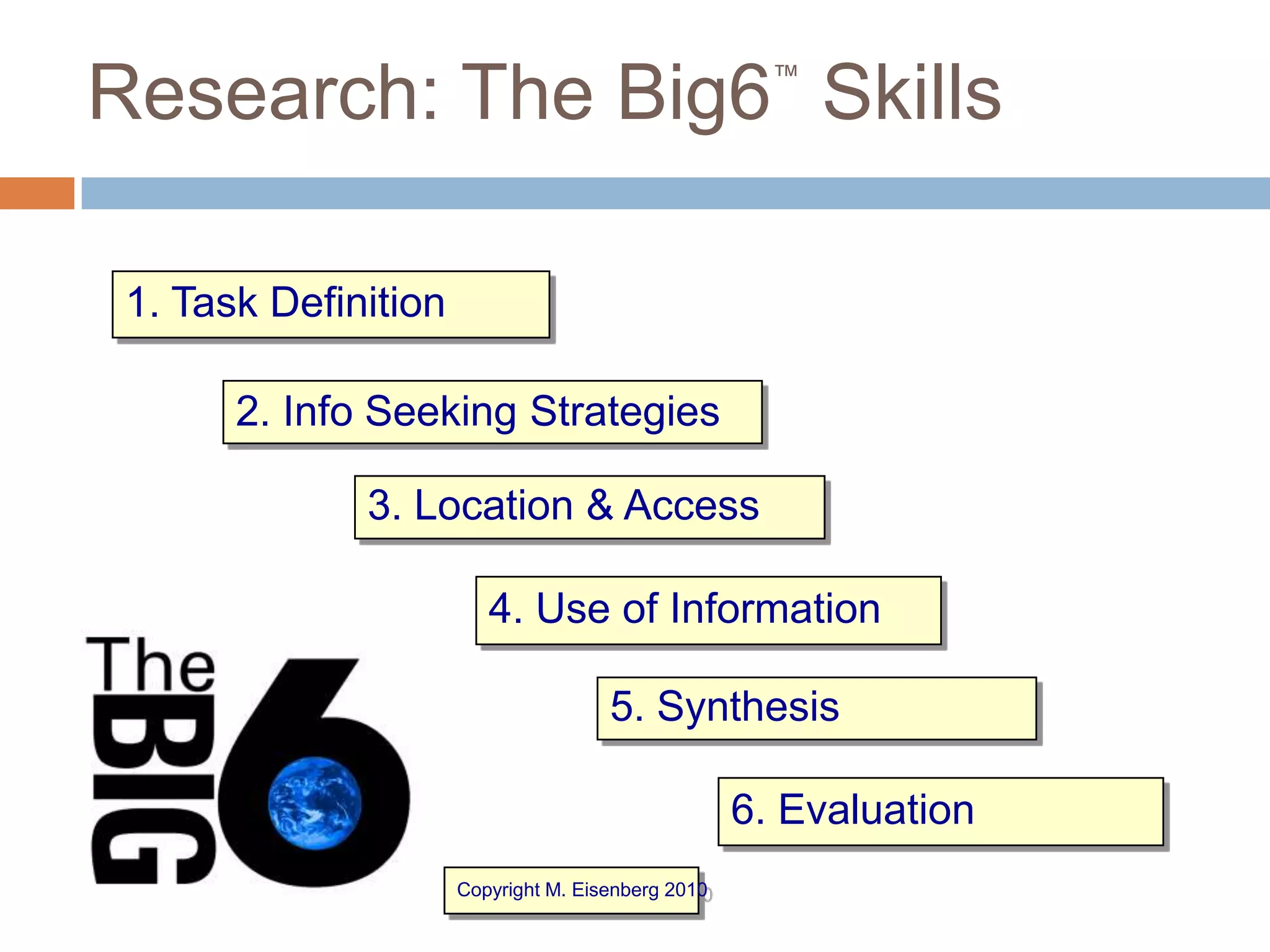
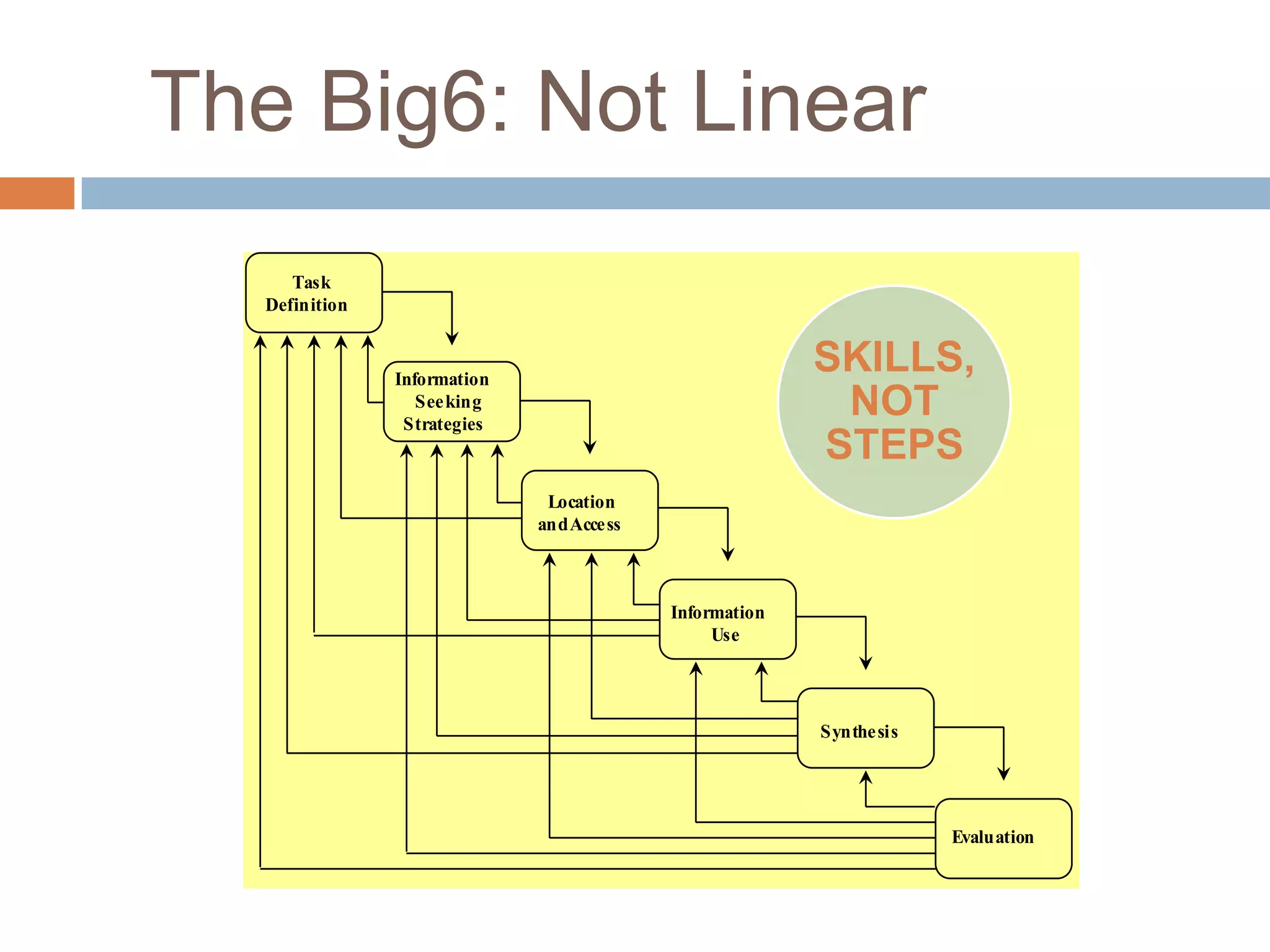
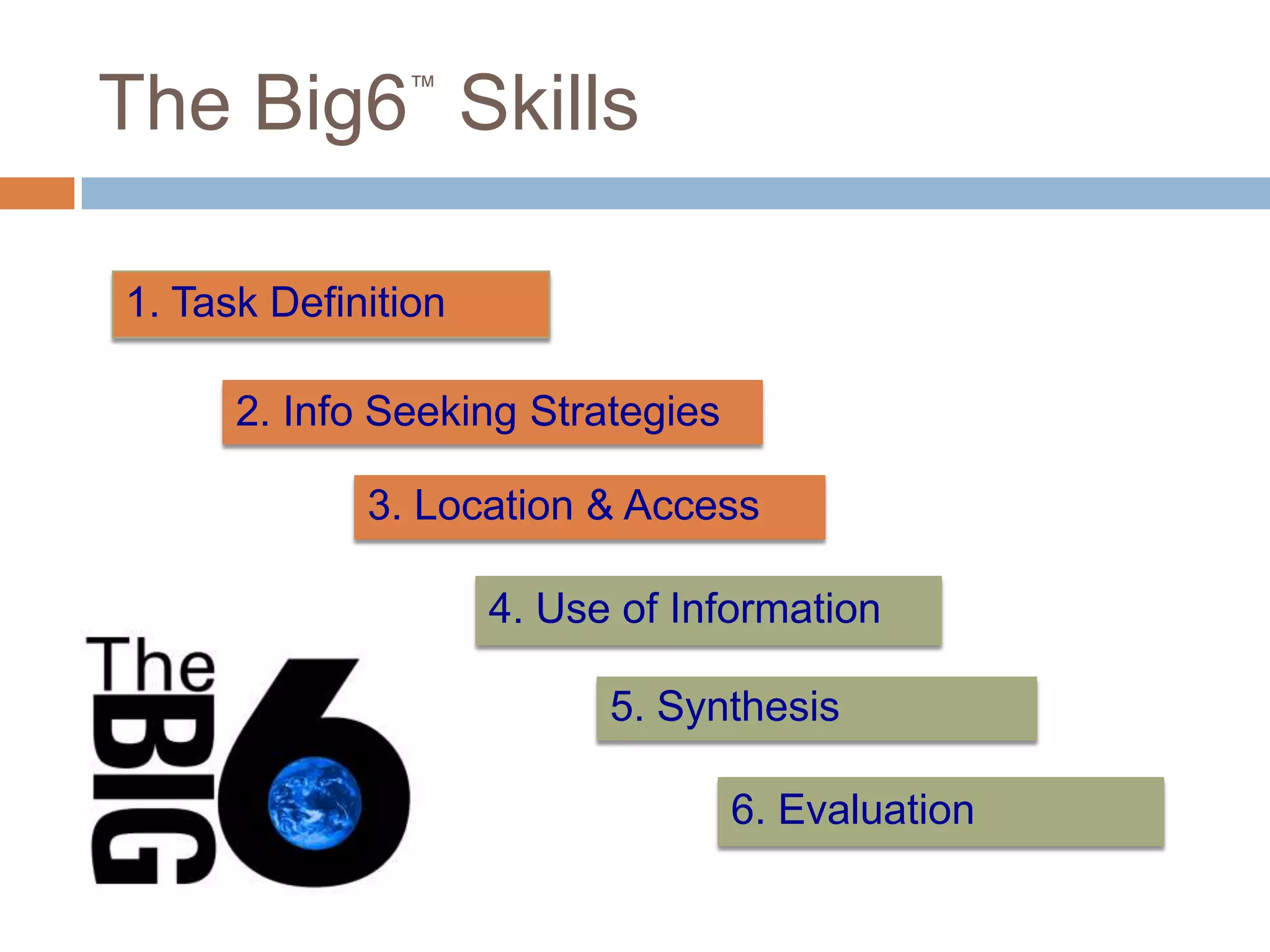
The document outlines the Big6 research skills framework for information literacy, emphasizing the importance of recognizing information needs and effectively locating, evaluating, and using information. It includes detailed strategies for task definition, information seeking, source evaluation, and source location, alongside practical examples and resources. The text also highlights the distinction between types of sources, both primary and secondary, and provides guidelines for selecting credible sources over less reliable ones like Wikipedia.