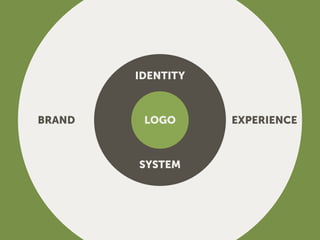
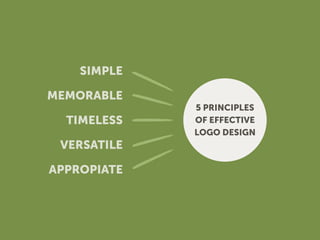
The document outlines the importance of creating a comprehensive brand identity system beyond just a logo for large organizations. It details the phases of logo and identity design, including the creation of a design brief, logo concept development, and the formulation of brand style guidelines. Additionally, it emphasizes the necessity of ongoing monitoring and potential rebranding as market conditions change.