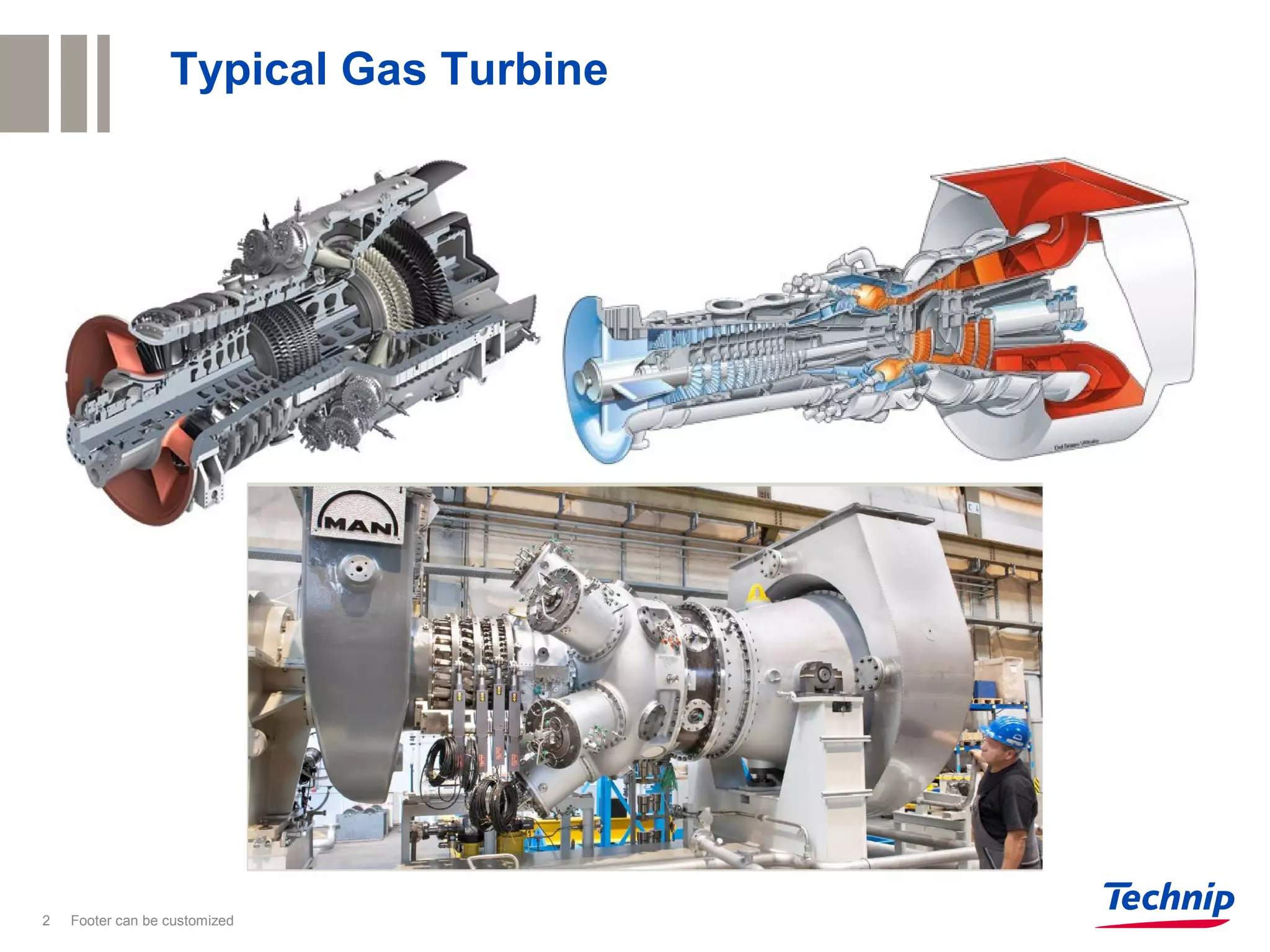
1. The document discusses a gas turbine generator site with power demands of 23MW. The gas turbines on site are Siemens SGT-400 models rated at 13.9MW each.
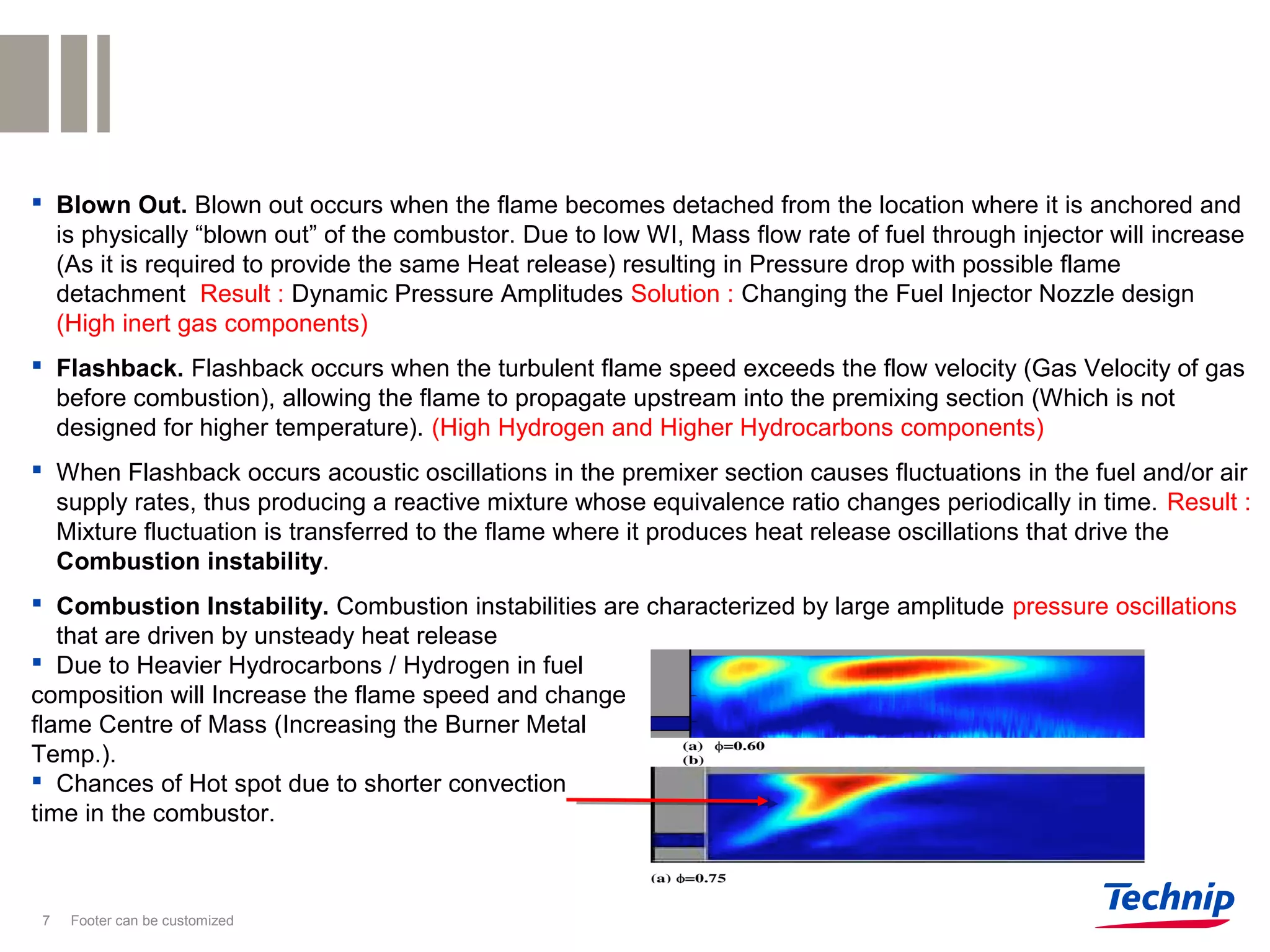
2. It describes challenges with using higher hydrocarbon and hydrogen-rich fuels in gas turbines, such as increased risk of flashback and combustion instability. Heavier fuels require heating to maintain a suitable modified Wobbe index.
3. Solutions proposed include heating the fuel gas to adjust its Wobbe index, and rig testing of combustors with higher calorific value, high hydrogen fuels to evaluate performance.