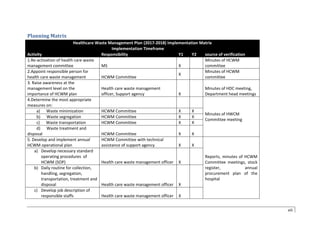
The document provides a healthcare waste management plan for District Trishuli Hospital in Nuwakot, Nepal. It begins with an assessment of the current waste management situation, finding issues like a lack of proper segregation and insufficient resources. The plan then outlines basic steps to improve management, including reactivating the waste management committee, providing staff training, developing standard operating procedures, and monitoring progress. The overall goal is to provide a framework to ensure safe and effective healthcare waste handling practices at the hospital.