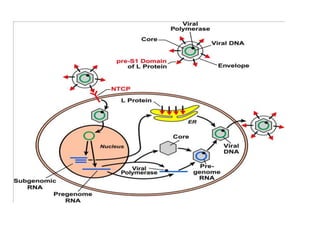
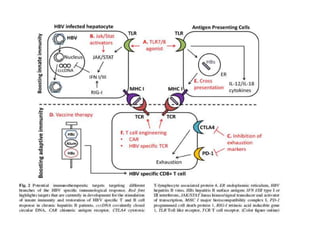
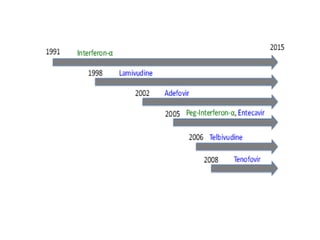
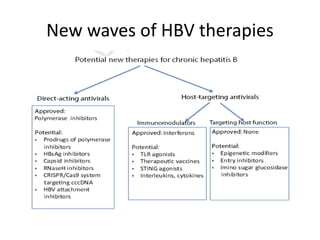
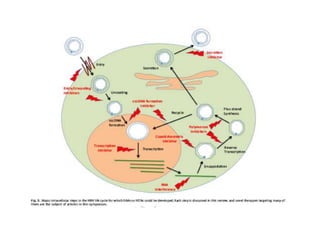
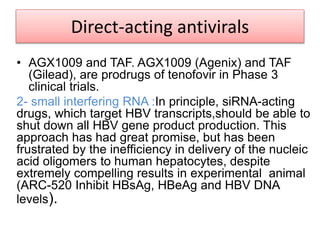
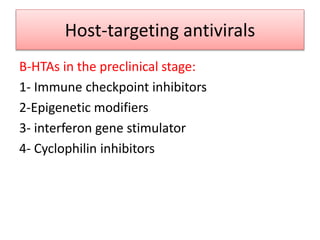
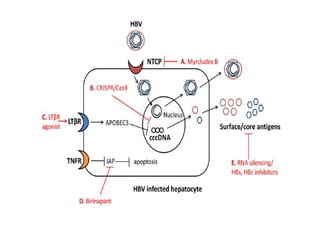
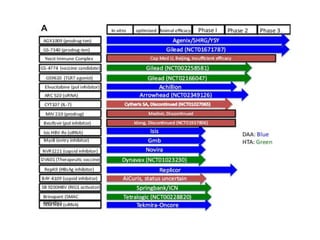
Chronic hepatitis B infection is a major global health issue, affecting around 248 million people. Current treatments like nucleoside analogues and interferon are not curative and have limitations. New therapies targeting the hepatitis B virus directly or the host immune response are in development. Direct-acting antivirals in clinical trials inhibit the viral polymerase, capsid formation, HBsAg secretion, and RNase H. Host-targeting approaches trial immune enhancers, viral entry inhibitors, vaccines, and pro-apoptotic drugs. Promising preclinical candidates additionally modulate immunity, epigenetics, interferons, and cyclophilins. These novel therapies aim to achieve functional cures for chronic hepatitis B.