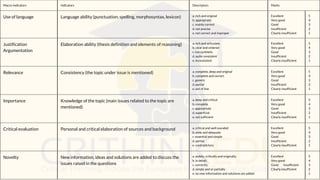
The document discusses the complexities of assessing critical thinking skills, emphasizing various activities and methodologies for effective evaluation. It outlines key cognitive skills and dispositions necessary for critical thinking, along with an overview of assessment methods, including open-ended questions and their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it encourages educators to design assessment tools tailored to their disciplines, aligning with established definitions of critical thinking.