Embed presentation
Downloaded 10 times












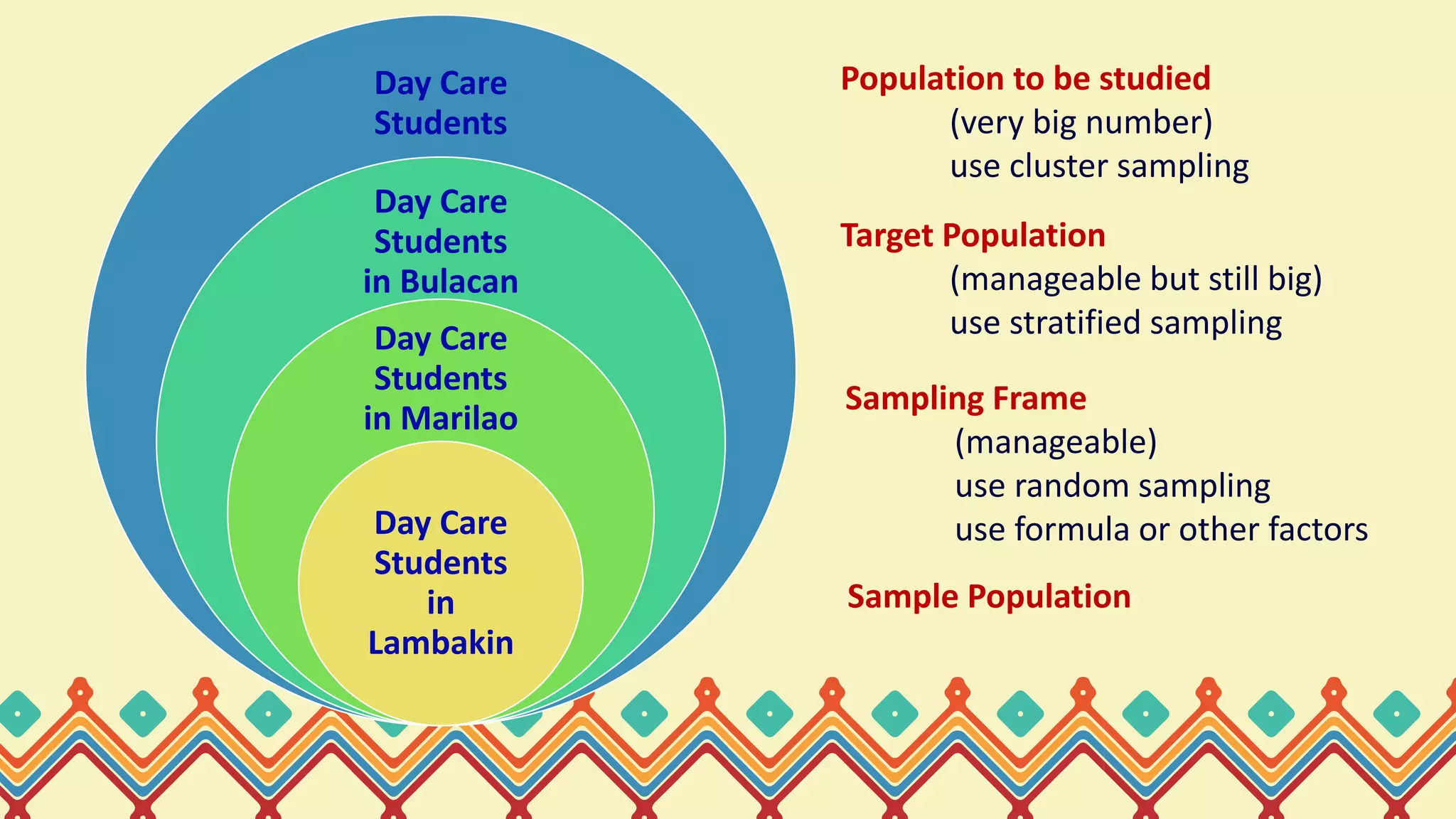



1. To determine a sample population, identify the overall population to study, the sampling frame, acceptable margin of error, and desired reliability. 2. Consider the size of the population to determine whether to use a probability or non-probability sampling procedure. Formulas like Slovin's or Calmorin's may be needed. 3. Multistage sampling divides a large population into stages, such as first sampling clusters then sampling individuals, to make the sampling process more practical for a very large population.
Introduction to determining sample populations, key values include population of interest, sampling frame, margin of error, and reliability.
Consideration of population size, differentiating between sizes less than or equal to 100 and greater than or equal to 100.
Exploration of sampling procedures, focusing on probability and non-probability sampling methods.
Introduction to sampling formulas, specifically Slovin’s Formula and Calmorin’s Formula for determining sample size.
Explanation of multistage sampling, a technique for dividing large populations into stages for practical sampling.
Summary of the sampling process: determining population, setting frames, identifying error margins, choosing techniques, and deciding on necessary formulas.
Examples of target populations for day care students in Bulacan, Marilao, and Lambakin, with appropriate sampling techniques for each.
A motivational quote about choices and their impact on our future, emphasizing the importance of decision-making.
Acknowledgment of resources and references utilized throughout the presentation.














