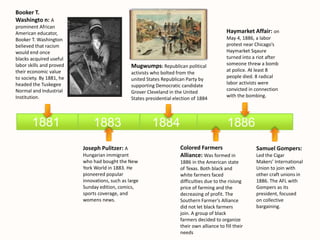
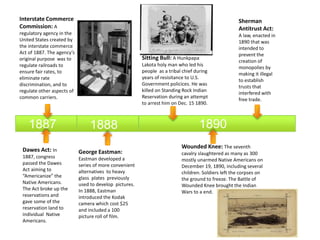
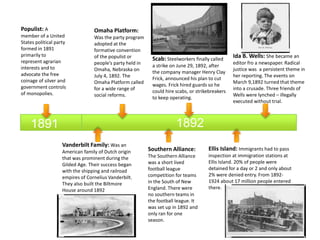
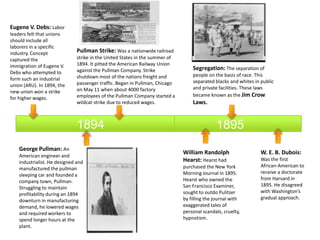
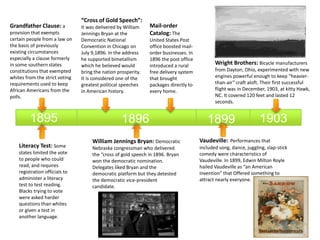
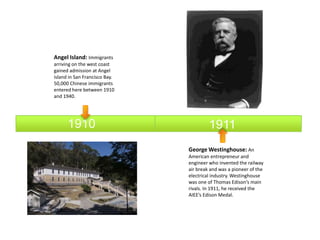
The document provides a timeline of important events in American history between 1865 and 1895. Some key events include:
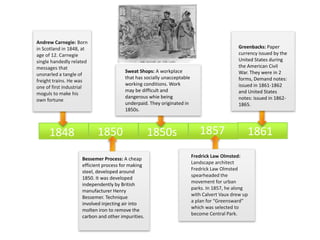
- Andrew Carnegie establishing himself as an industrial mogul in the steel industry in the late 1860s.
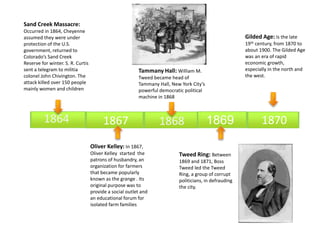
- The passage of the Homestead Act in 1862, which offered free land to settlers, and the transcontinental railroad being completed in 1869.
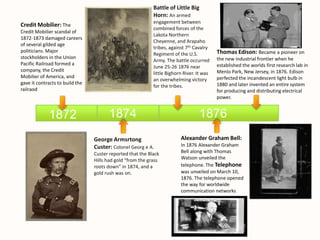
- Thomas Edison establishing the first research lab in 1876 and inventing the incandescent light bulb. Alexander Graham Bell unveiling the telephone the same year.
- The Battle of Little Bighorn in 1876 resulting in victory for Native American tribes over the 7th Cavalry.
- The Pullman Strike of 1894 shutting down most rail traffic as