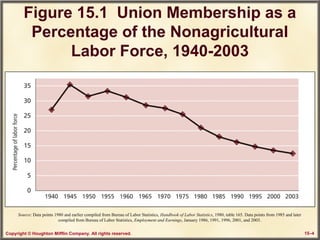
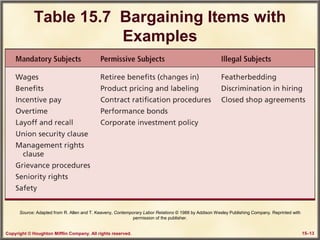
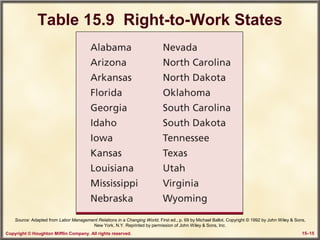
This chapter discusses labor relations and collective bargaining. It covers the historical and legal context of unions in the United States. It describes the union organizing process and how unions are formed through authorization card campaigns and secret ballot elections overseen by the NLRB. The chapter also discusses collective bargaining between unions and management, including bargaining structures, items, and contract clauses. Procedures for resolving disputes like strikes and the grievance process are also outlined.