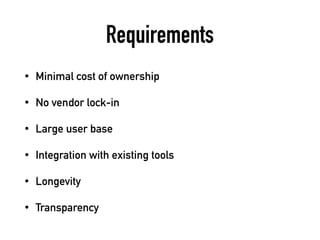
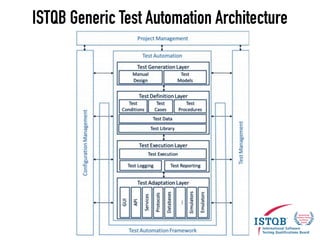
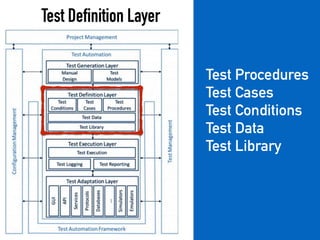
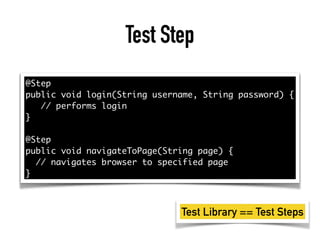
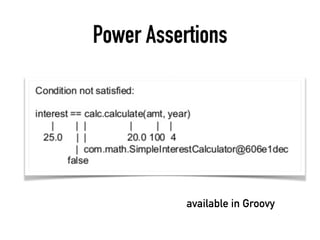
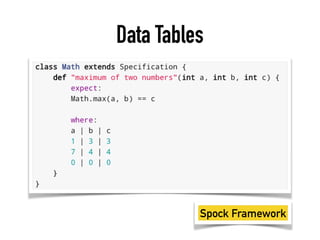
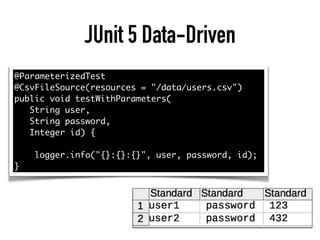
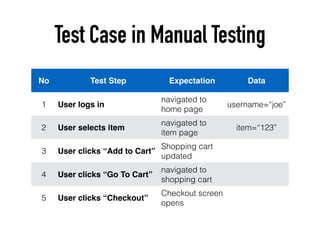
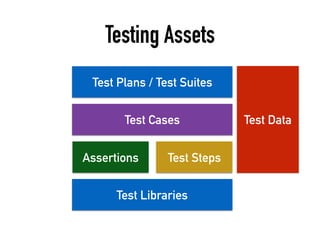
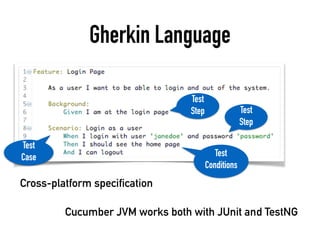
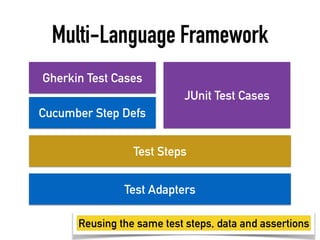
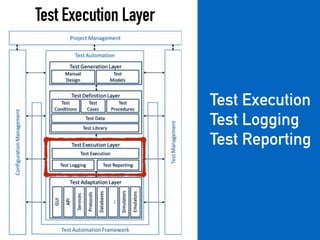
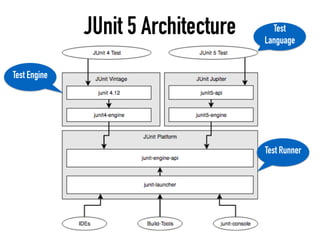
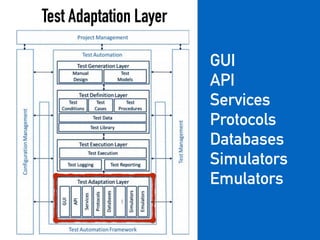
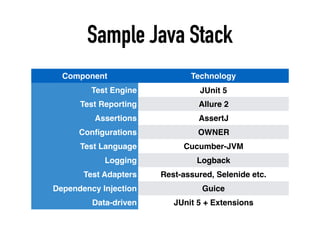
The document provides a detailed guide on building a test automation framework, emphasizing requirements like minimal cost of ownership, integration with existing tools, and transparency. It discusses the distinction between frameworks and libraries, outlines essential components such as test libraries, test cases, and assertion strategies, and introduces various technologies involved like JUnit 5 and Cucumber. Additionally, it highlights the importance of logging, reporting, and configuration, concluding with a call to action for test automation enthusiasts.