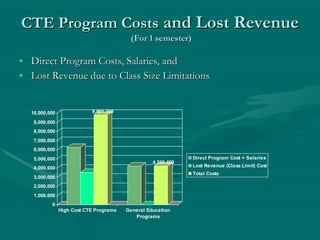
Trade Technical College has been offering career technical programs for over 95 years, educating over 75,000 students in those programs over the past 5 years. 29 of their career technical programs are considered "high cost" due to specialized equipment, lab space, and instructional needs. A cost study found that direct costs for high-cost career technical programs are over 5 times higher than general education programs, and revenues are 68.7% lower due to smaller class sizes. Other states have implemented differential funding multipliers between 1.19 to 2.0 on average to compensate for these higher costs of career technical programs. The recommendation is for the college to approve a 1.59 multiplier to help fund their high-cost career technical programs.











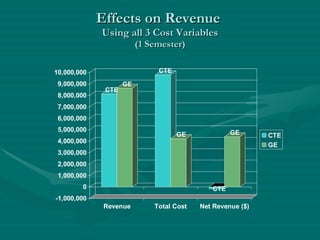






![Recommendation To approve and implement a funding differential multiplier of 1.59 / FTES for high cost CTE programs. [Note: this multiplier equals both the total cost difference between CTE and GE programs at the college AND the average CTE multiplier of other states with differential funding]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/high-cost-program-presentation-1226911072220608-8/85/High-Cost-Program-Presentation-20-320.jpg)