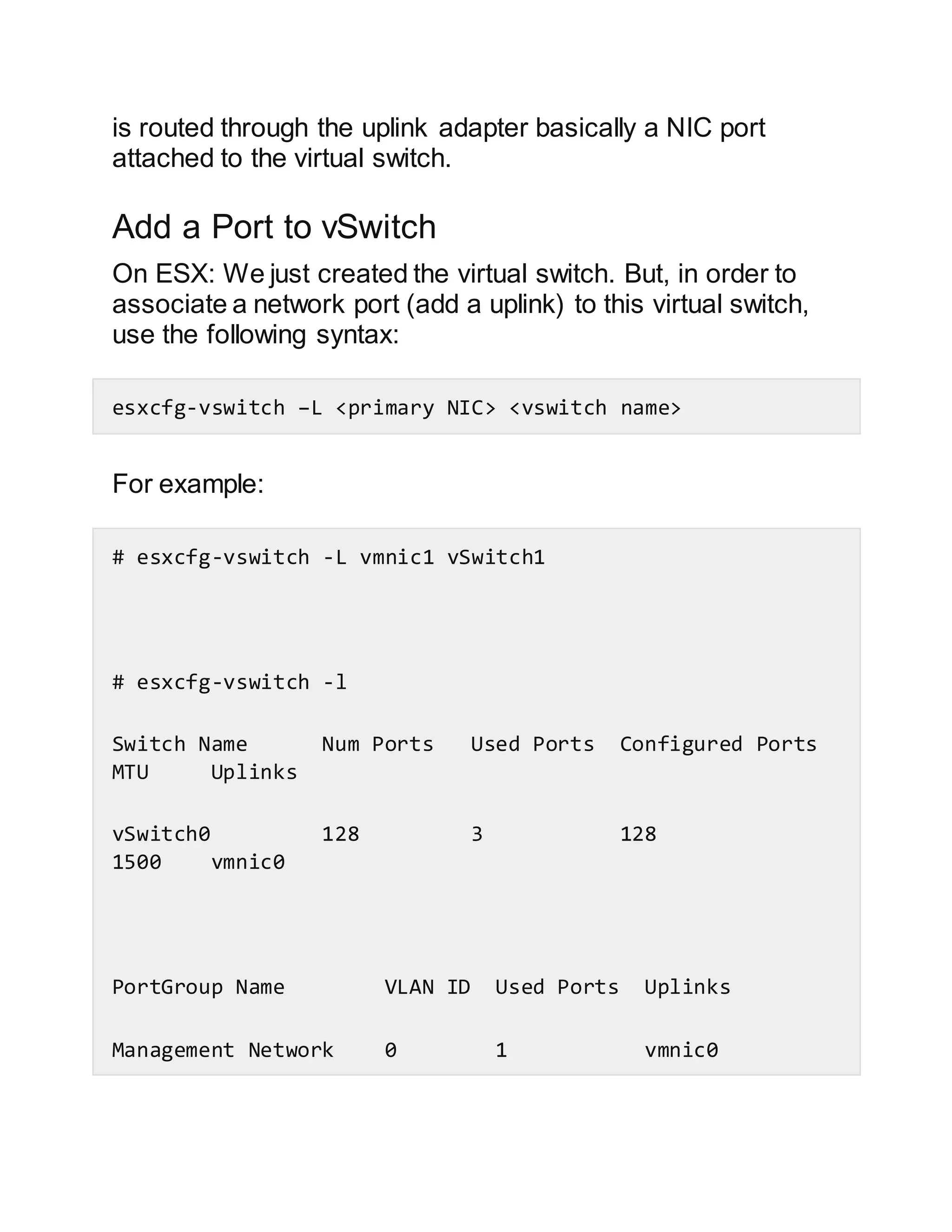
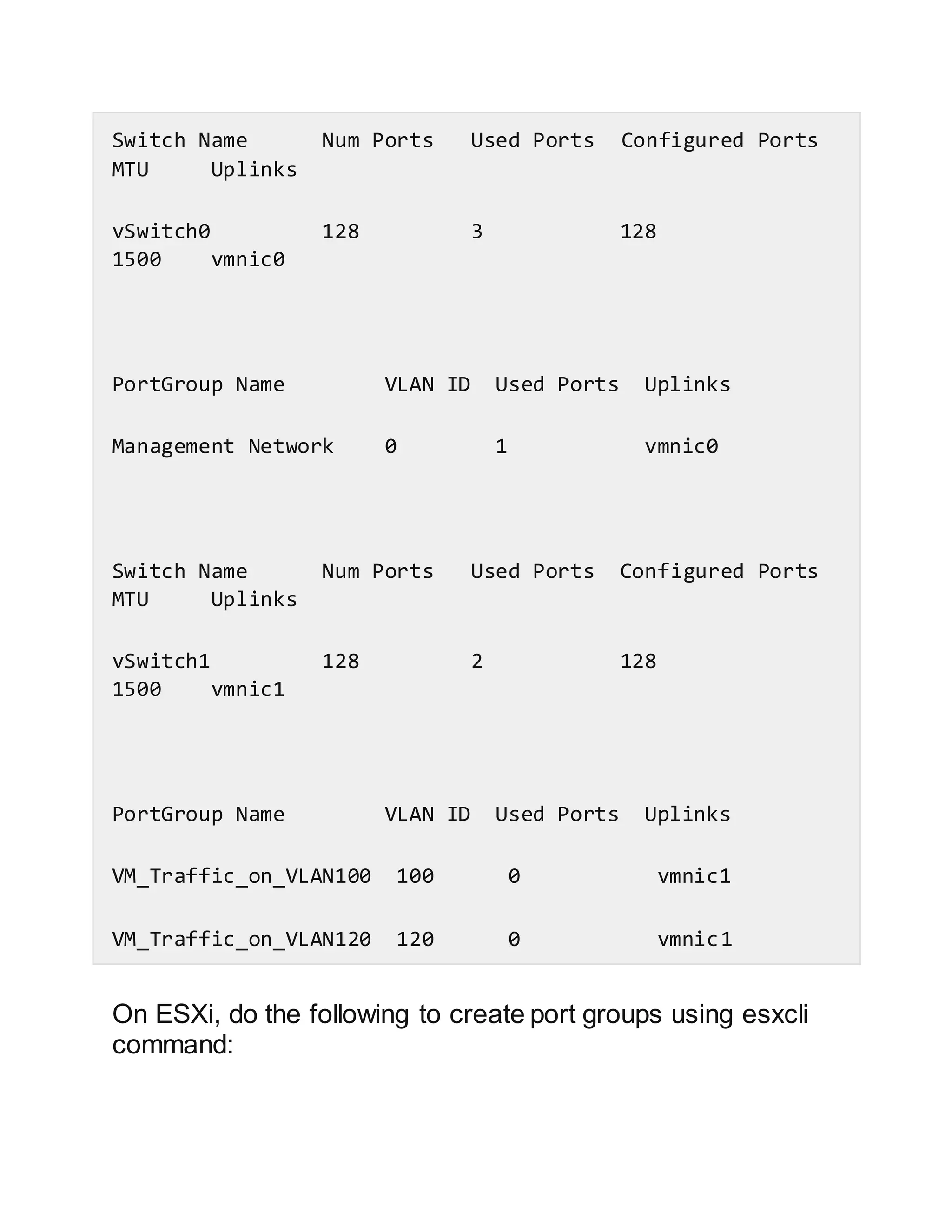
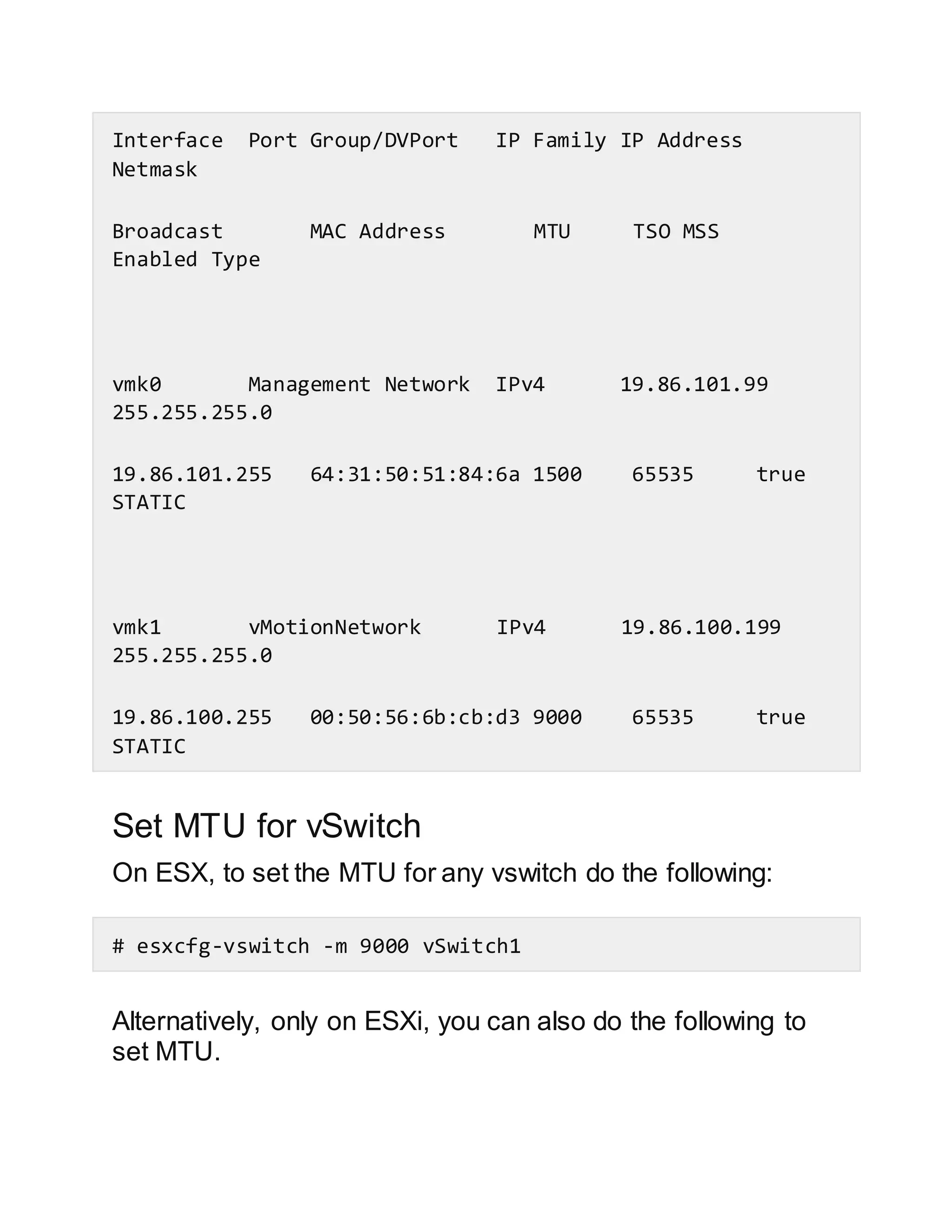
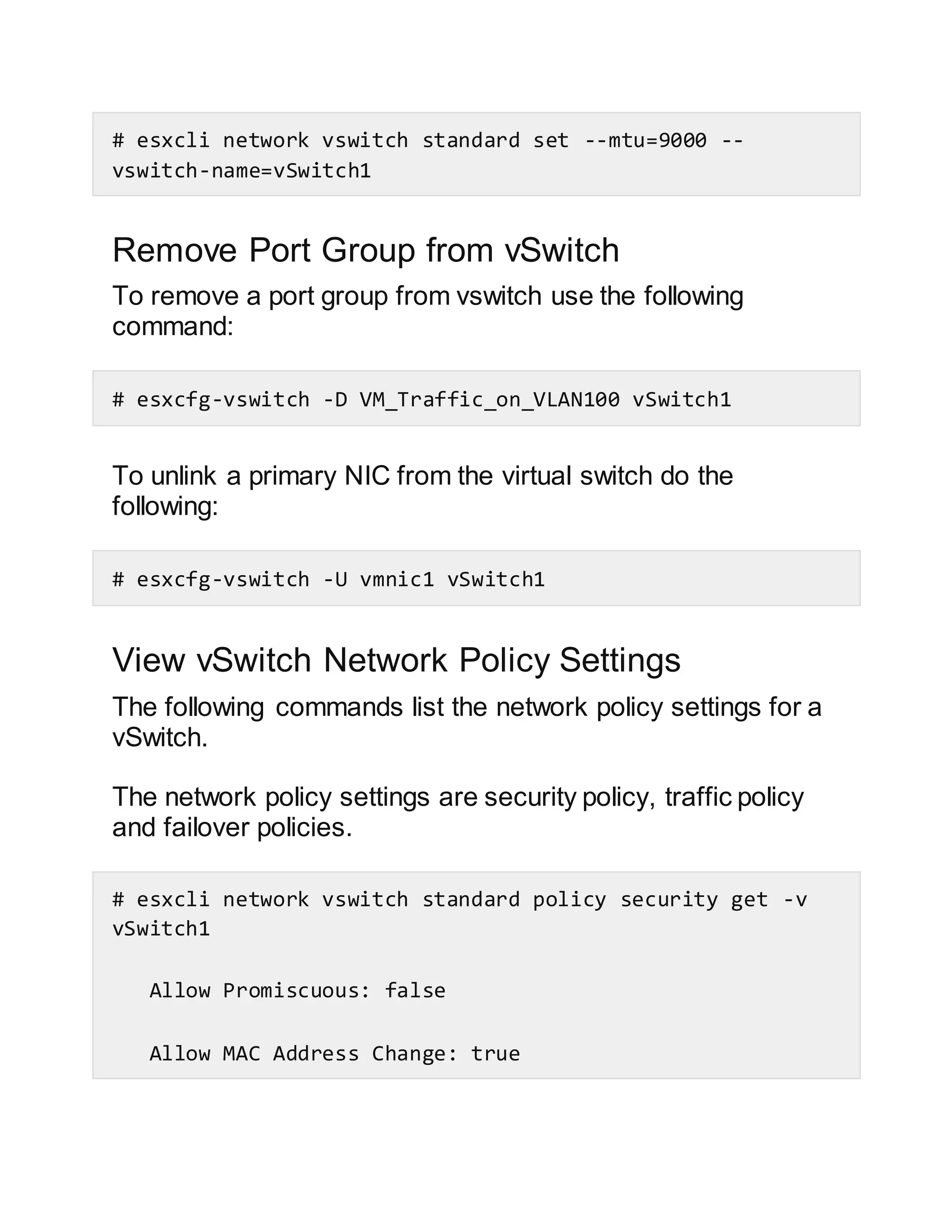
This document discusses how to configure vSwitches from the command line in VMware ESX and ESXi. It provides examples of how to list existing vSwitches, add new vSwitches, add ports/uplinks to vSwitches, create port groups, verify switch and port group existence, add a vMotion network, set the MTU, remove port groups, and view/change network policy settings using the esxcfg-vswitch and esxcli commands.