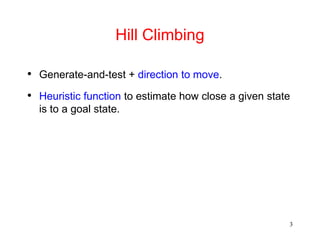
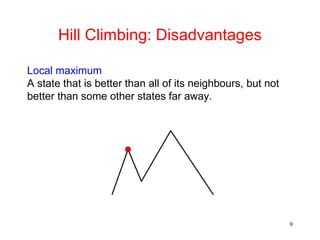
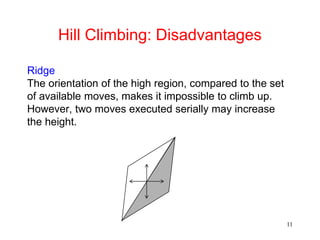
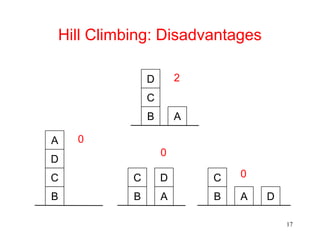
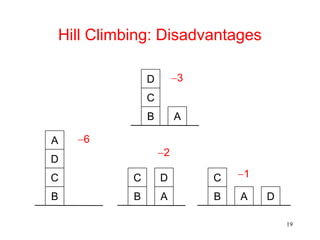
The document discusses hill climbing, an optimization technique used in problem solving. Hill climbing works by starting with an initial state and iteratively moving to a neighboring state that has a better value based on a heuristic evaluation function, until reaching a goal state. Simple hill climbing evaluates each new state, keeping it if better than the current state. Steepest-ascent hill climbing considers all moves and selects the best neighboring state. Potential issues are getting stuck in local maxima, plateaus, or ridges rather than the global maximum. The document provides an example of applying hill climbing to solve a blocks world problem.