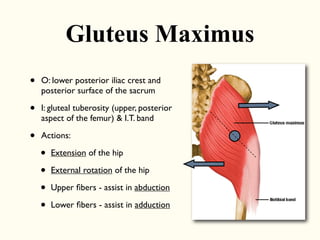
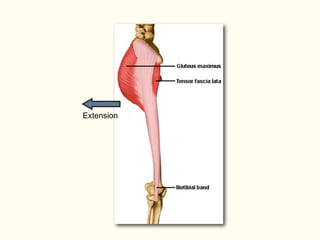
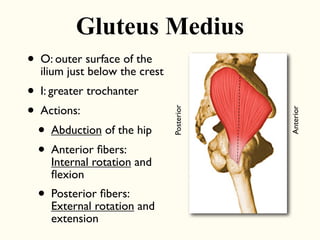
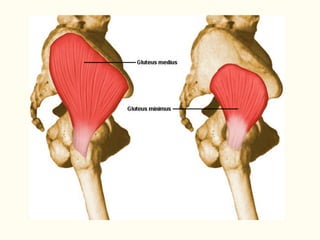
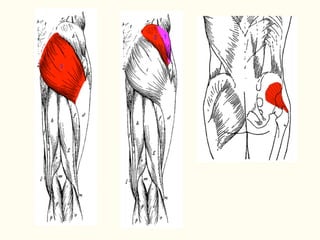
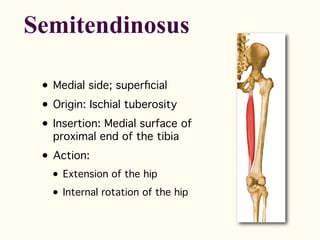
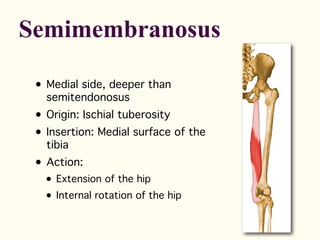
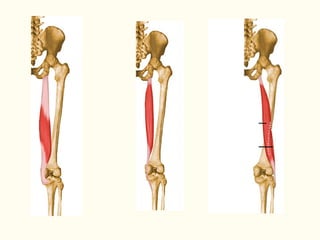
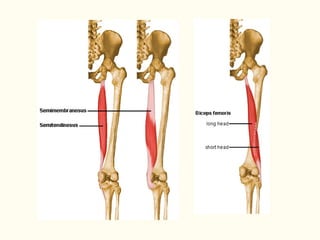
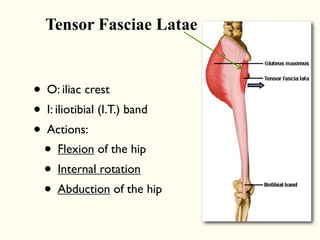
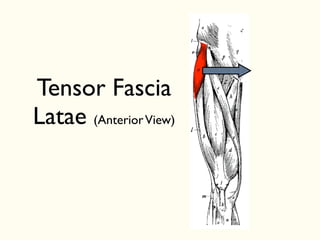
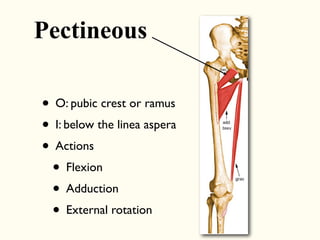
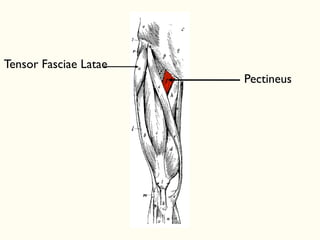
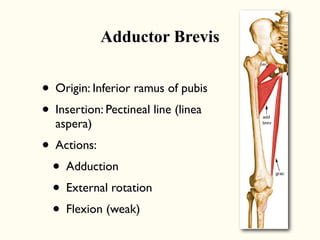
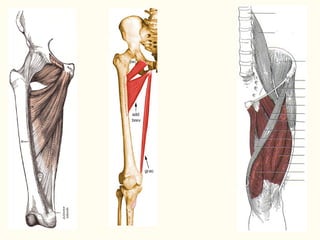
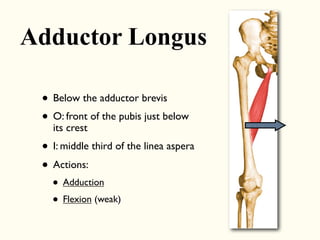
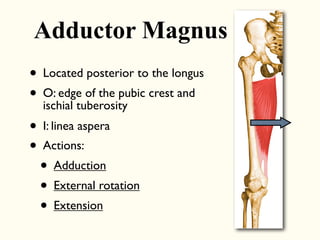
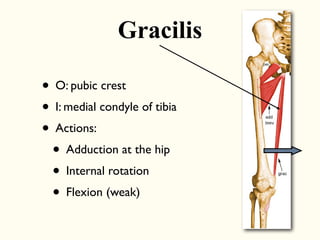
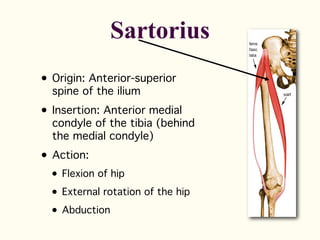
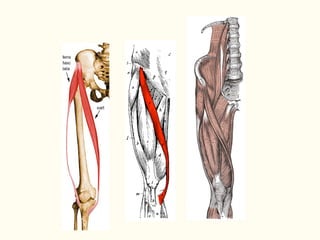
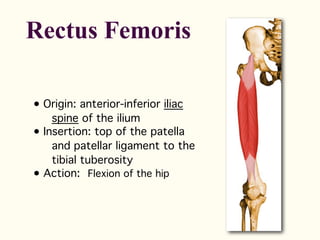
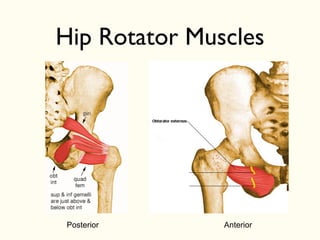
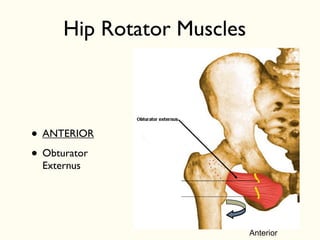
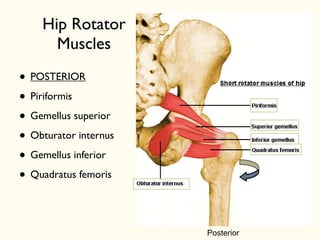
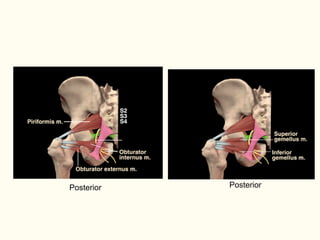
This document describes the origins, insertions, and actions of various muscles around the hip joint. It includes the gluteal muscles (maximus, medius, and minimus) which extend, abduct, and externally rotate the hip. The hamstring muscles (biceps femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus) extend and internally rotate the hip. Other muscles like the tensor fasciae latae, iliopsoas, pectineus, adductors, gracilis, sartorius, and rectus femoris flex, adduct, abduct, internally and externally rotate the hip. The six small posterior hip rotator muscles are also noted.