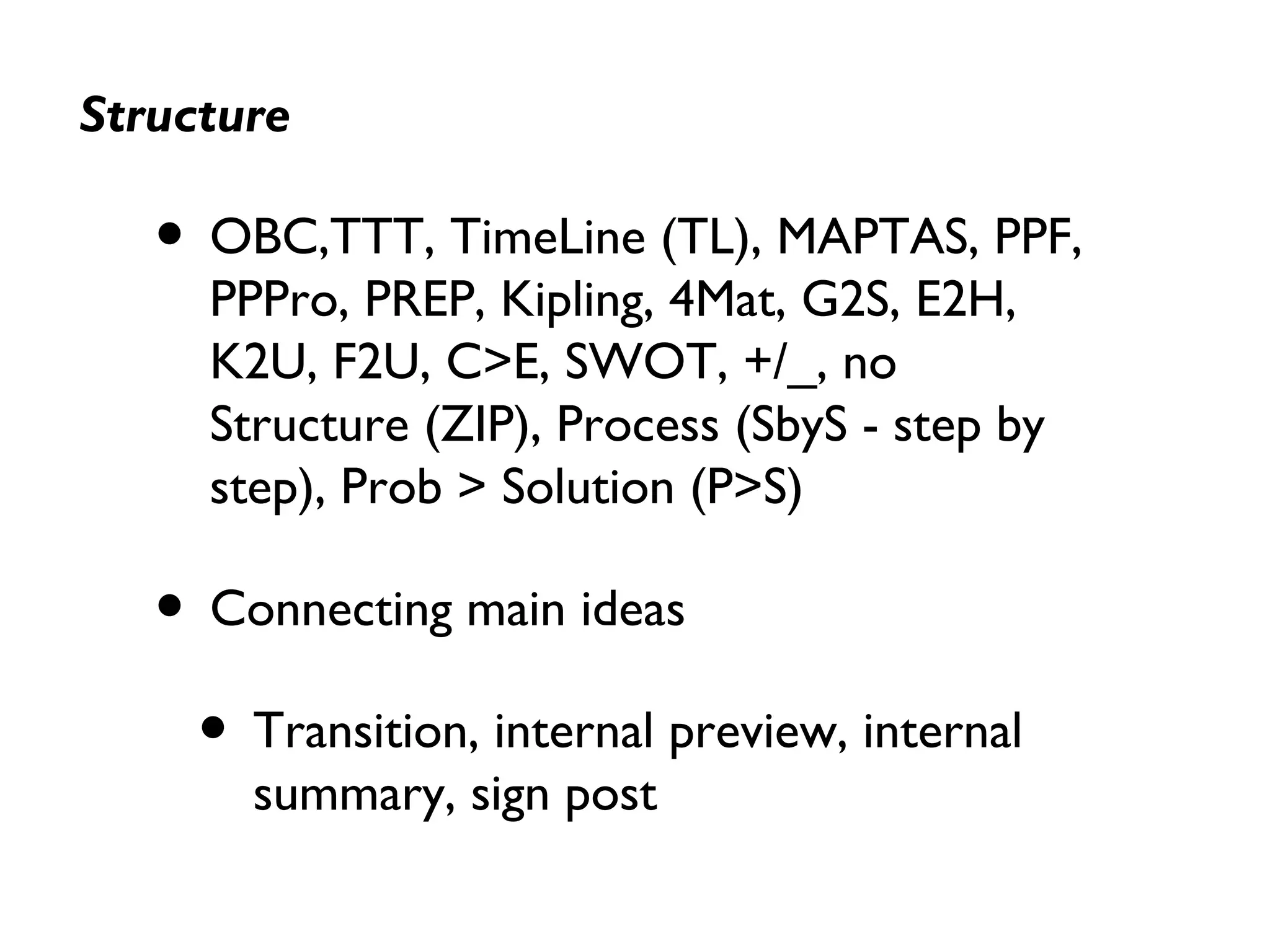
The document provides comprehensive guidance on effective presentation techniques, emphasizing the importance of communication skills for speakers. It covers key areas such as purpose, content development, structure, delivery methods, and evaluation, offering numerous strategies for engaging audiences. The various techniques listed can be tailored to different contexts to enhance the presentation experience.