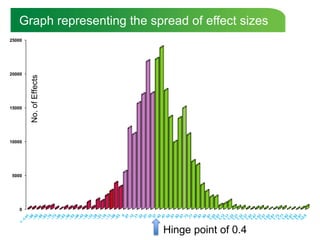
This document summarizes key findings from John Hattie's meta-analysis of over 900 studies involving over 50,000 studies on factors that influence student achievement. Some of the main findings include:
- Formative evaluation of teachers, how pupils rate their teachers, and teacher-student relationships have among the highest effects on student achievement.
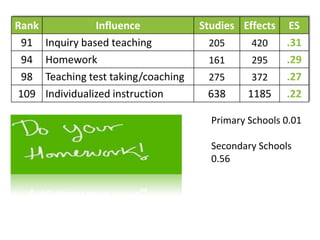
- Factors like matching learning styles, teachers' subject knowledge, and class size have smaller effects.
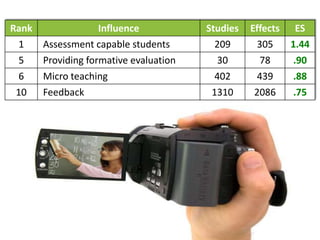
- Visible learning research shows that assessment capable students, providing formative evaluation to teachers, and microteaching have the top influences on student achievement.
- Warmth, encouragement of higher-order thinking skills, empathy, and non-directivity most influence student-