This document provides an overview of host modulation therapy. It defines host modulation therapy and discusses its historical background and rationale. The key points are:
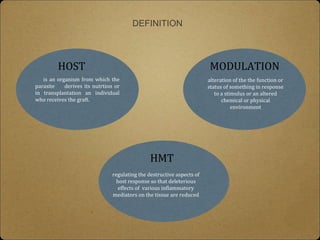
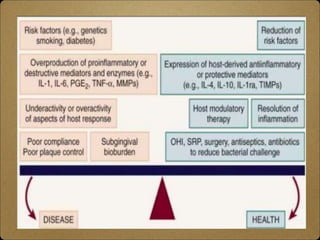
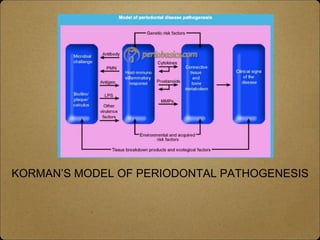
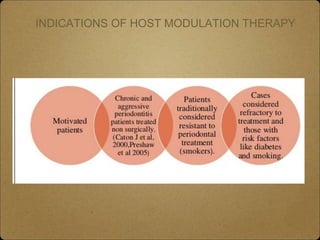
- Host modulation therapy aims to regulate the destructive aspects of the host response to periodontal disease to reduce tissue damage. It works by modifying inflammatory mediators.
- Pioneering work in the 1970s by Golub and colleagues first demonstrated that tetracycline could inhibit host-derived collagenases and reduce tissue destruction. This laid the foundation for host modulation therapy.
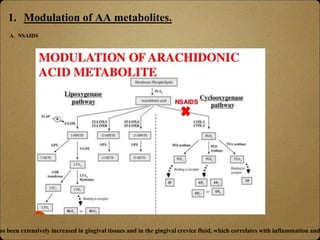
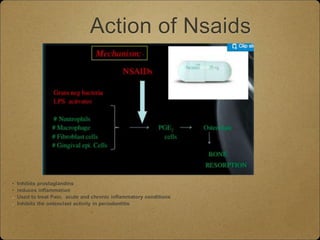
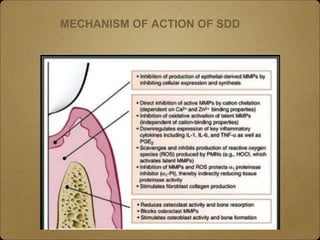
- Locally administered agents like subantimicrobial dose doxycycline and NSAIDs have been shown to reduce inflammatory mediators like MMPs and prostaglandins that contribute to periodontal breakdown