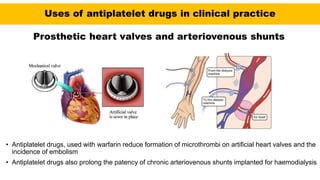
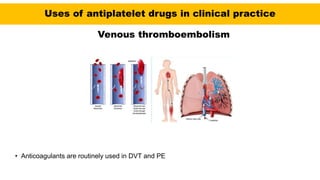
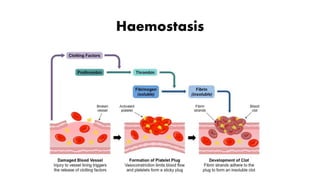
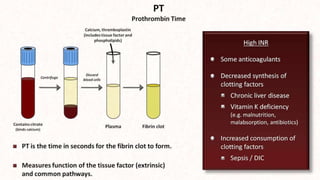
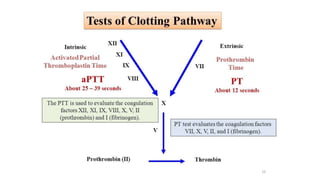
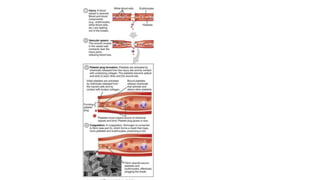
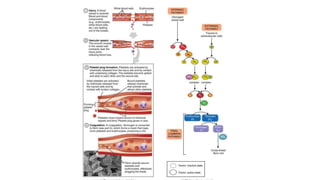
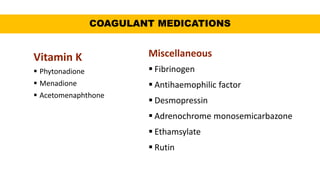
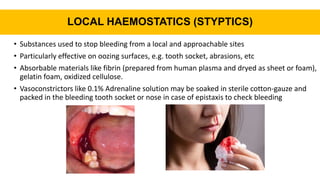
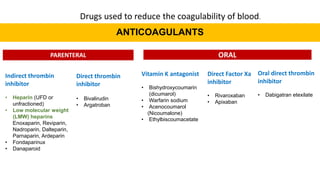
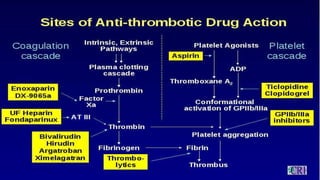
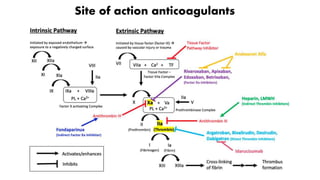
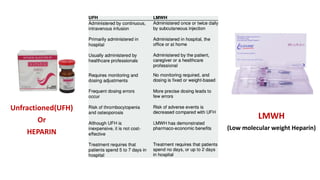
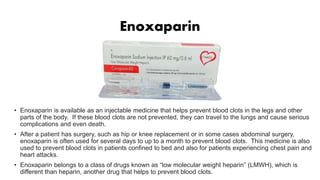
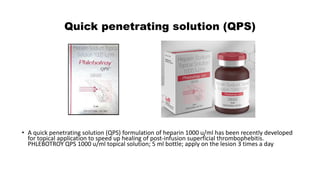
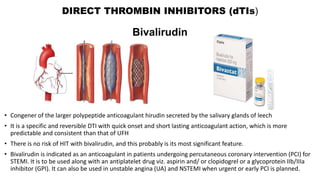
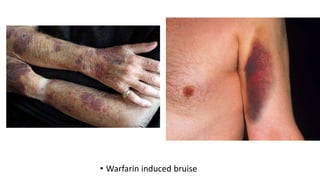
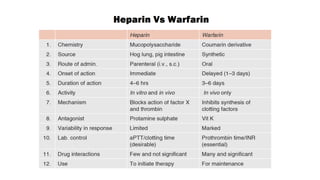
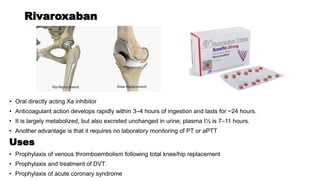
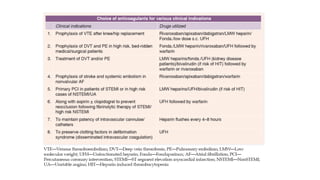
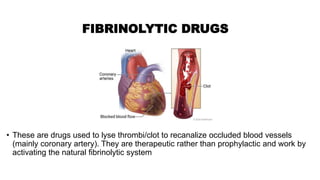
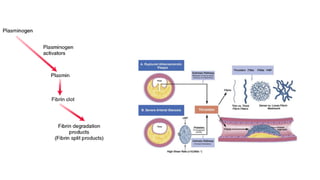
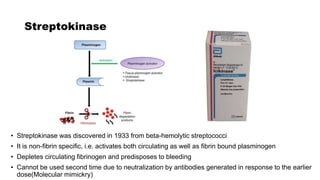
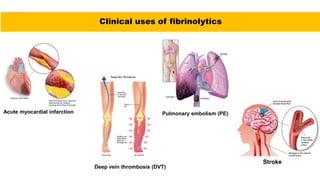
This document discusses anticoagulants and antiplatelet drugs. It describes how anticoagulants prevent blood clotting by inhibiting coagulation factors, while some occur naturally in animals. Common anticoagulants discussed include heparin, low molecular weight heparins like enoxaparin, and vitamin K antagonists like warfarin. The mechanisms and sites of action are explained for different classes of anticoagulants. Advantages of LMWH over unfractionated heparin include better bioavailability and more predictable response. Bleeding is a major adverse effect of anticoagulant overdose.

































![ANTIPLATELET DRUGS
(Antithrombotic drugs)
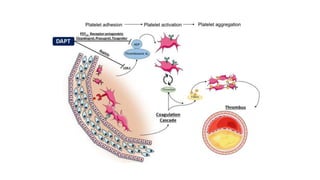
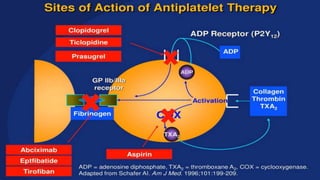
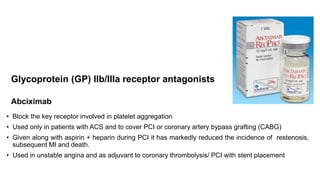
• These are drugs which interfere with platelet function and are useful in the prophylaxis of
thromboembolic disorders.
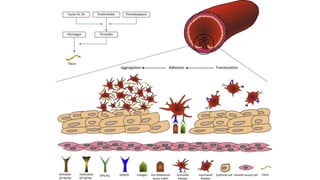
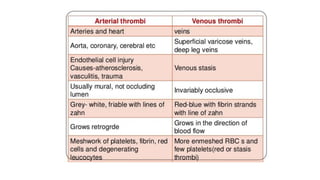
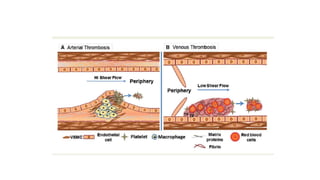
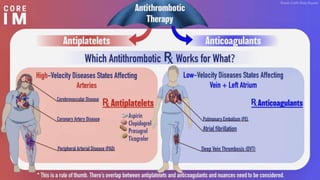
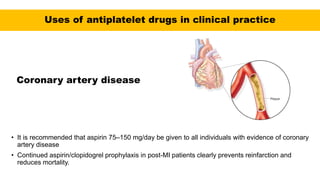
• In arteries, platelet mass is the main constituent of the thrombus. Antiplatelet drugs are,
therefore, more useful in arterial thrombosis, while anticoagulants are more effective in venous
thrombosis.
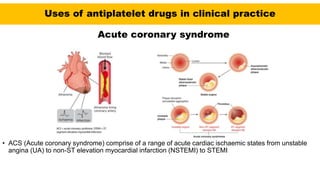
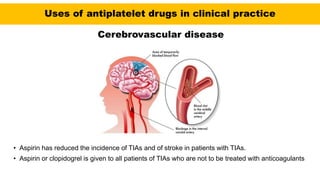
• The major role of antiplatelet drugs in clinical practice is to prevent the adverse clinical
sequelae of thrombosis in atherosclerotic arteries to the heart (acute coronary syndromes
[ACS]), brain (ischaemic stroke), and limbs (intermittent claudication and rest pain); and
thrombosis of stagnant blood in veins](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anticoagulants-cmk-final-210808190757/85/Anticoagulants-medications-67-320.jpg)