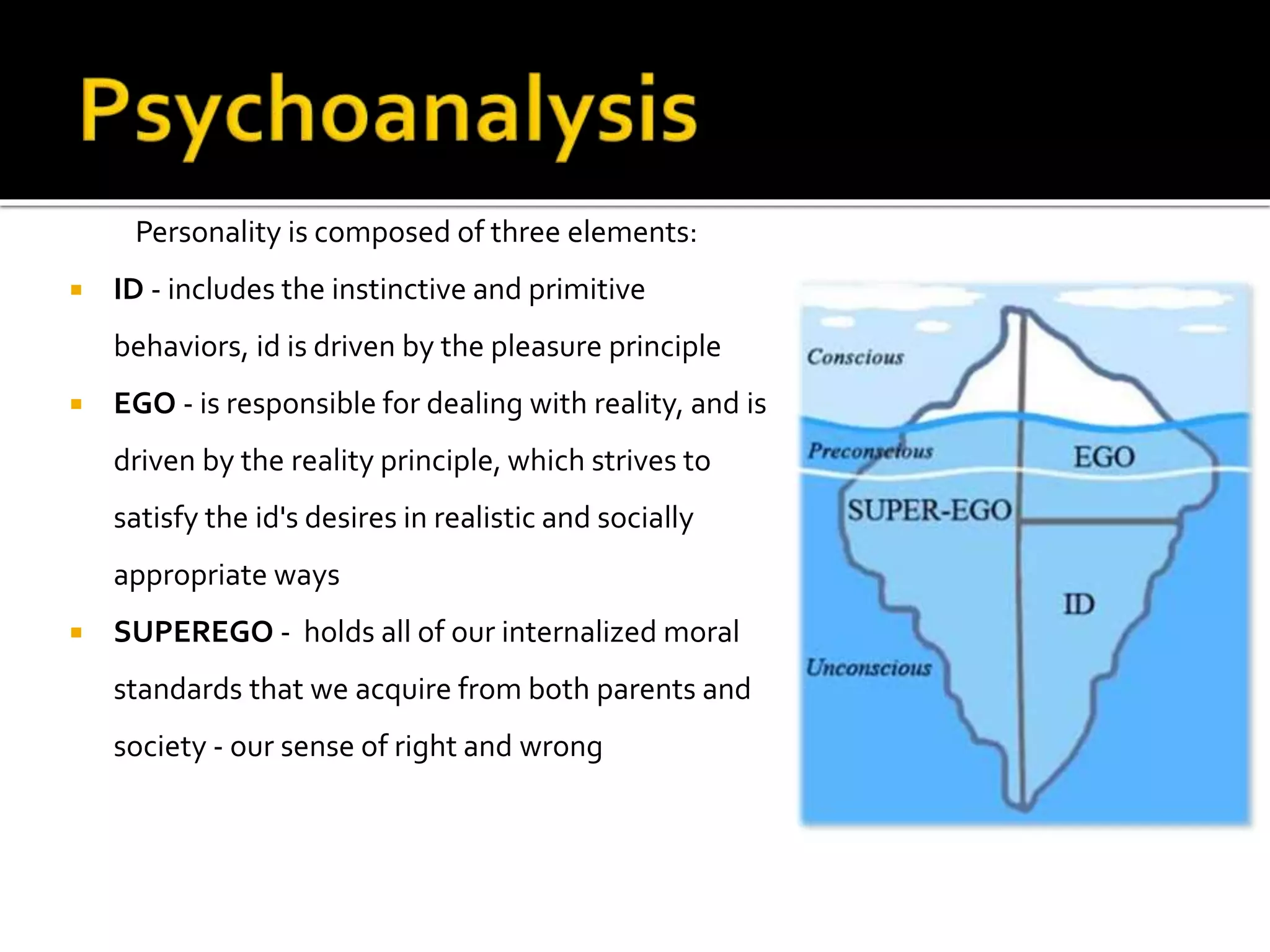
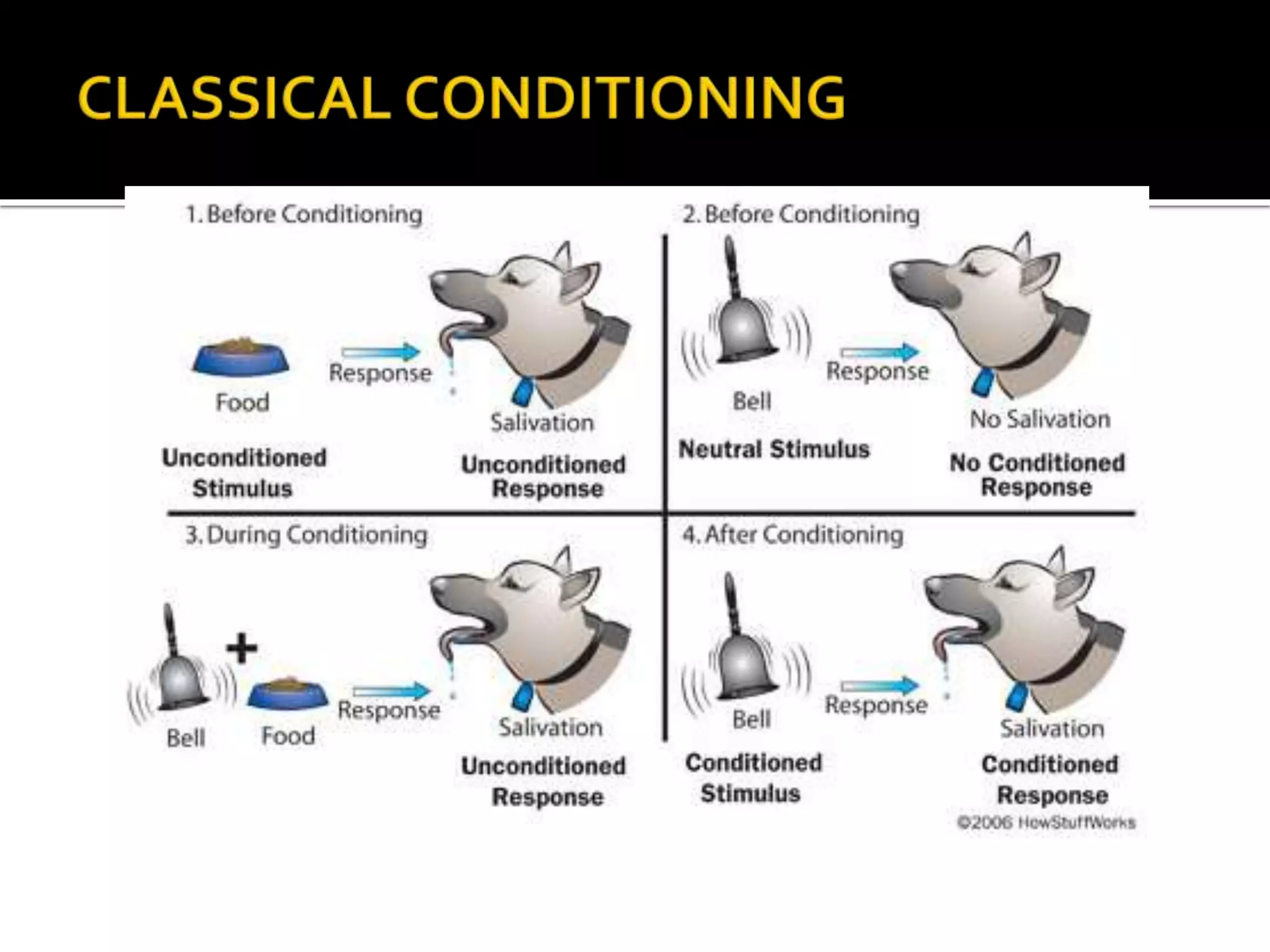
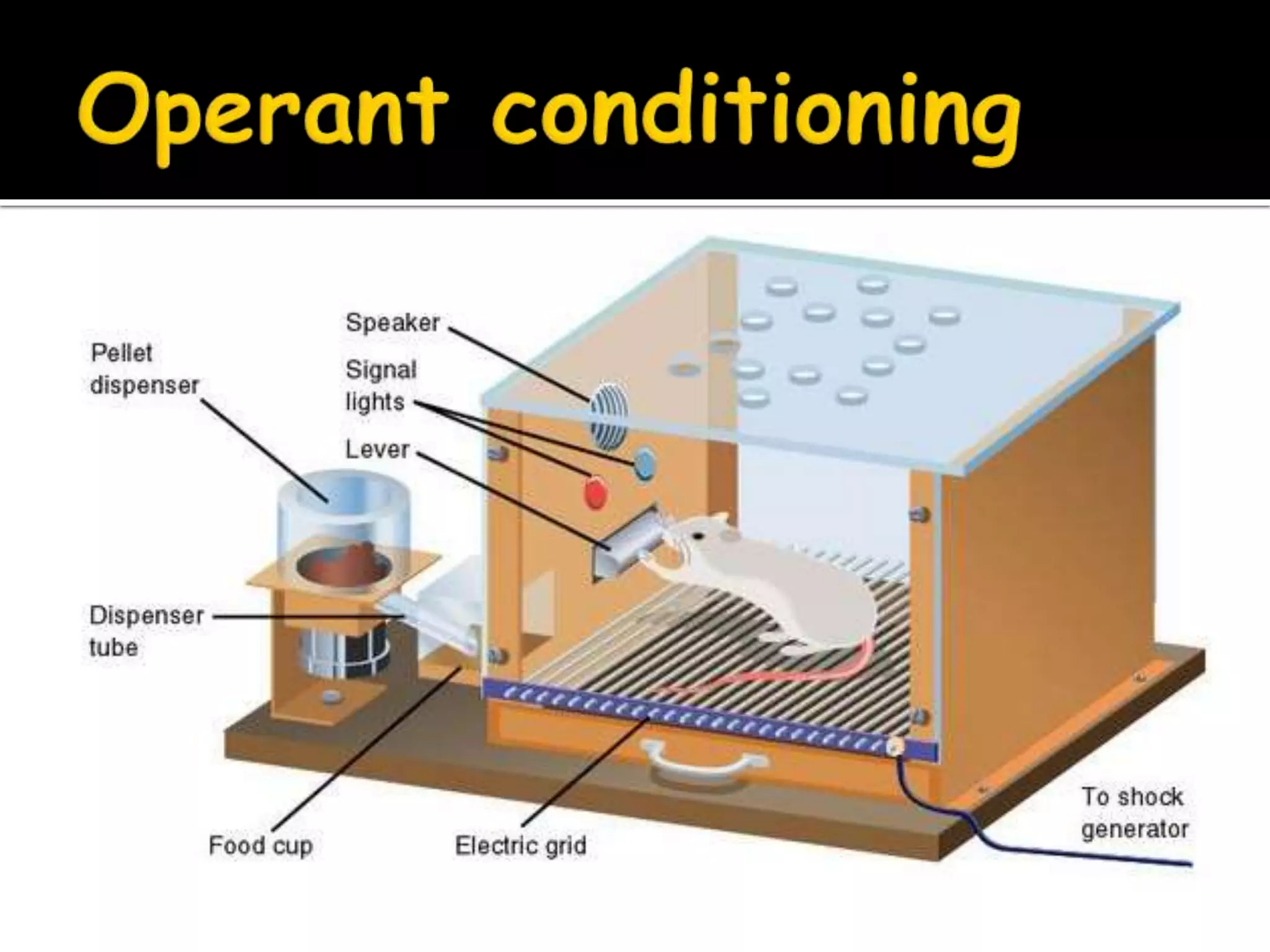
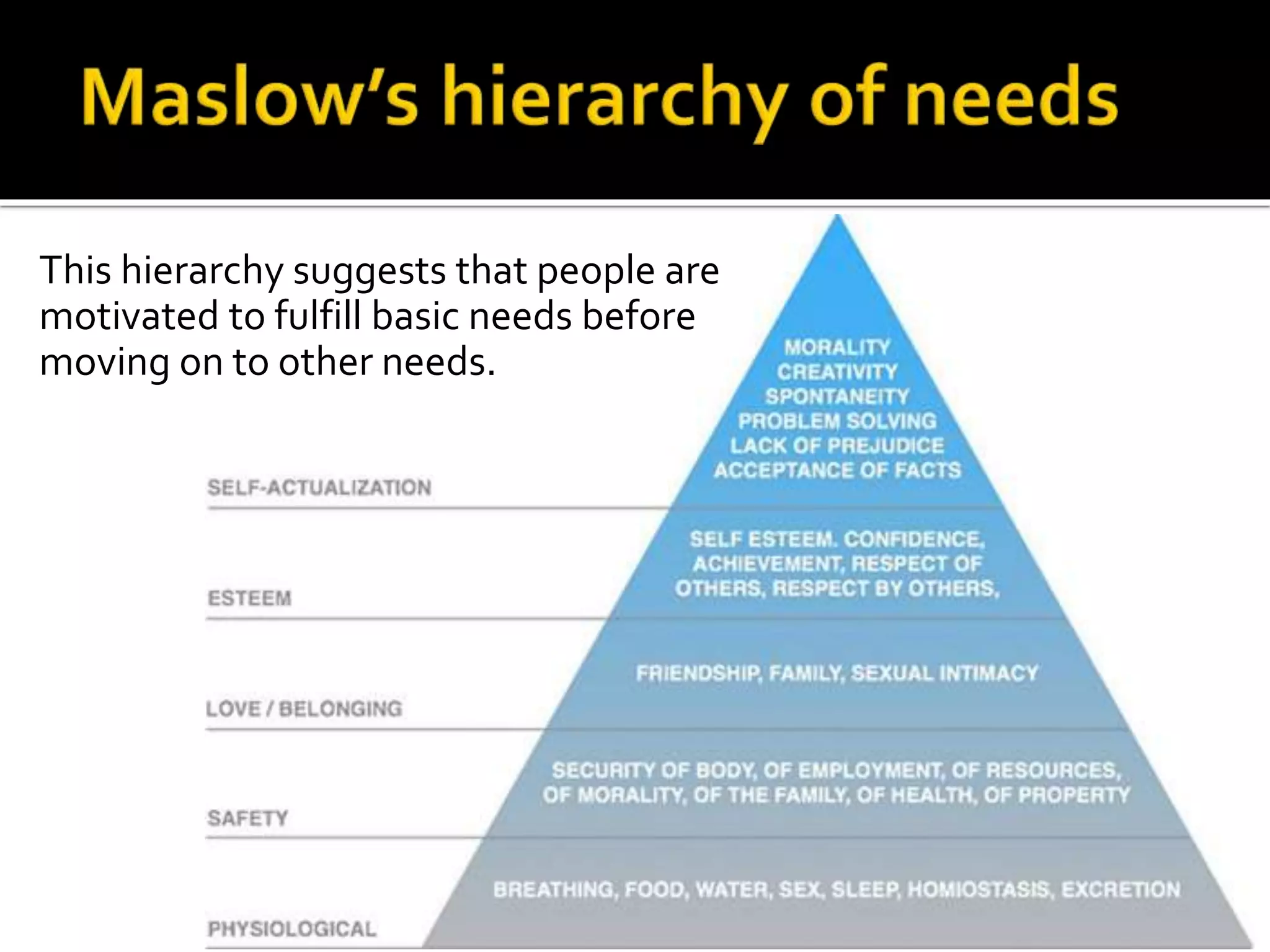
Psychology is the scientific study of the human mind and behavior. Some key developments in the field include Wilhelm Wundt opening the first psychology lab in 1879, Sigmund Freud founding psychoanalysis and developing talk therapy in the late 1800s, John Watson establishing behaviorism in the early 1900s, and Abraham Maslow and Carl Rogers founding humanistic psychology in the mid-1900s with its emphasis on self-actualization and free will. The field has sought to understand human behavior through scientific research methods including experiments, theories, and various psychological perspectives.