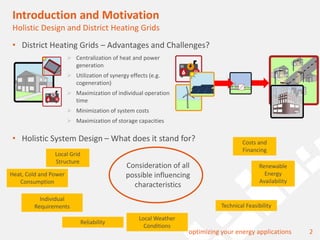
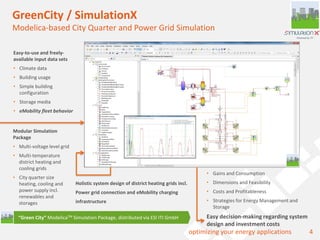
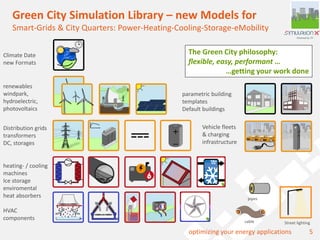
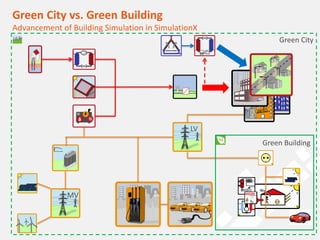
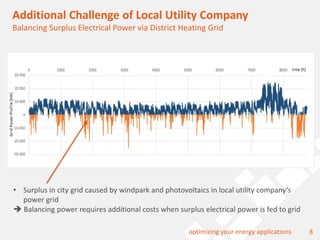
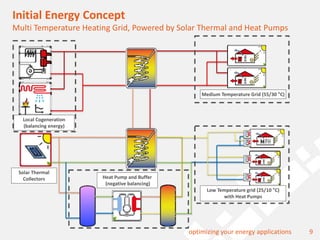
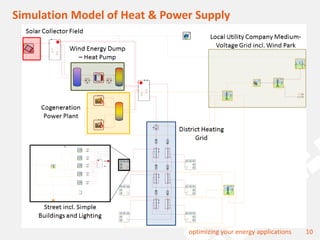
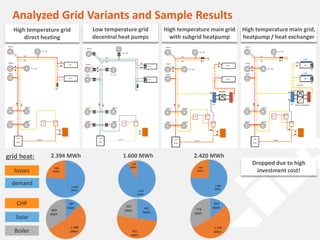
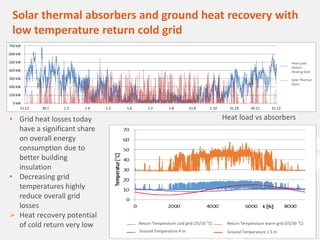
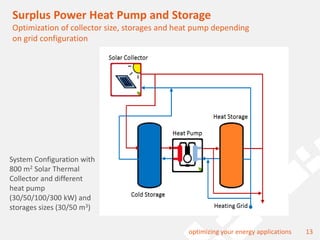
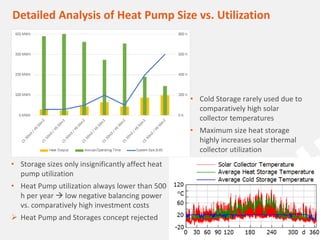
The document discusses a holistic district heating grid design using SimulationX, emphasizing buildings as central components of smart grids due to their predictable heating and cooling demands. It details the implementation of a local heating grid in Bavaria, utilizing renewable solar heat and heat pump systems to balance surplus electrical power. The presentation highlights the use of simulation models to optimize energy applications and identify optimal configurations for district heating grids and their integration with power and cooling systems.


![7optimizing your energy applications
New Residential Area – Osterfeld, City of Haßfurt
Small Town Detached Housing and Appartement Buildings
[google maps]
[Stadt Haßfurt]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/easystemsschwanungeresisimulationxuserforum-170216142313/85/Holistic-District-Heating-Grid-Design-with-SimulationX-Green-City-8-320.jpg)


![Thank you for your
attention
[Esters2012]
Contact:
EA Systems Dresden GmbH
Würzburger Str. 14
01187 Dresden
+49-351-467-136-52
torsten.schwan@ea-energie.de](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/easystemsschwanungeresisimulationxuserforum-170216142313/85/Holistic-District-Heating-Grid-Design-with-SimulationX-Green-City-19-320.jpg)