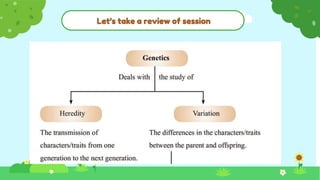
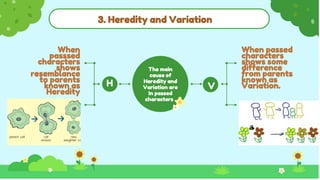
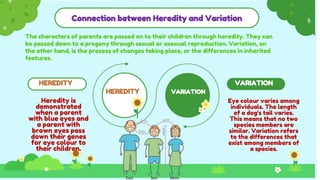
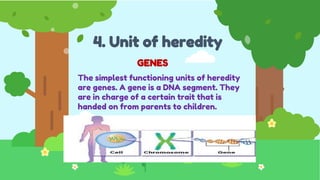
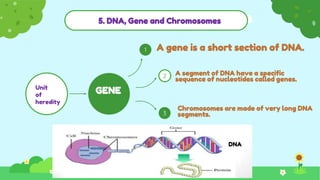
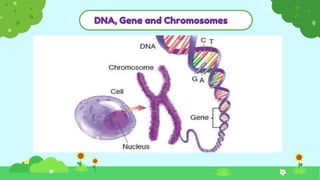
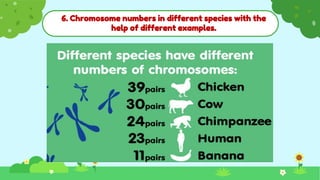
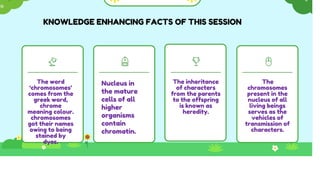
This document discusses heredity and variation, explaining how traits are passed from parents to offspring and the significance of genetics as a branch of biology. It highlights key concepts such as genes, DNA, chromosomes, and the variation among species, alongside contributions from notable scientists. The document outlines the structure and function of genetic material, emphasizing the connection between heredity and variation.