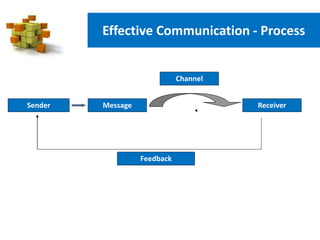
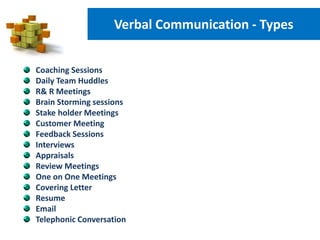
The document discusses effective communication. It covers the purpose of communication which is to understand and be understood. It also discusses the communication process which involves a sender, message, channel, receiver, and feedback. Key aspects of effective communication include knowing your subject, having clear objectives, preparation, audience analysis, delivery, and analyzing feedback. It also discusses types of communication including verbal and non-verbal, as well as listening, benefits of listening, tips for listening, and barriers to effective listening. Finally, it provides tips for effective communication and how positive and negative emotions can impact communication.