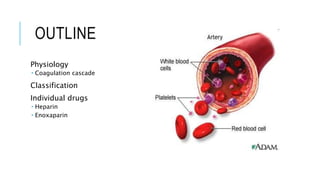
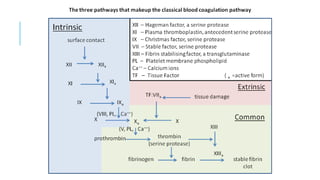
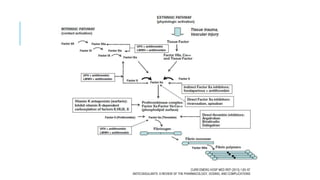
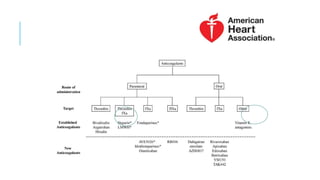
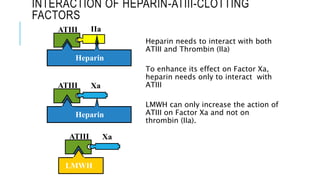
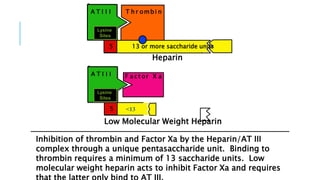
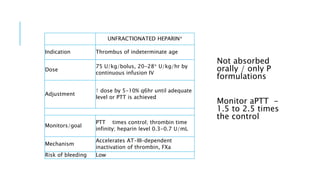
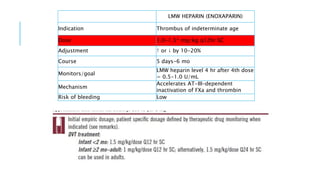
This document discusses heparin and enoxaparin, two anticoagulant drugs. It begins by outlining the coagulation cascade and where these agents act to inhibit it. Specifically, it notes that heparin inhibits thrombin and factor Xa by enhancing antithrombin, while enoxaparin primarily inhibits factor Xa. The document then covers the indications, dosing, monitoring, and adverse effects of both unfractionated heparin and enoxaparin. Key differences are that enoxaparin has higher bioavailability, longer duration of action, and is dosed subcutaneously rather than via intravenous infusion like unfractionated heparin.