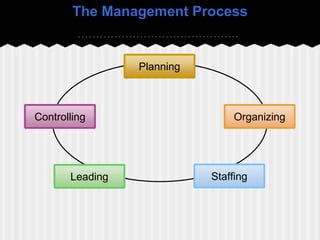
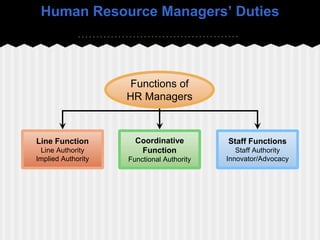
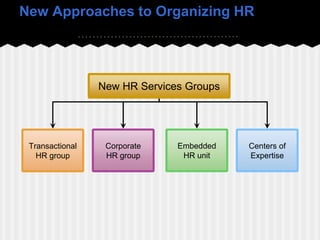
This document provides an introduction to human resource management. It defines HRM as acquiring, training, appraising, and compensating employees while also attending to labor relations, health, safety, and fairness concerns. The key HRM processes include acquisition, training, appraisal, compensation, labor relations, health and safety, and fairness. Personnel aspects of a manager's job include conducting job analyses, planning labor needs, recruiting, selecting, orienting, training, managing compensation, appraising performance, and developing employees. The document outlines different types of personnel mistakes and the roles of line managers, staff managers, and human resource specialists in carrying out HRM responsibilities.