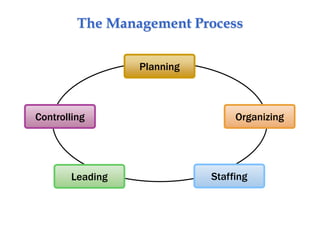
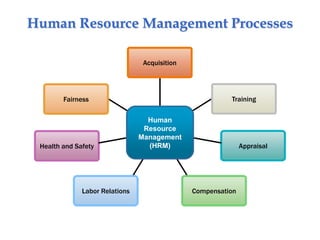
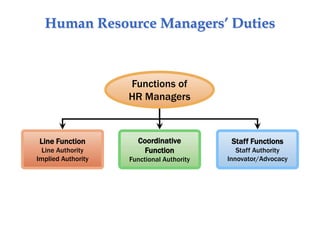
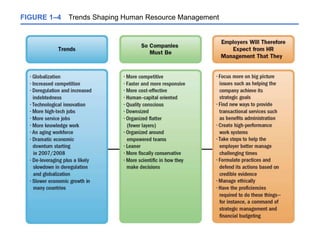
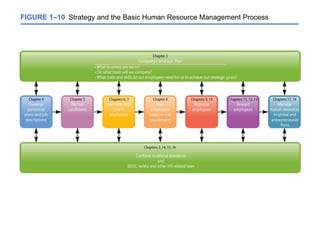
The document provides an introduction to human resource management, explaining what it is, why it's important to managers, and the responsibilities of both line and staff managers in HRM. It discusses the key aspects of HRM like acquisition, training, compensation, and health and safety. Additionally, it outlines trends shaping HRM and ethical issues managers may face.