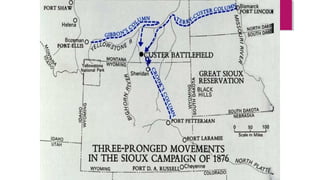
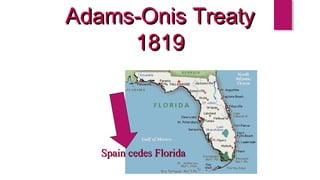
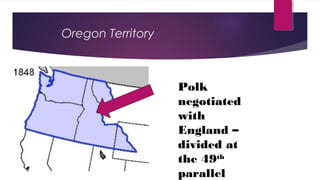
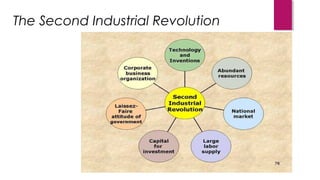
General Custer and 268 of his troops were killed at the Battle of Little Bighorn in 1876 in a major defeat by Native American forces led by Sitting Bull and Crazy Horse. Westward expansion in the 19th century was driven by gold miners, farmers, Chinese laborers, and European immigrants. The development of the West was also impacted by several key laws and events, including the Homestead Act of 1862 which gave settlers land, the Transcontinental Railroad which connected the country, and the invention of barbed wire which enabled the enclosure of open ranges.