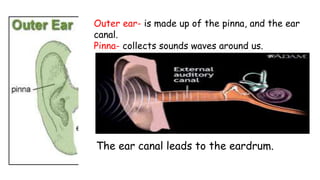
The three main parts of our ears are the outer, middle, and inner ear. The outer ear collects sound waves and channels them through the ear canal to the eardrum. The eardrum connects to three tiny bones in the middle ear that transmit vibrations to the inner ear. The inner ear contains fluid-filled semicircular canals and the cochlea, which sends sound messages through the auditory nerve to the brain for interpretation. Common ear problems include infections caused by germs entering the ear through the Eustachian tube, resulting in pain, fever, discharge, or hearing loss.