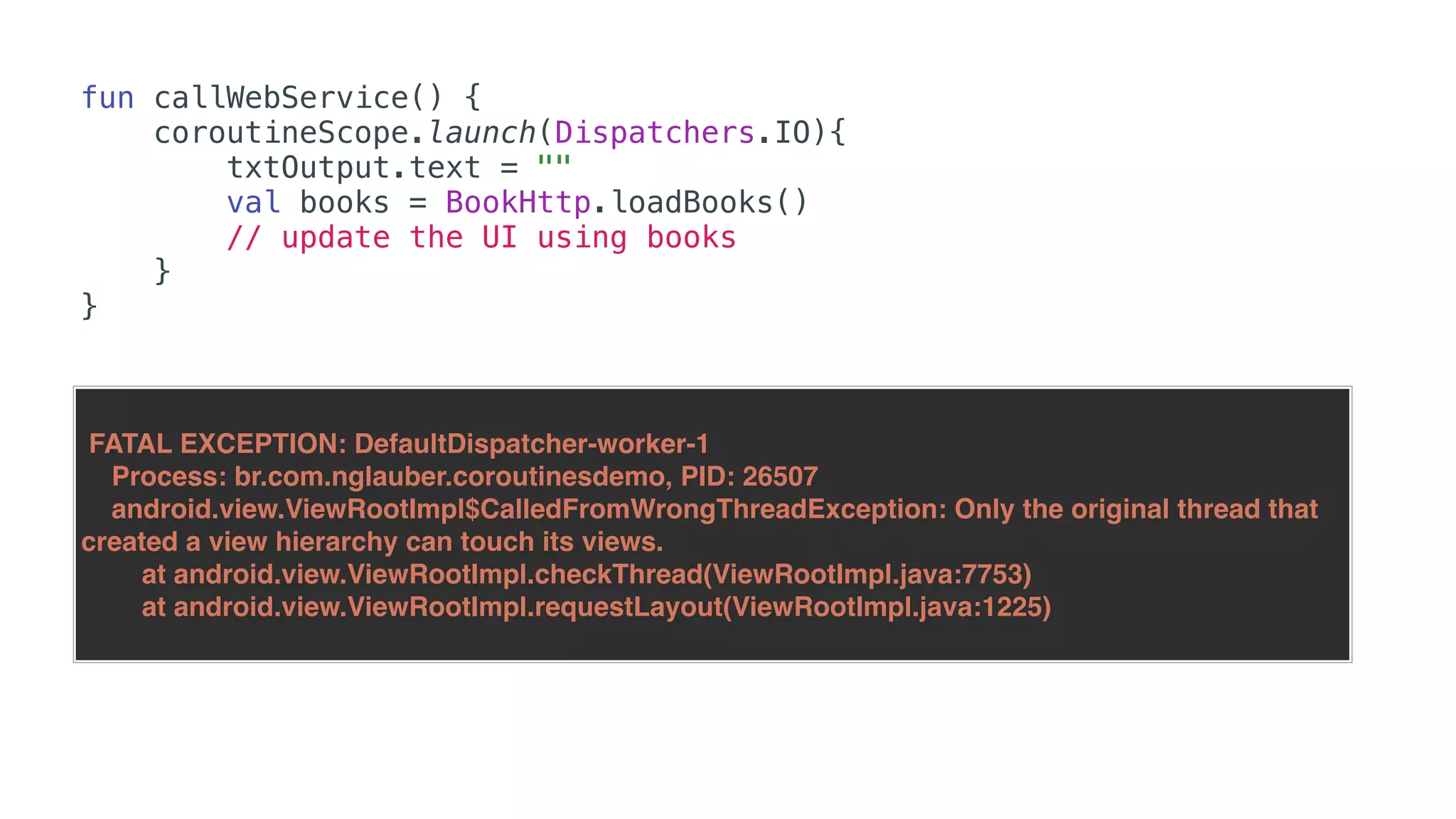
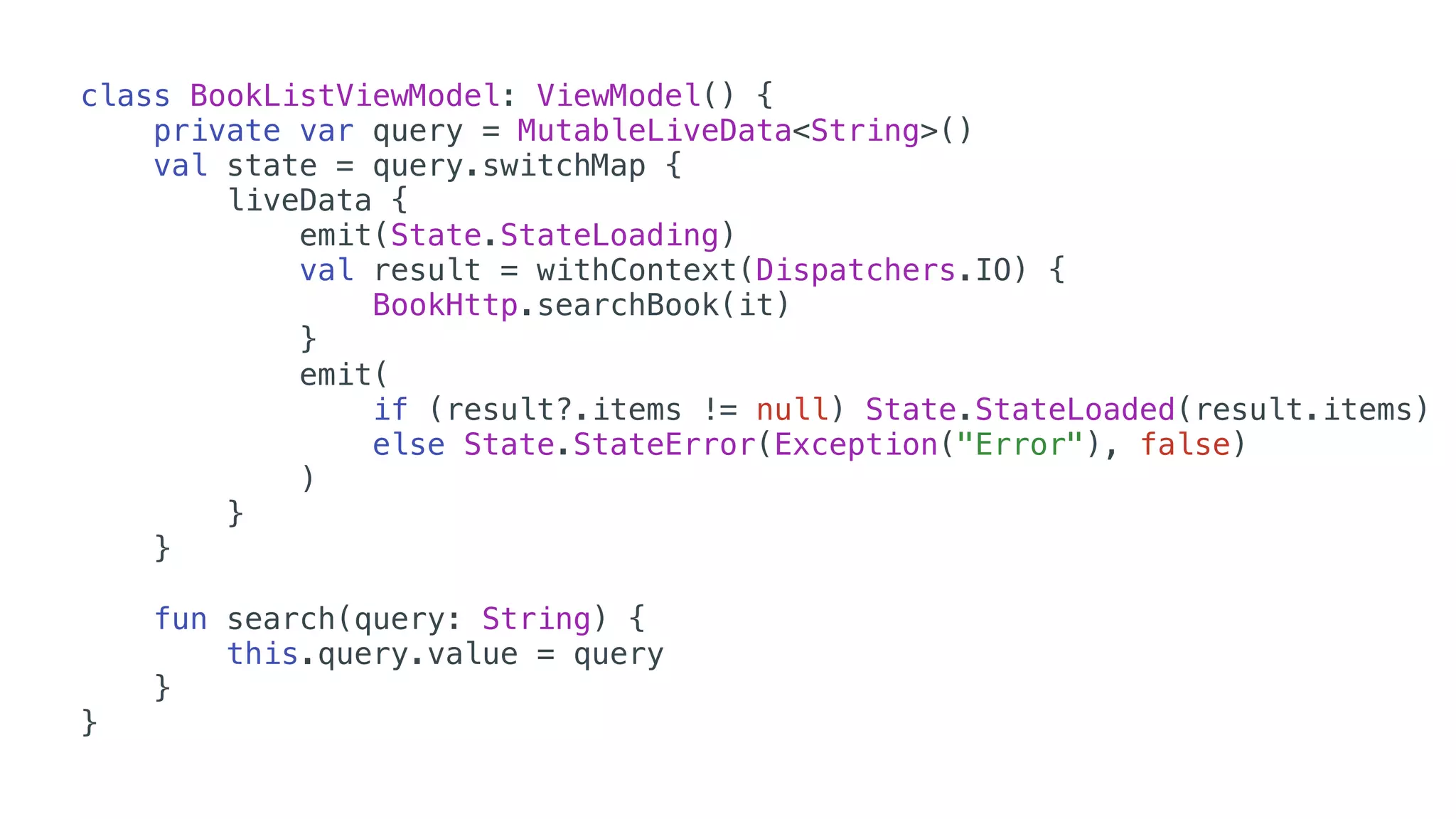
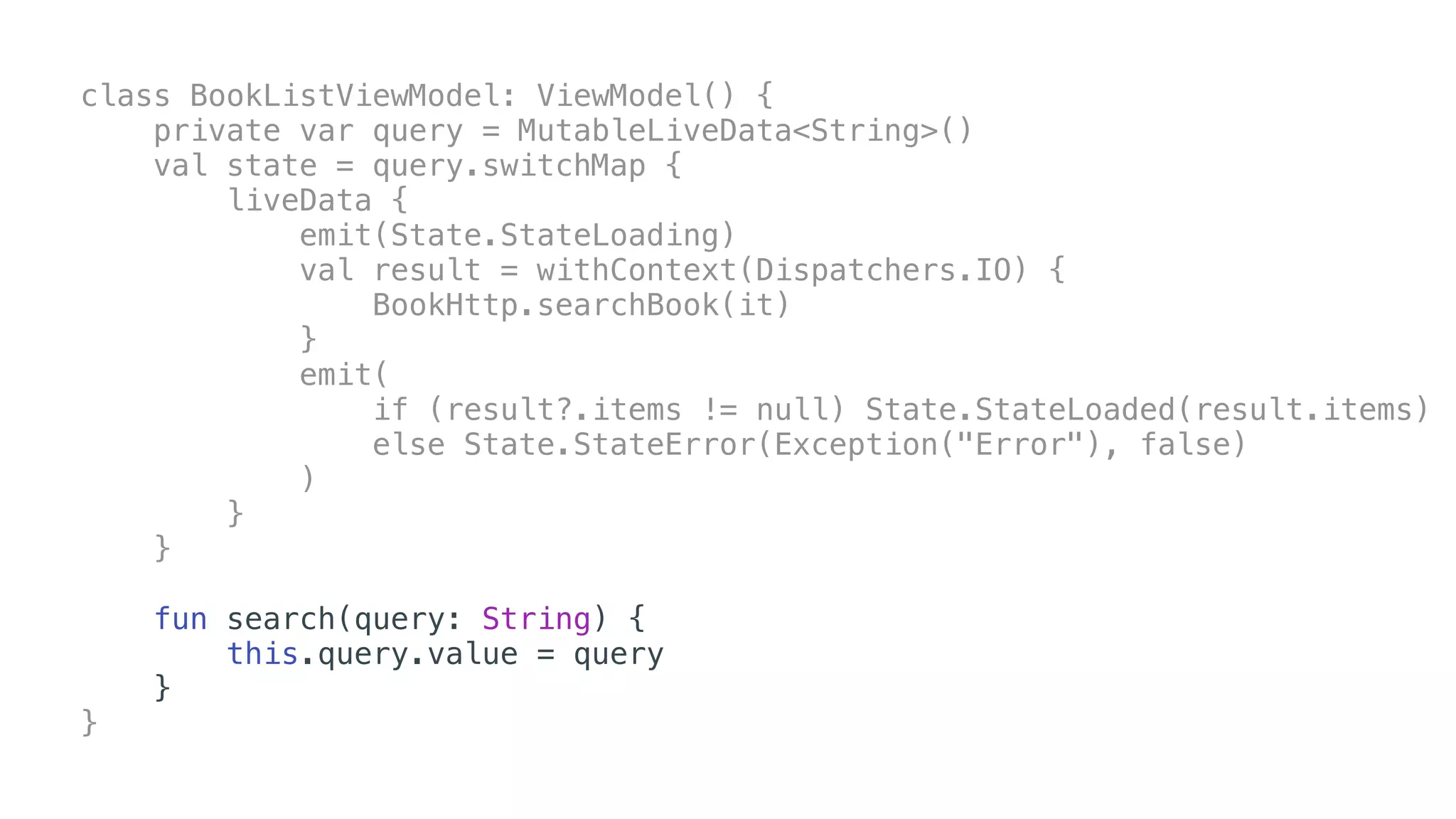
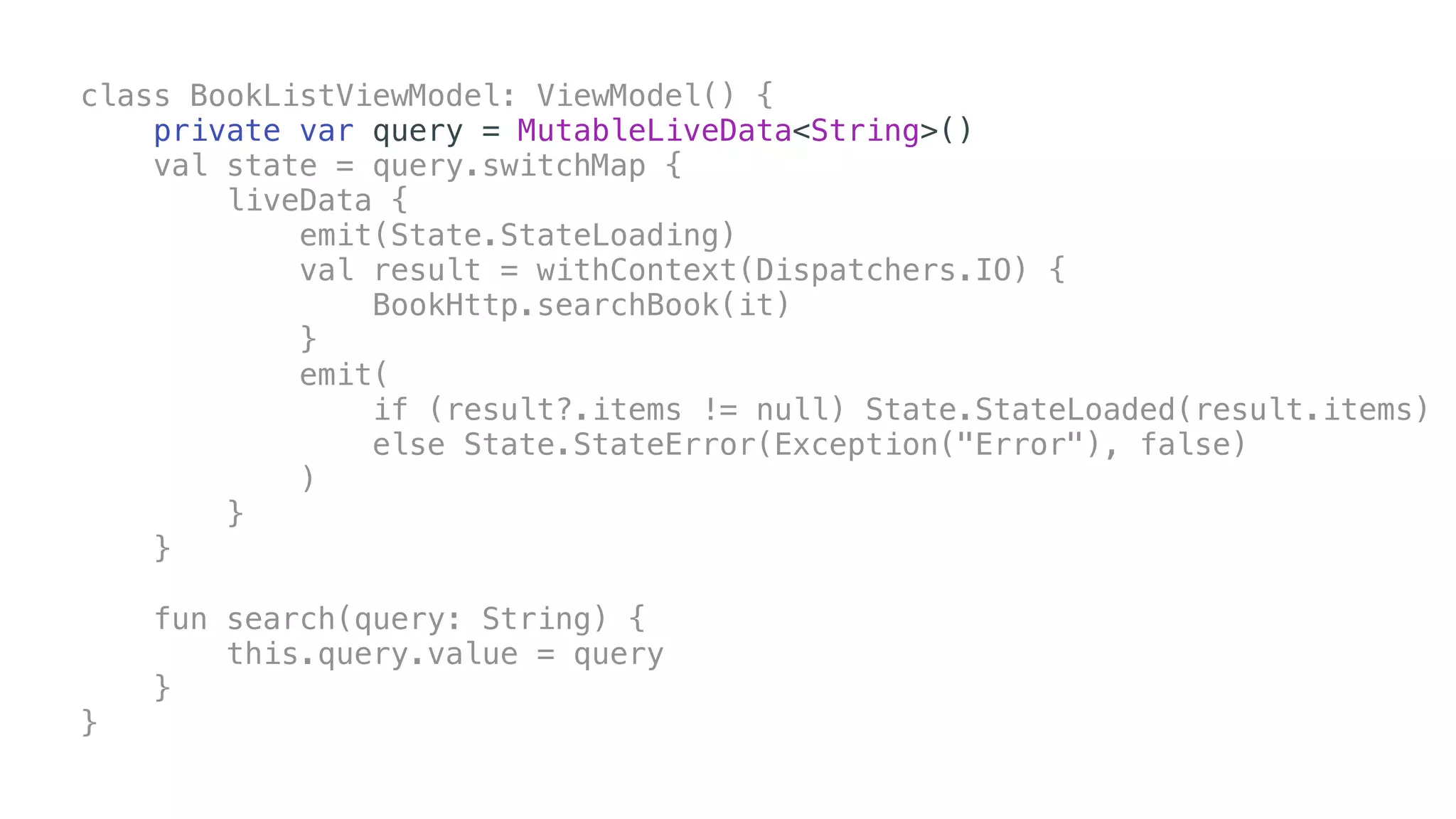
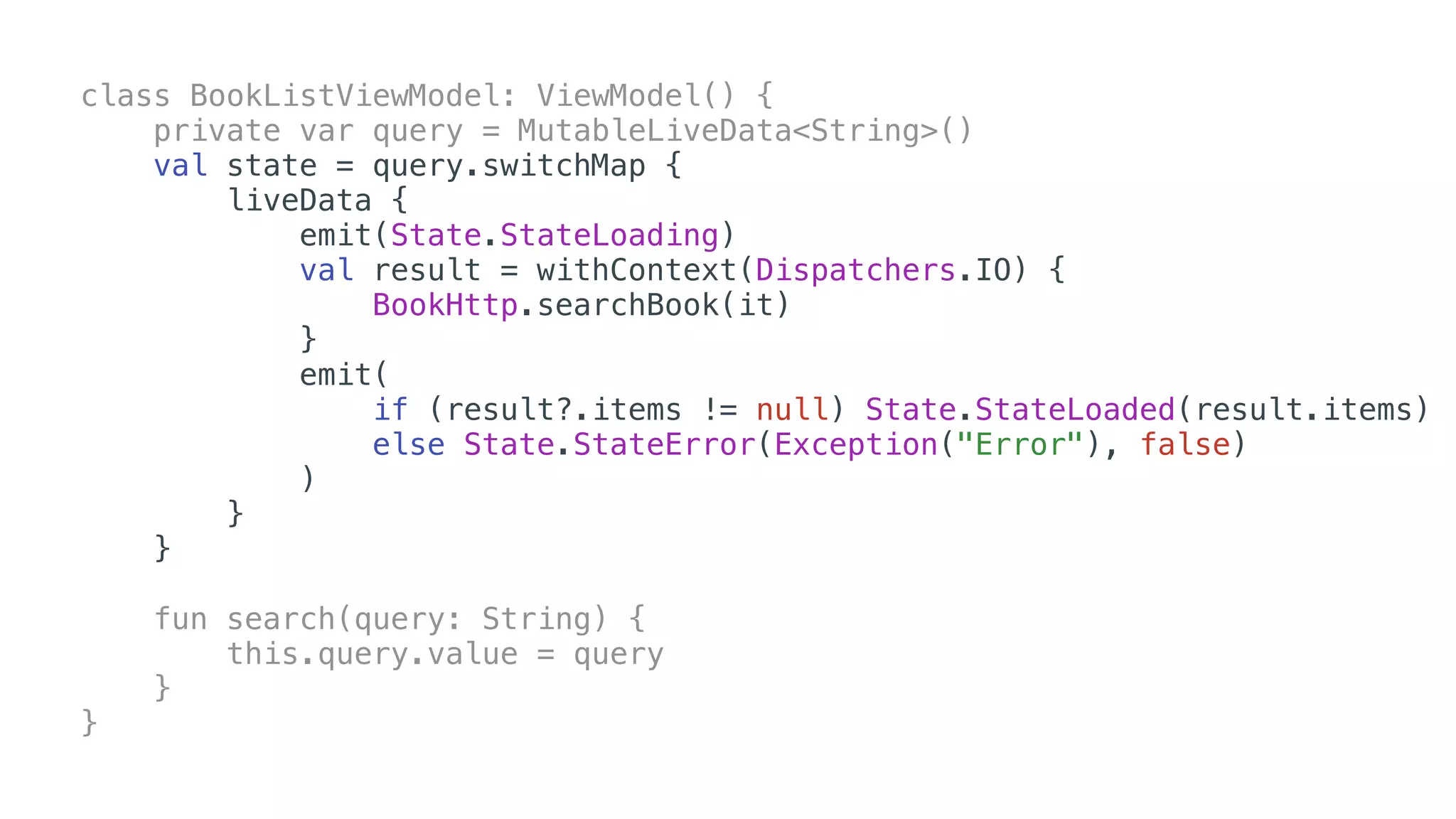
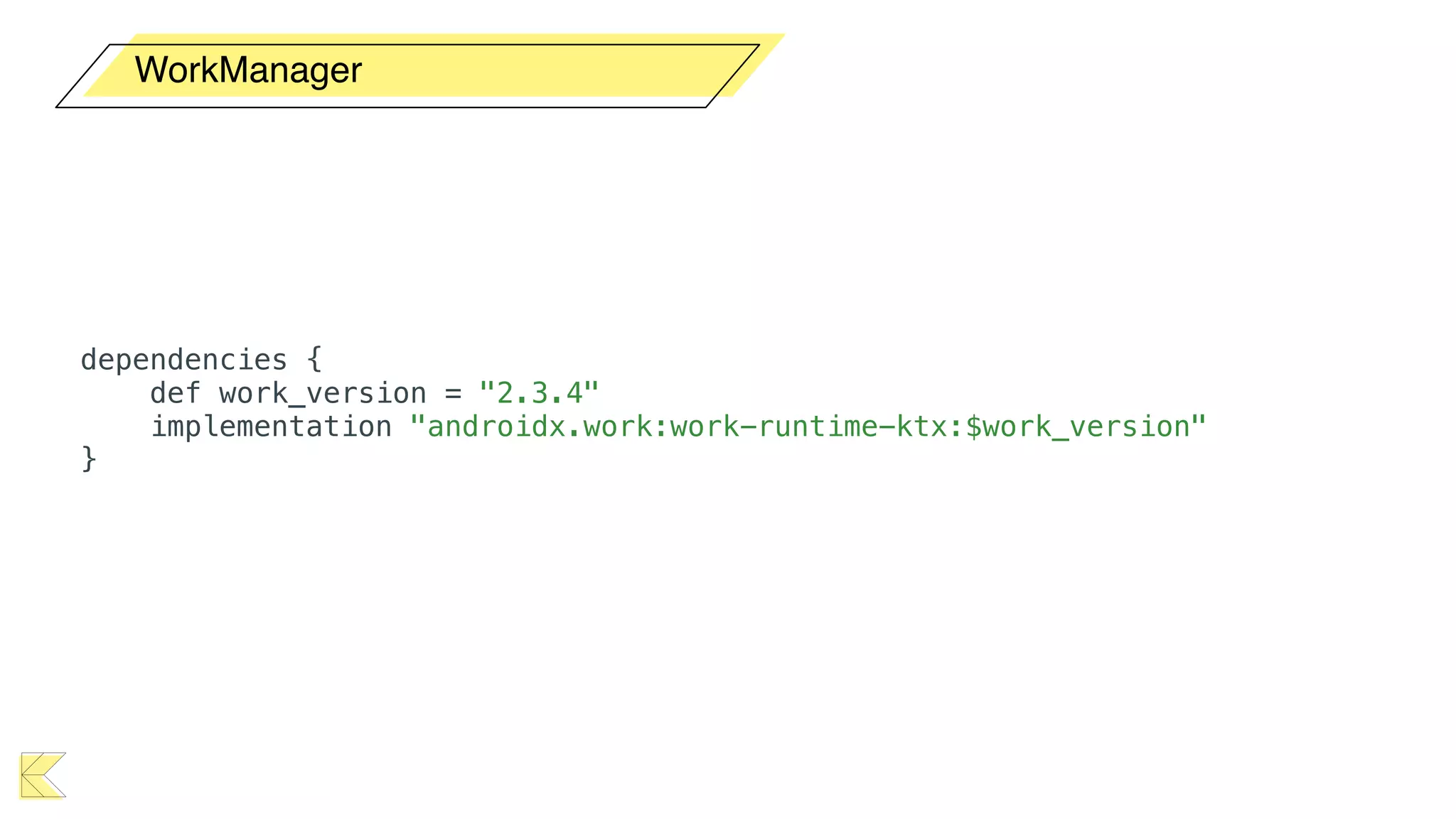
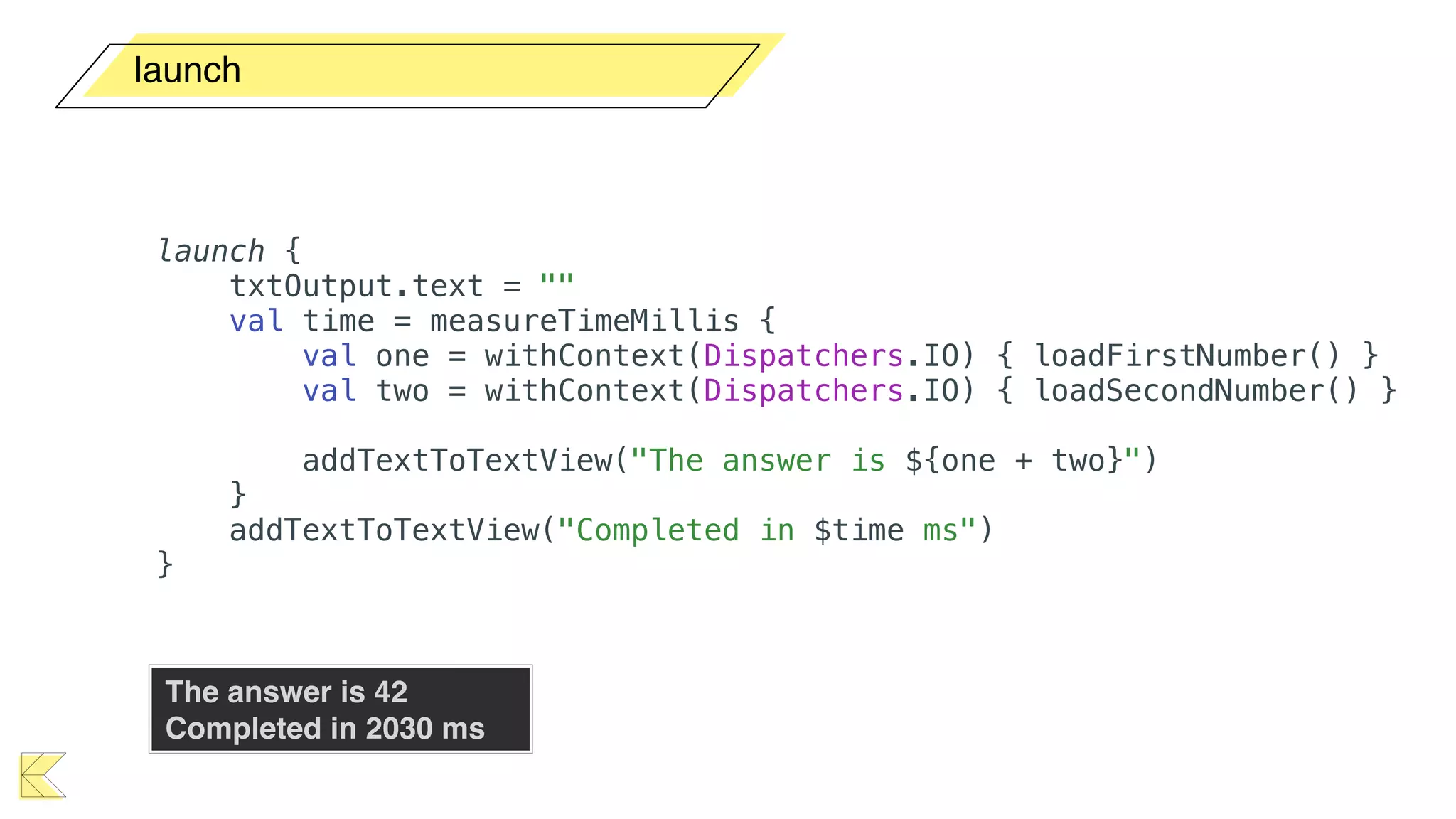
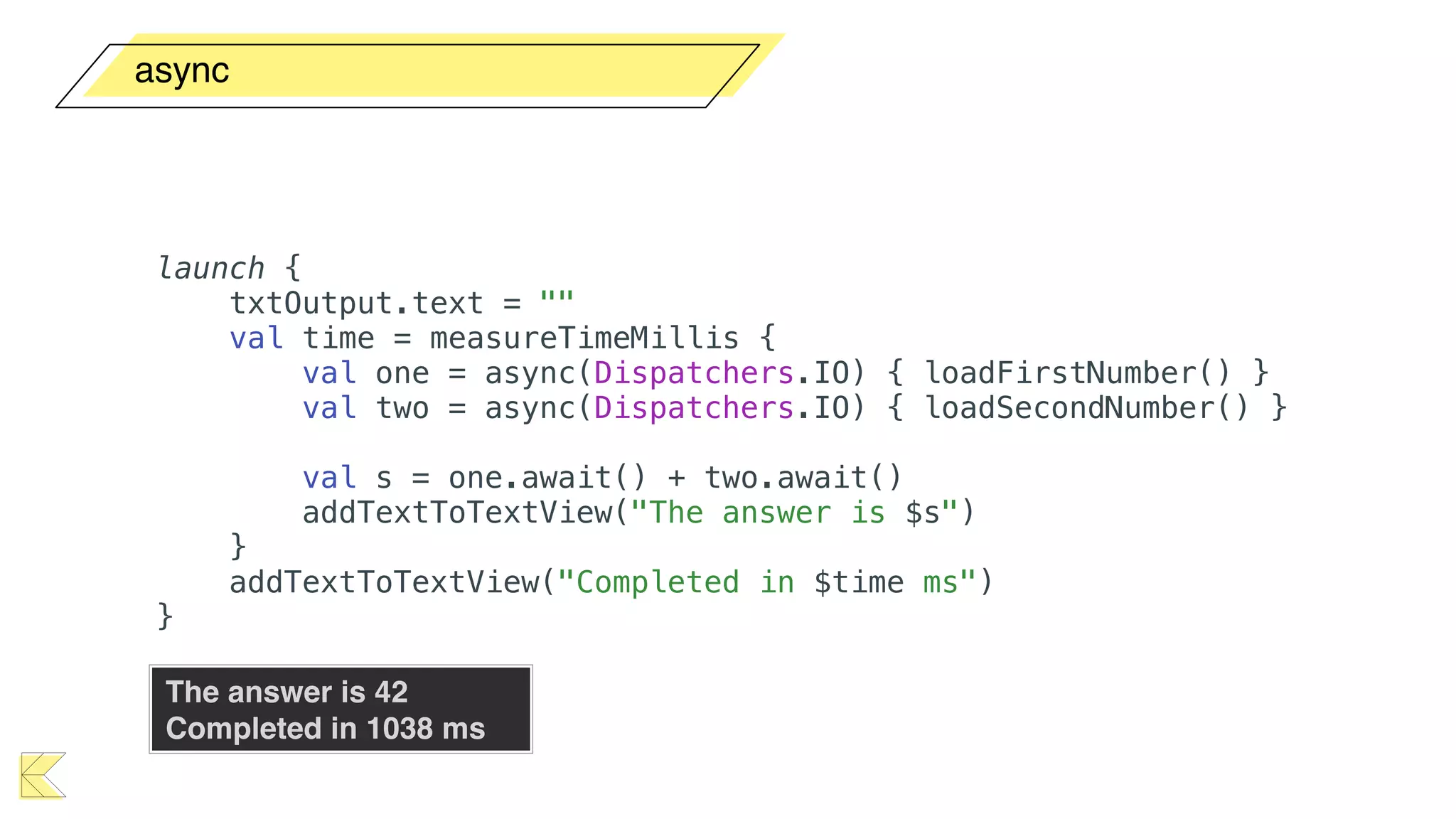
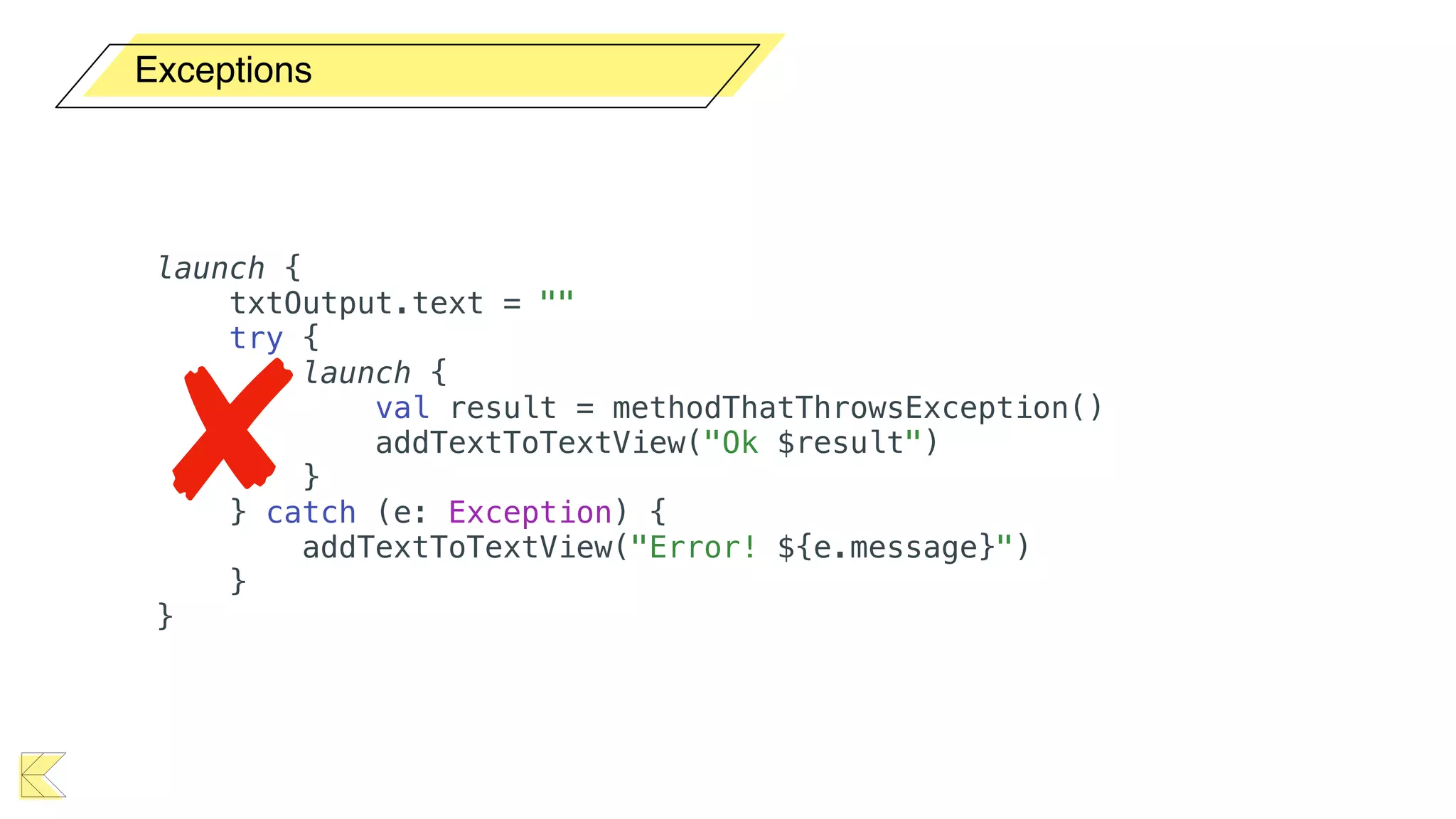
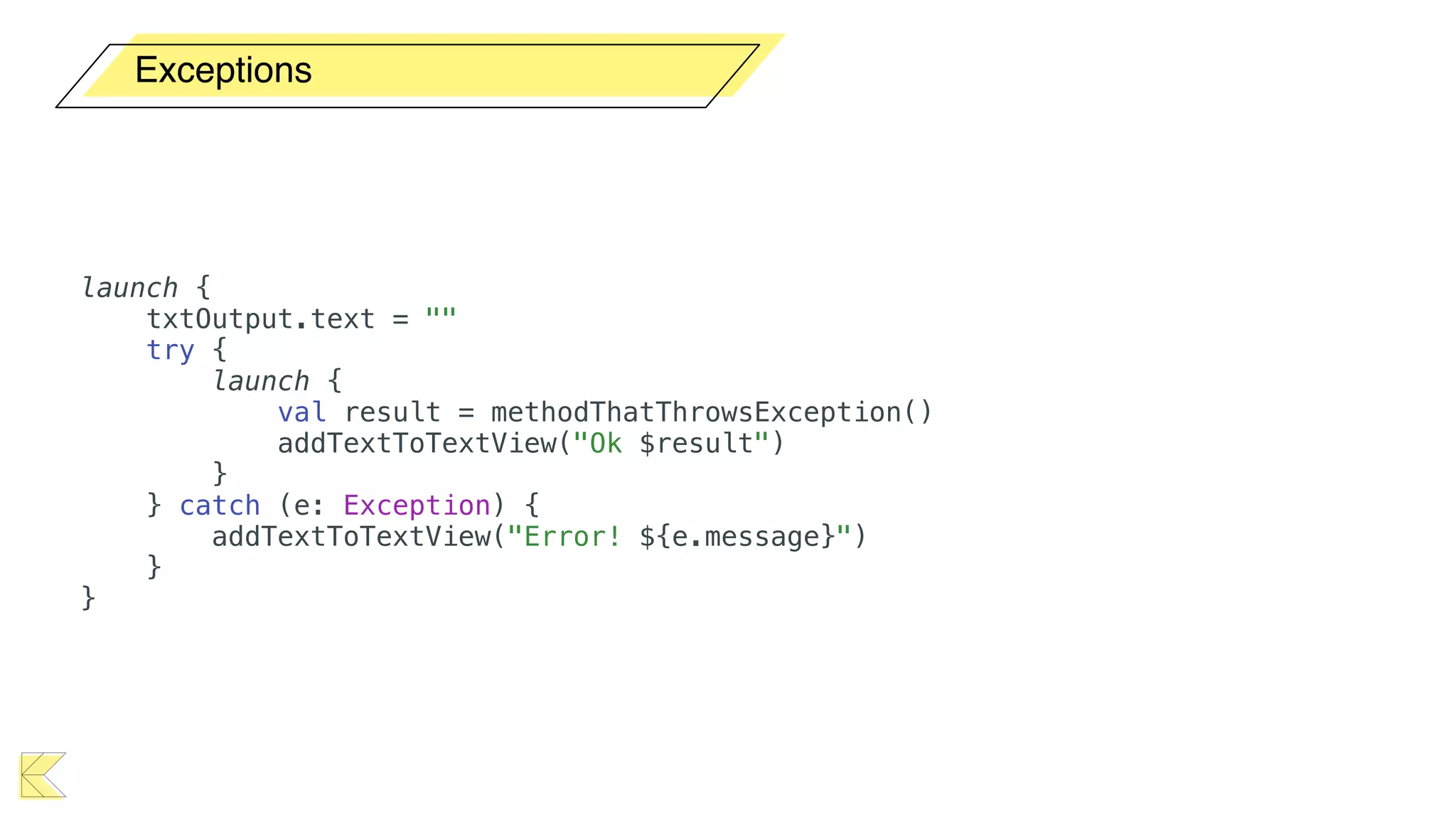
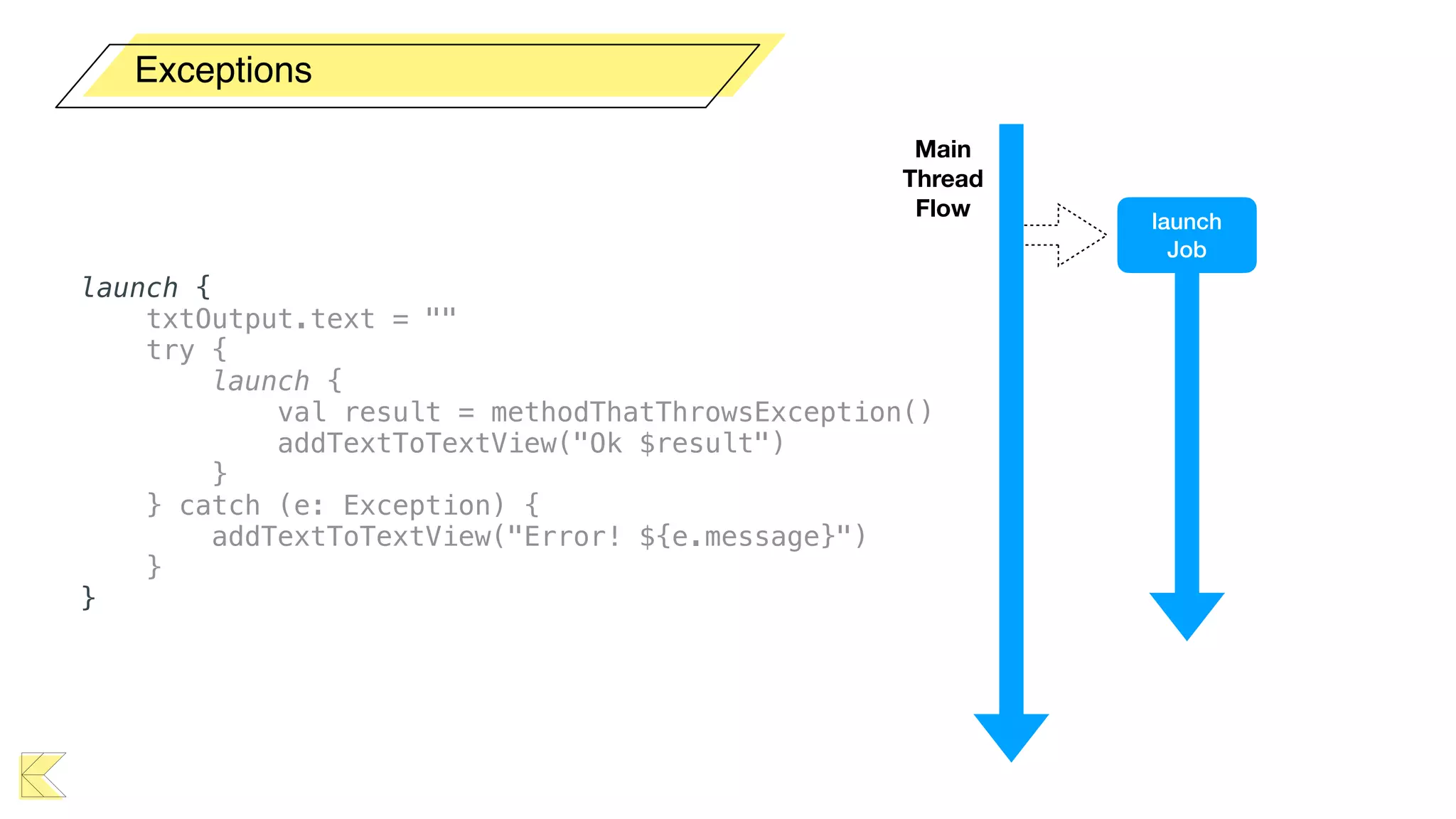
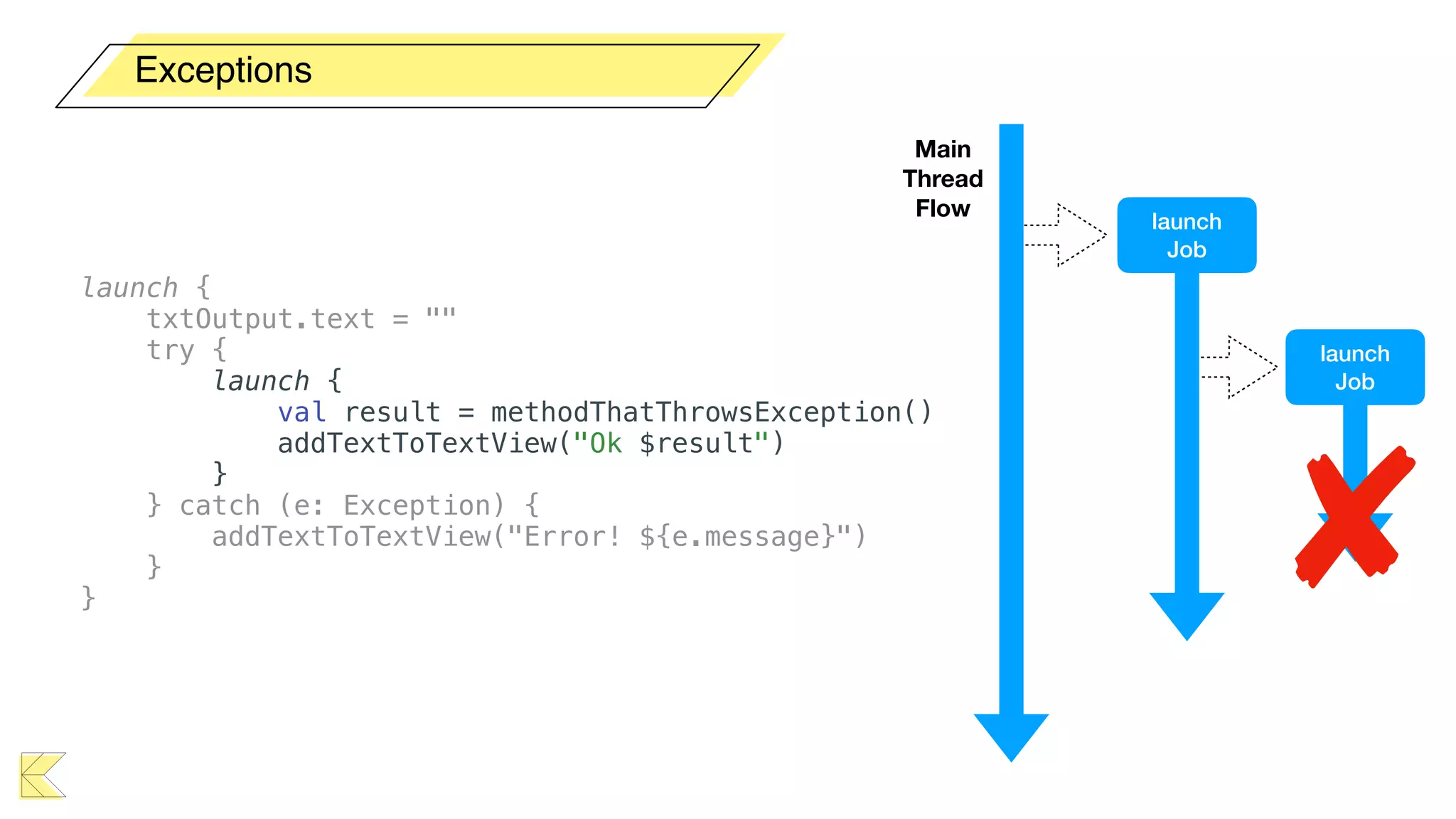
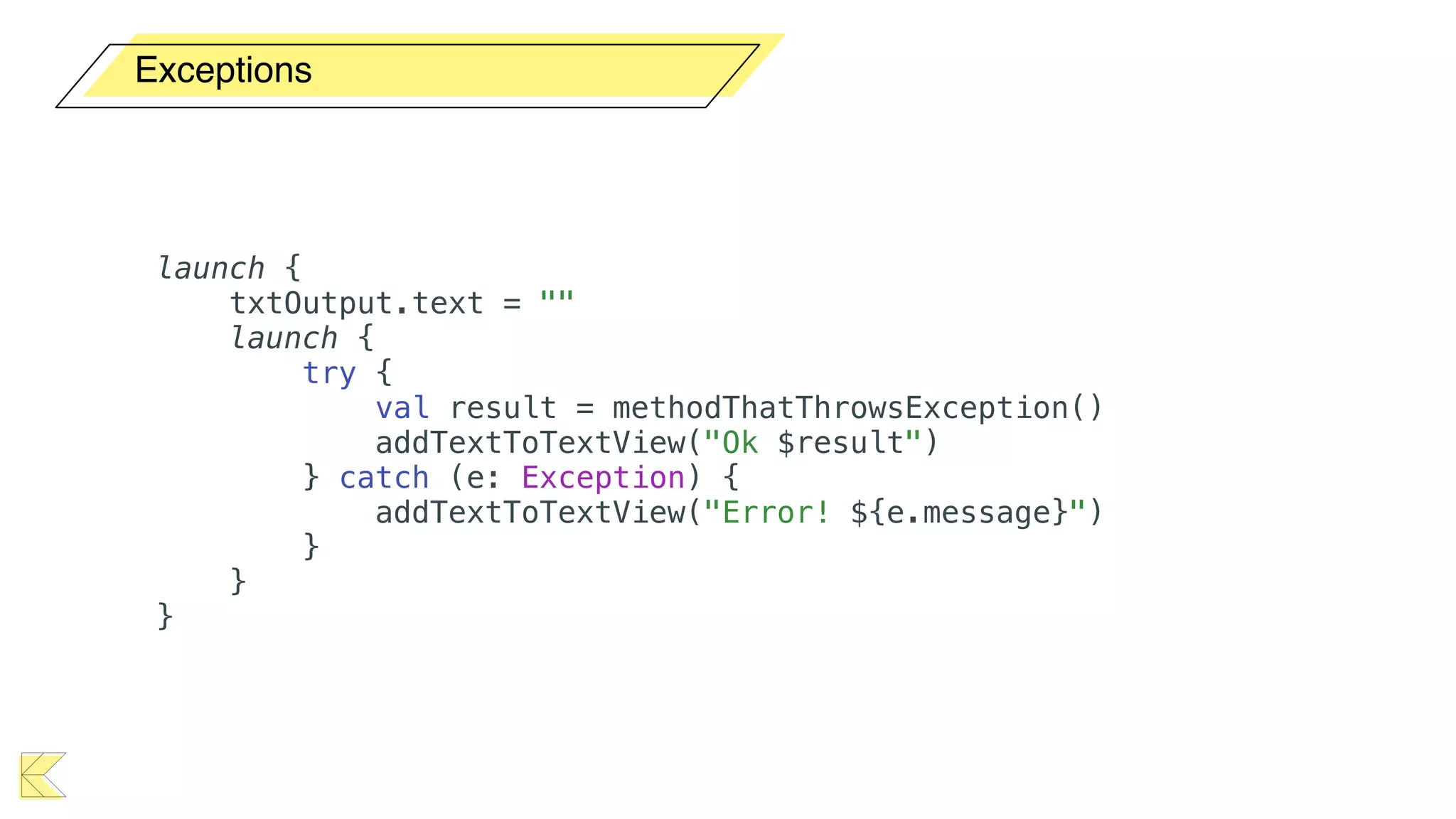
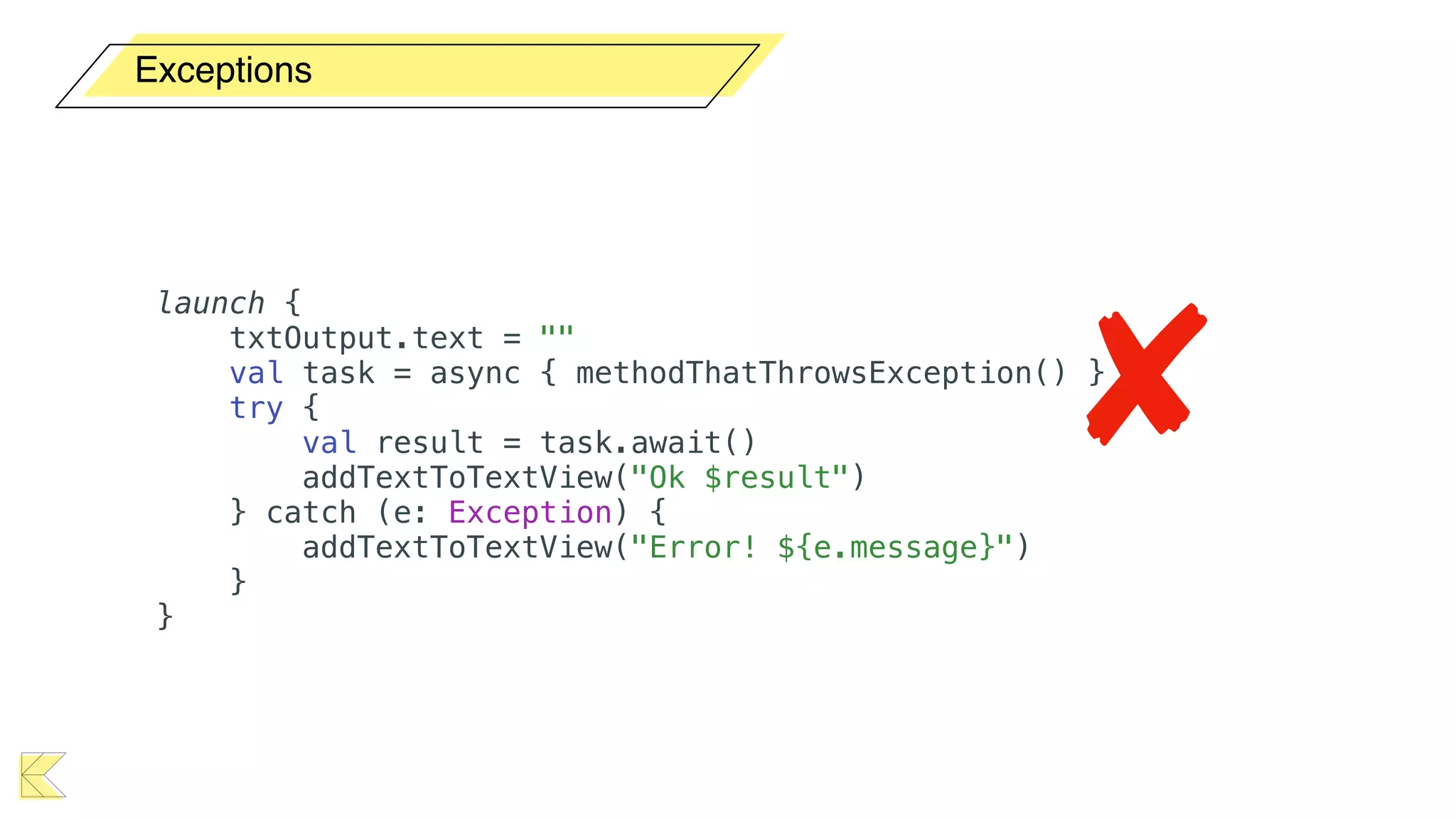
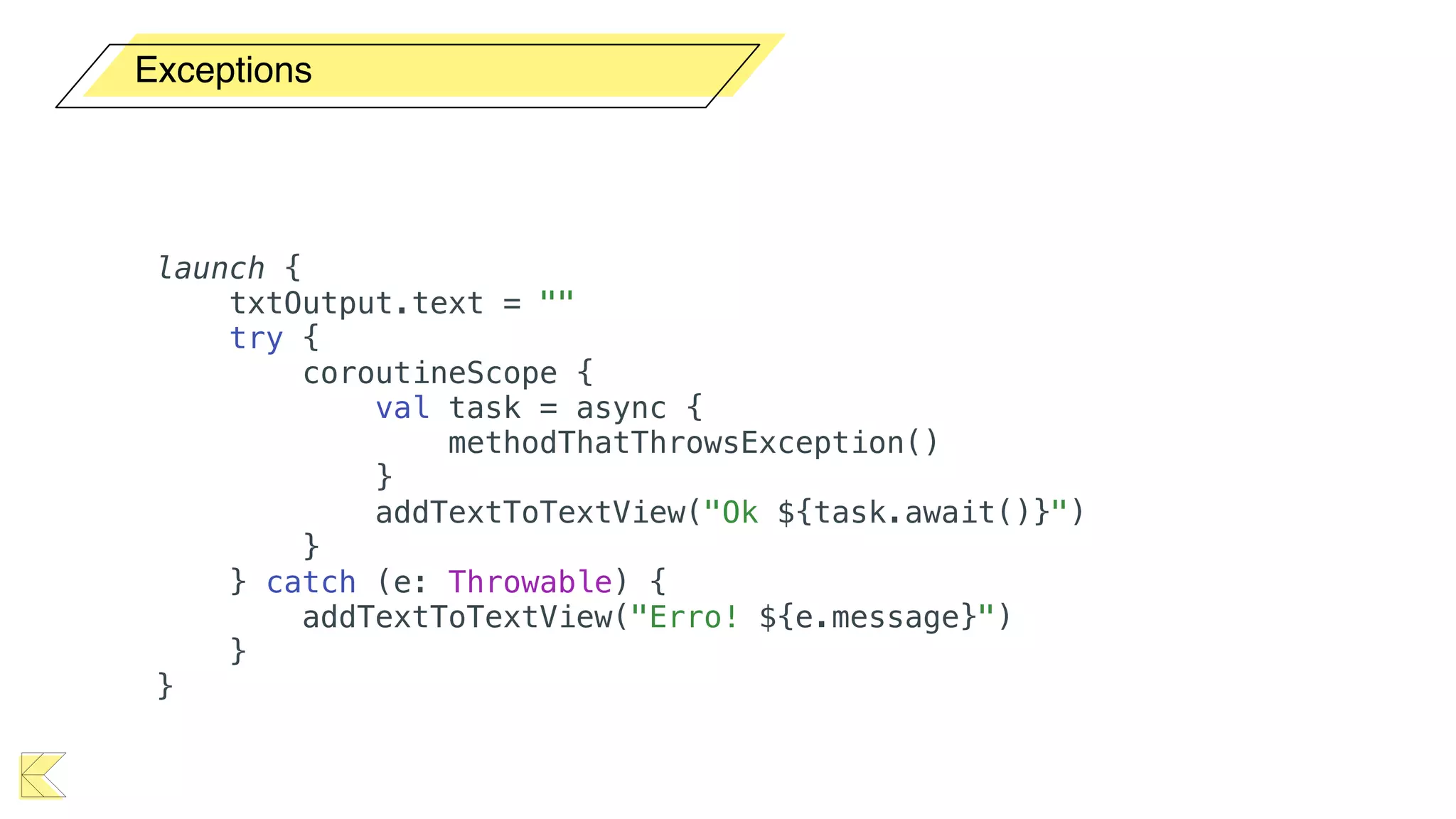
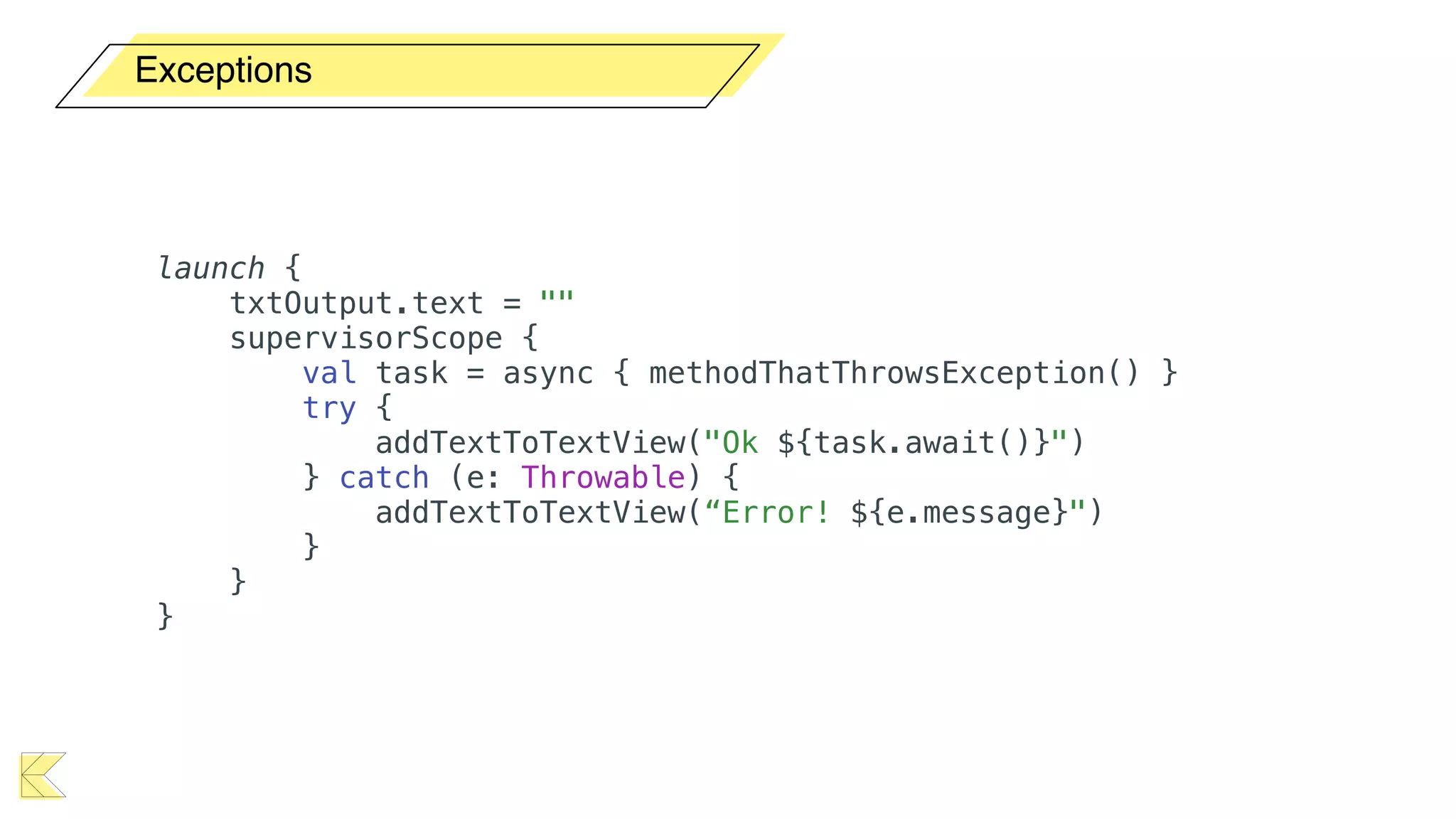
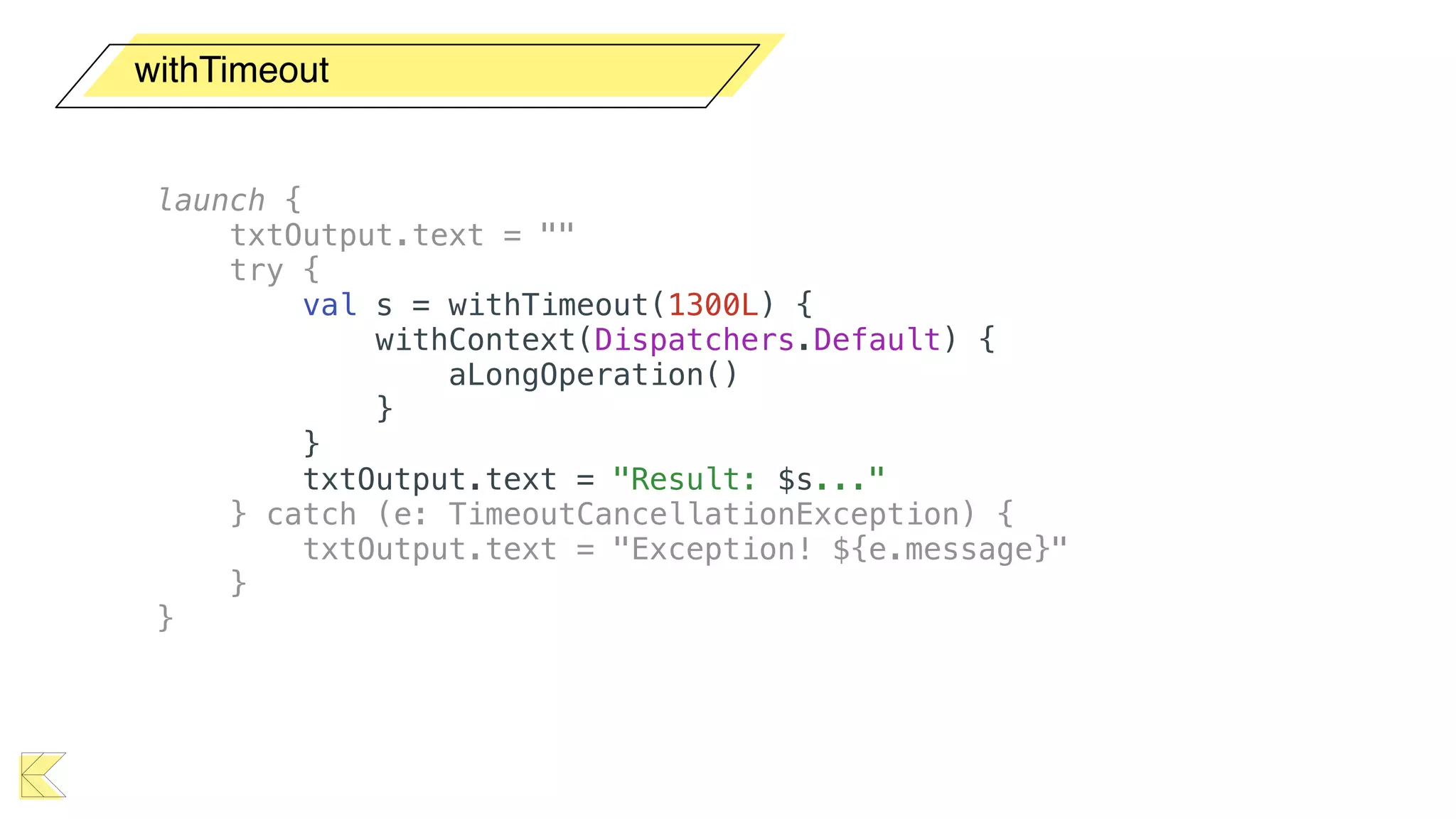
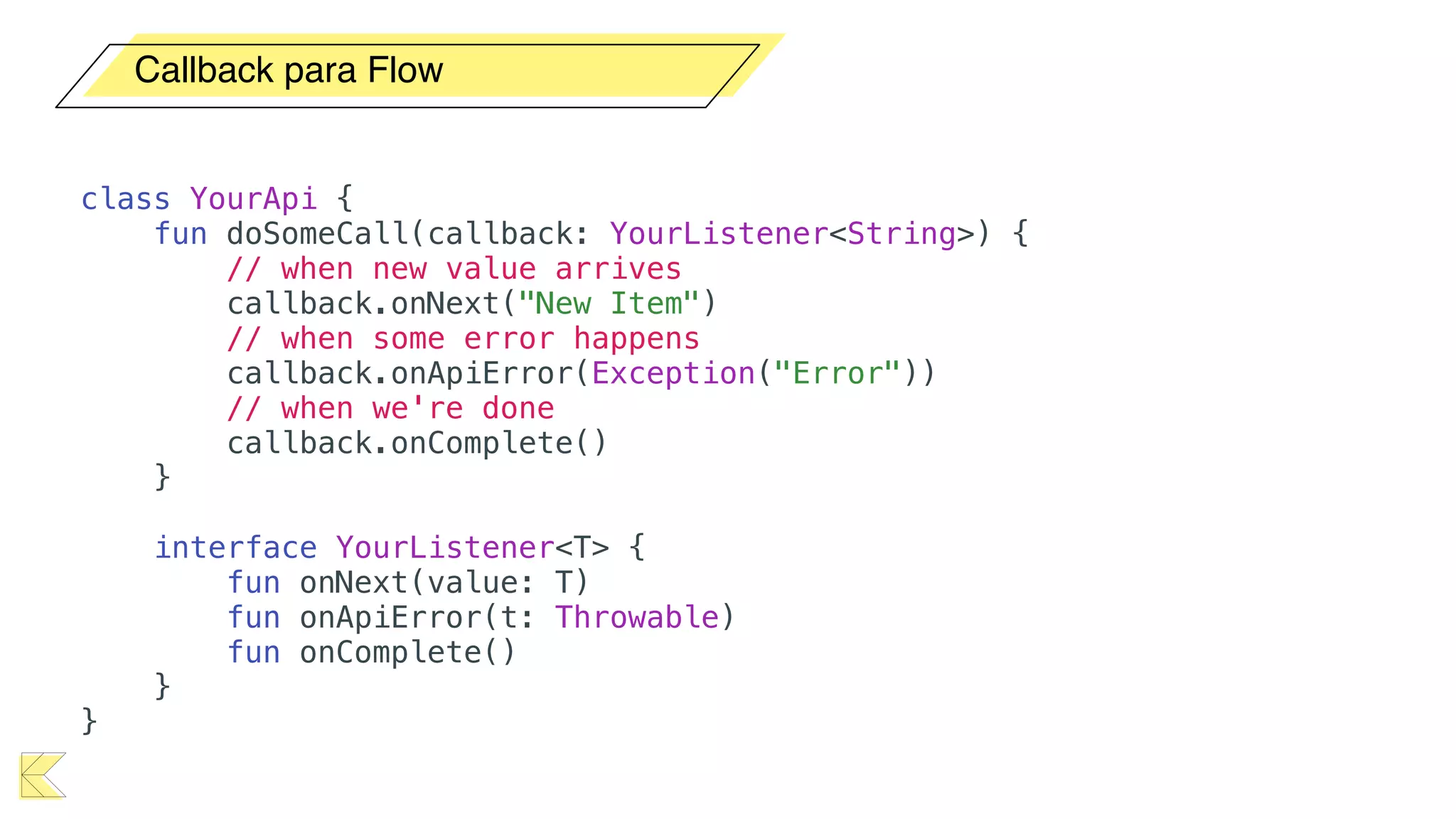
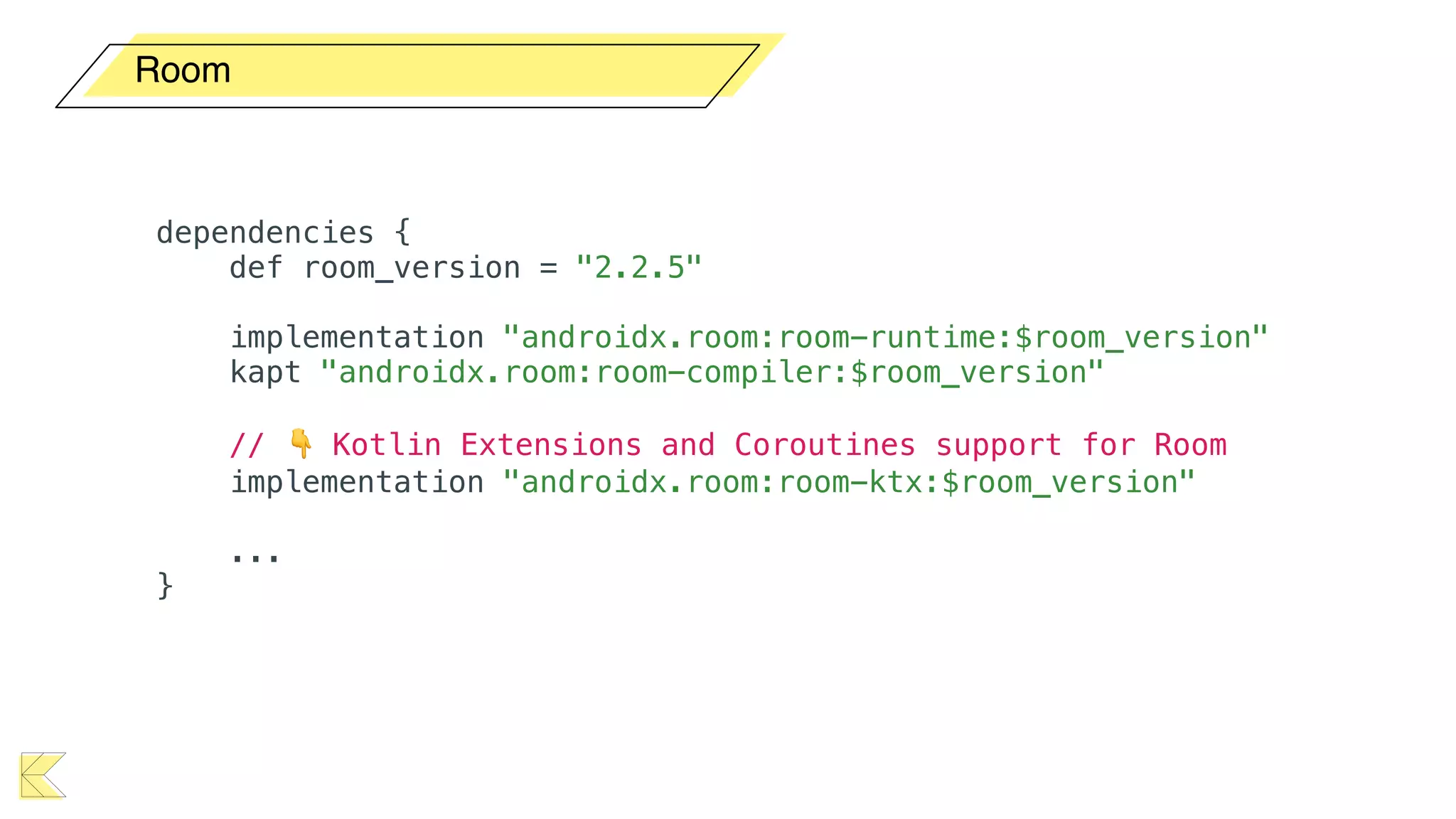
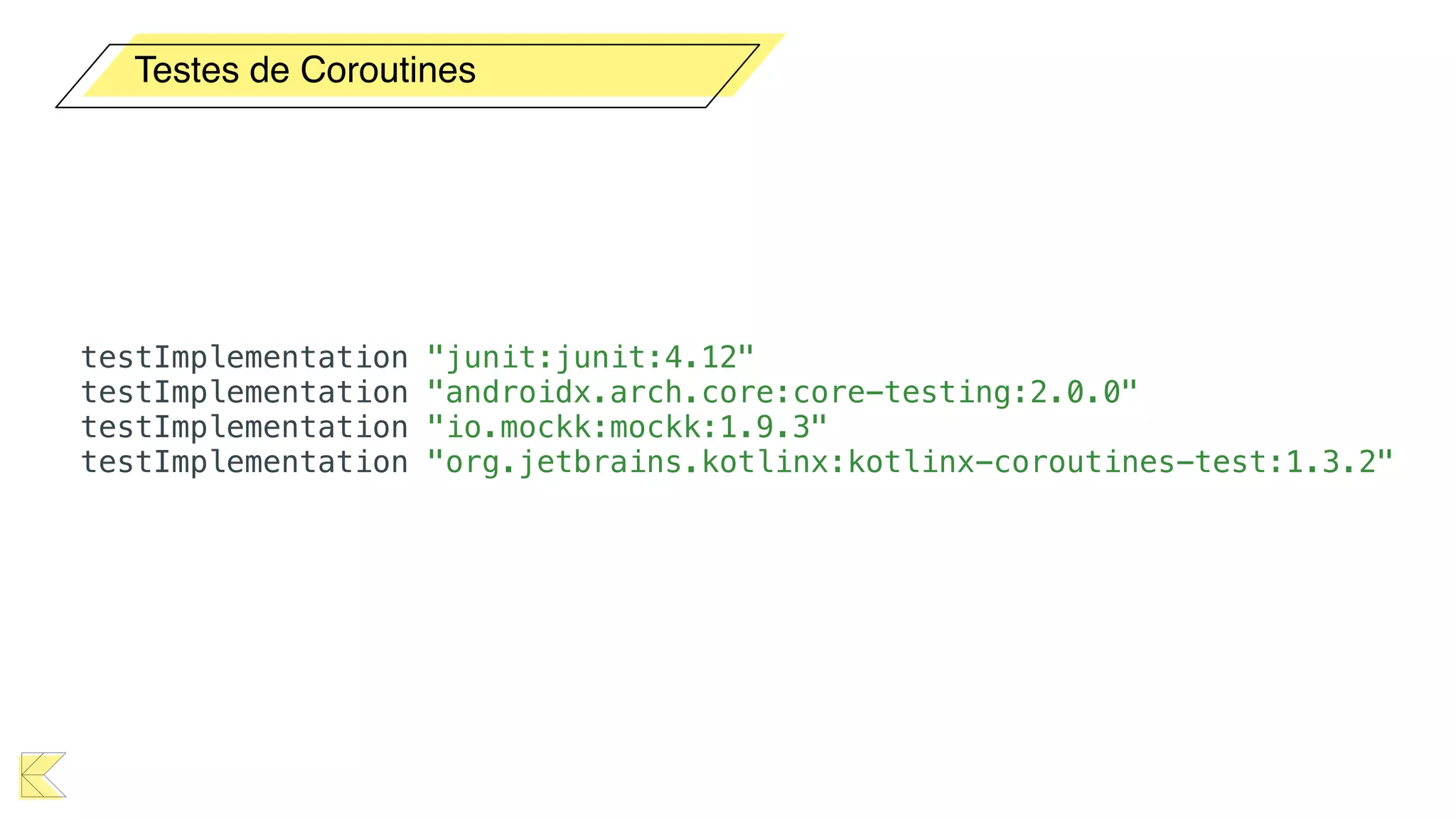
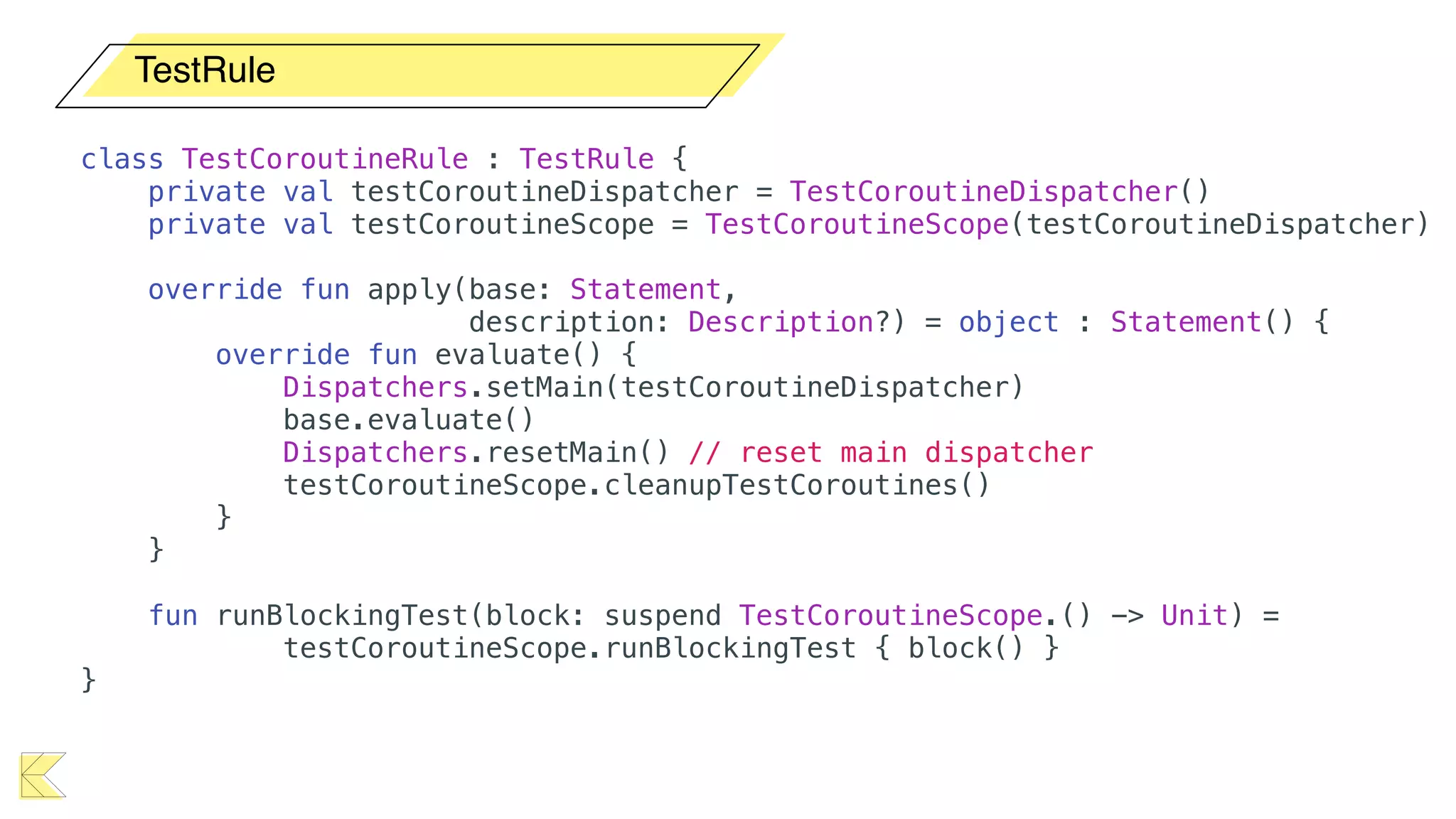
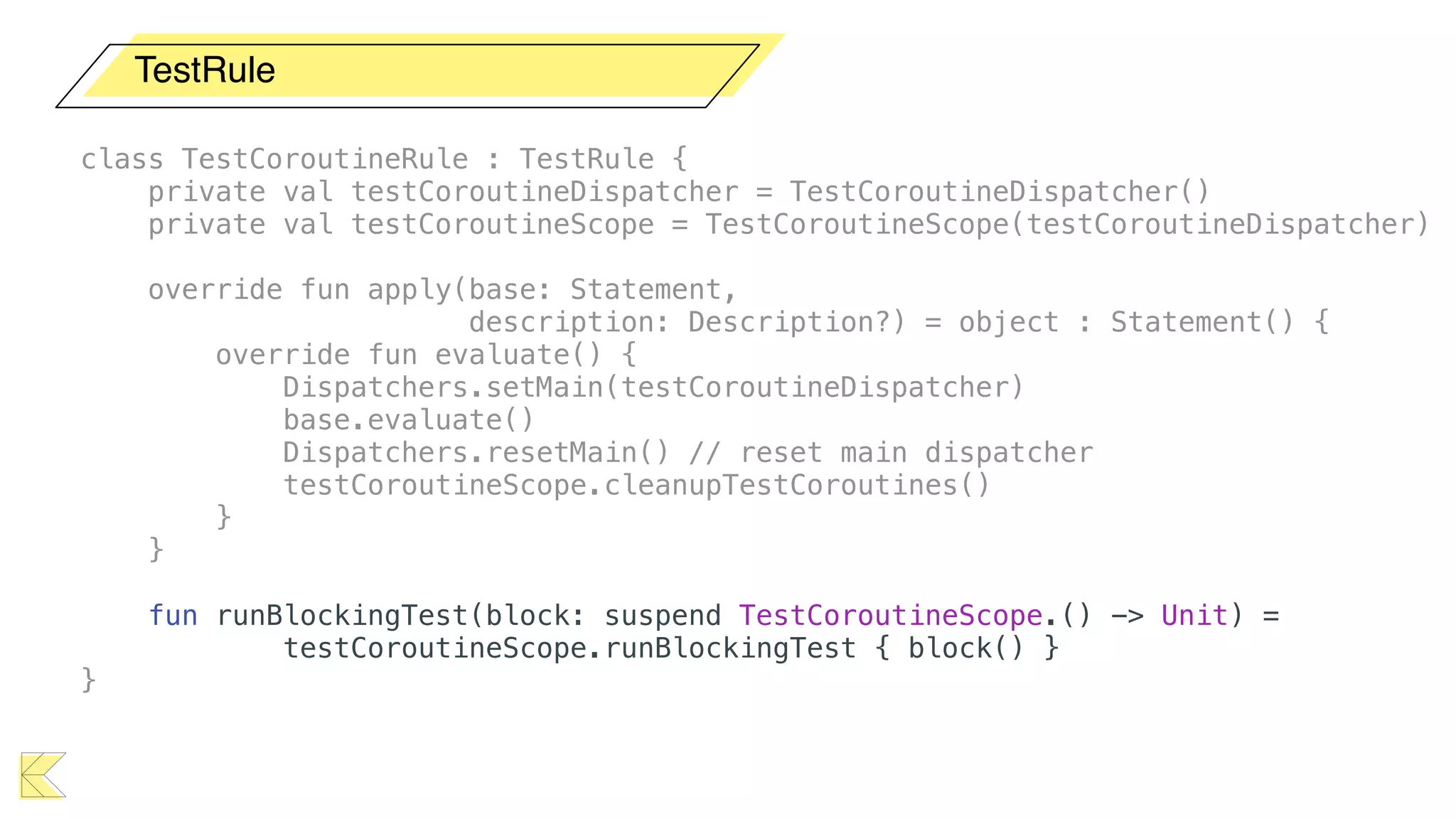
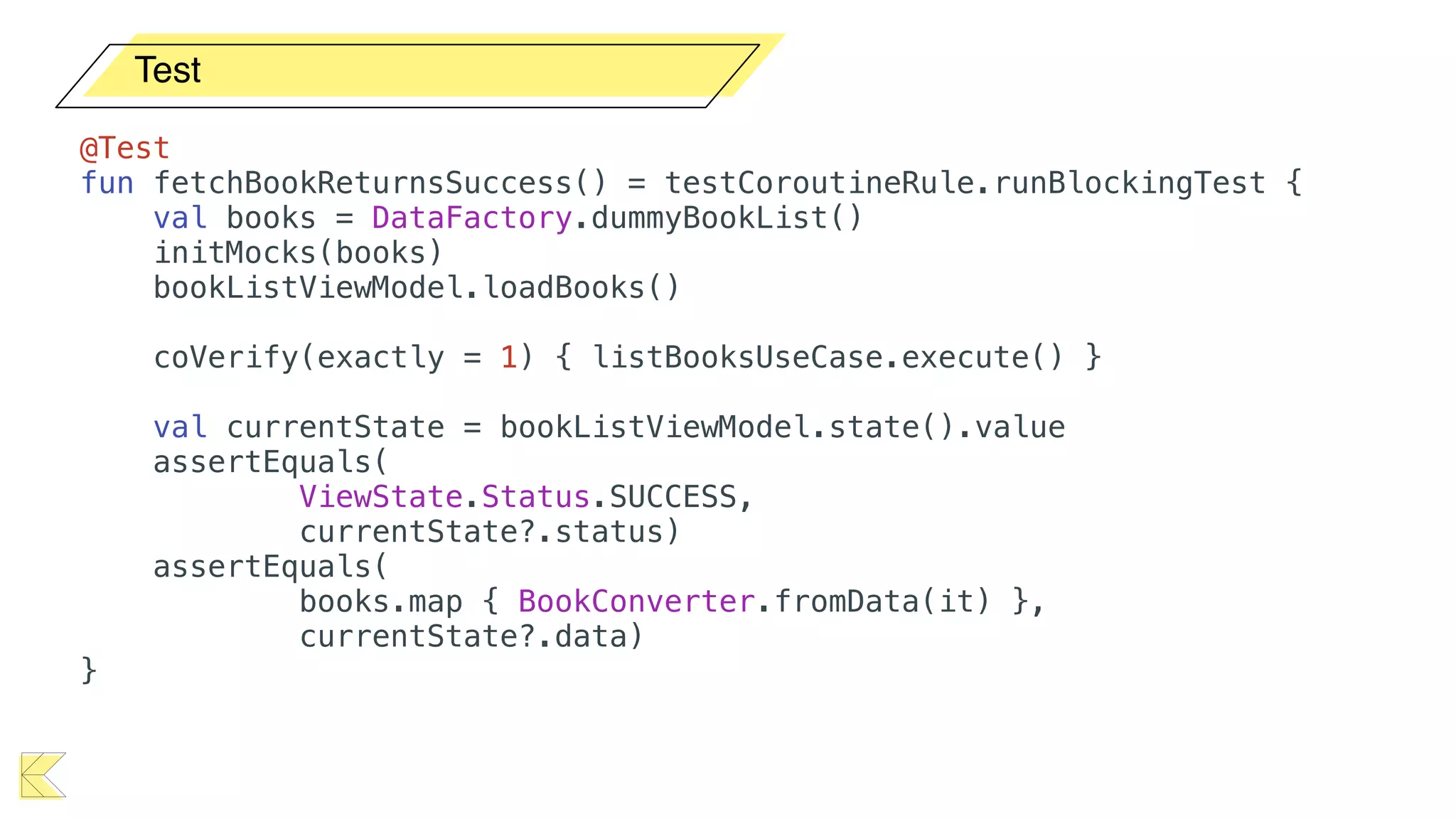
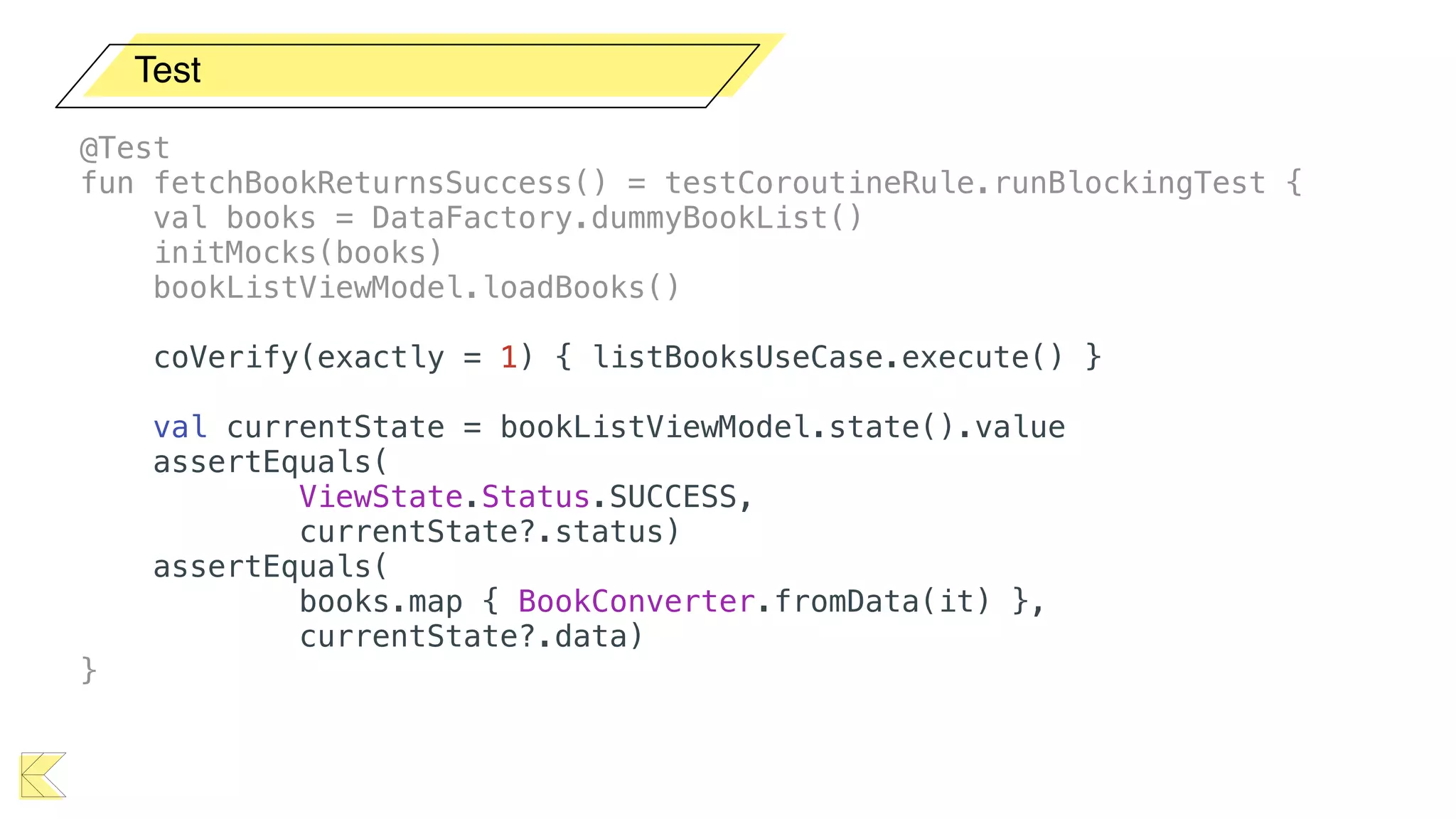
O documento explora o uso de coroutines no Android para implementar aplicações assíncronas, destacando sua facilidade de uso em comparação com métodos anteriores como AsyncTask e RxJava. Ele descreve conceitos como funções suspensas, ciclos de vida de coroutines, escopos e contextos, além de discutir o uso de ViewModel e WorkManager em conjunção com coroutines. Exemplos de implementação e tratamento de exceções também são fornecidos, ilustrando como gerenciar tarefas assíncronas de forma eficiente.