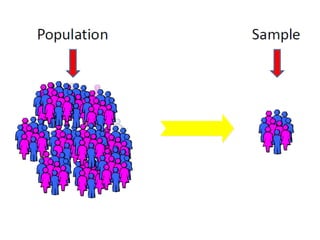
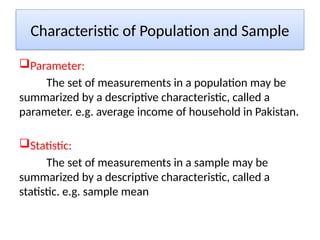
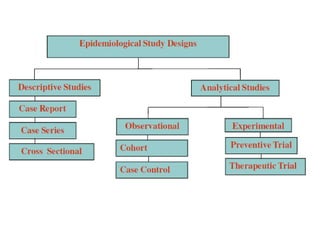
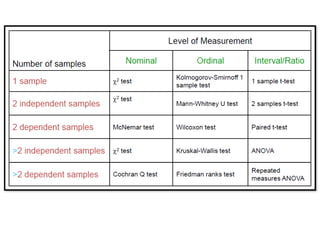
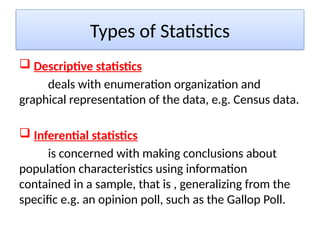
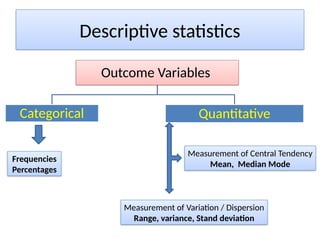
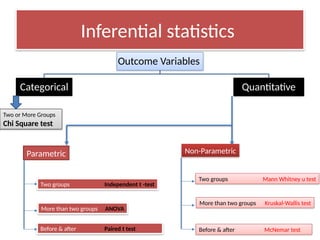
The document outlines the principles of statistical analysis using SPSS, detailing the definitions of population and sample, as well as the concepts of parameters and statistics. It categorizes the types of scales used in statistics and distinguishes between descriptive and inferential statistics, highlighting various outcome variables and tests applicable to different data types. Additionally, it provides examples of descriptive and inferential statistics methods, including tests for comparing groups.