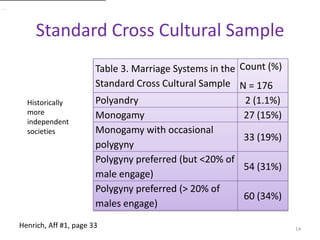
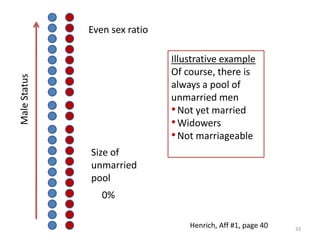
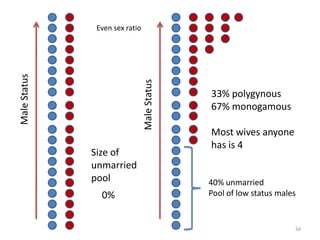
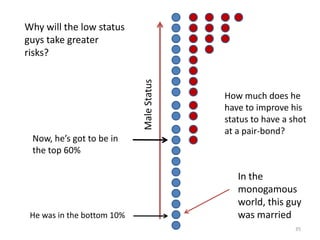
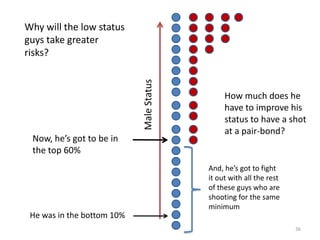
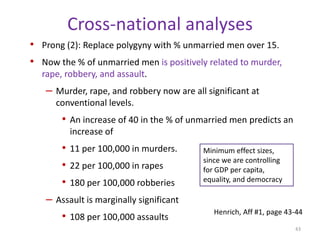
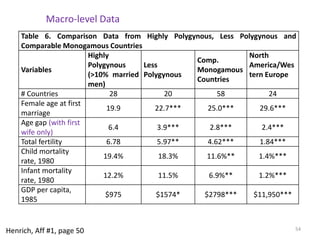
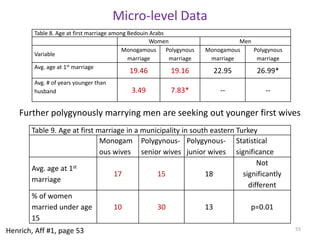
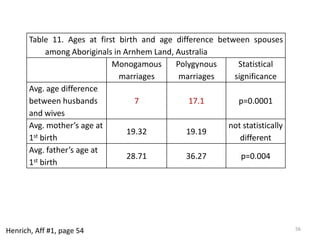
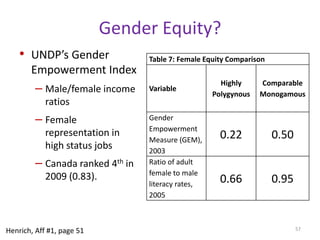
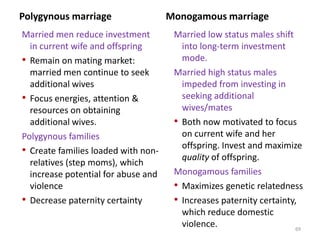
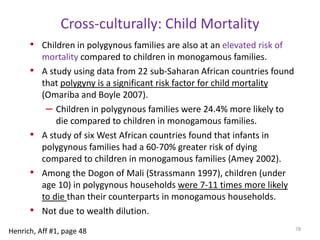
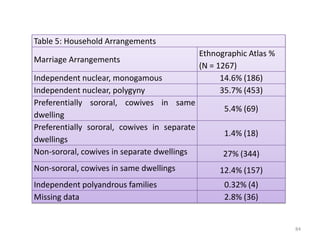
The document explores the evolution of human mating systems and marriage, emphasizing the differences in male and female mating psychologies and their societal impacts. It discusses how cultural norms influence the prevalence of polygyny and monogamy, illustrating the nuanced relationships between social status, paternal investment, and family dynamics. Furthermore, it presents data suggesting that monogamous marriages may reduce crime and improve outcomes for low-status males compared to polygynous systems.