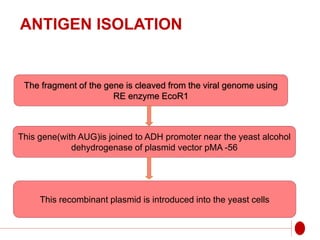
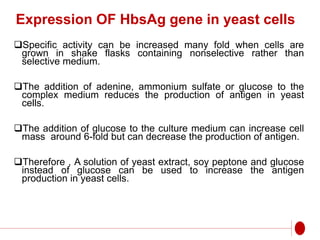
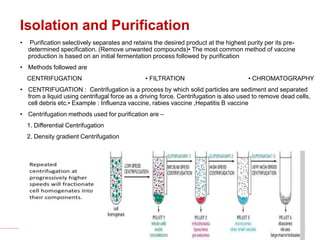
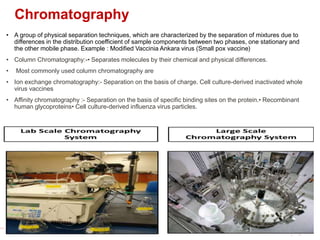
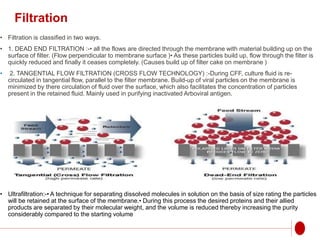
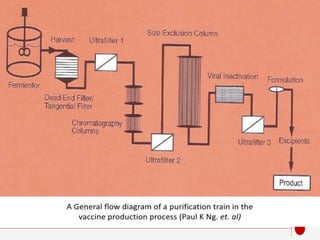
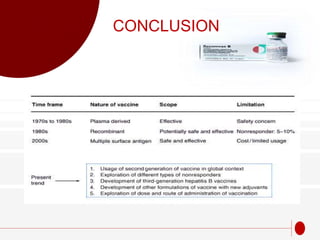
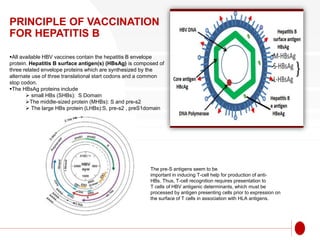
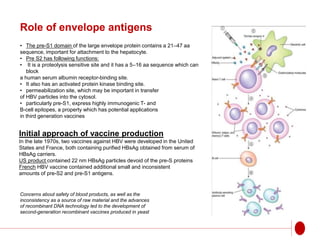
The document discusses recombinant DNA technology for producing hepatitis B vaccines. It begins by introducing the different types of hepatitis viruses and diseases. It then describes the structure and life cycle of the hepatitis B virus. The key aspects of producing recombinant hepatitis B vaccines are using the viral surface antigen gene isolated from the hepatitis B virus genome and expressing it in host cells like yeast or mammalian cells. The vaccines produced this way have been found to be safe and effective alternatives to plasma-derived vaccines.

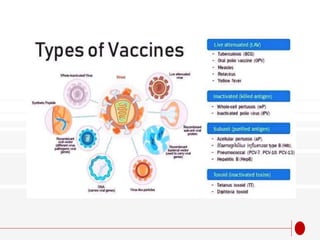




![Recombinant vaccines
two recombinant vaccines :
Engerix-B (SmithKline Biologicals, Belgium)
RECOMBIVAX HB-Vax II (Merck & Co., USA) [22,23].
These two vaccines contain non-glycosylated SHBs p24, which must be released from
the yeast during the manufacturing process](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hepatitisbvaccine-221027175831-dee944f2/85/hepatitis-B-vaccine-pptx-13-320.jpg)