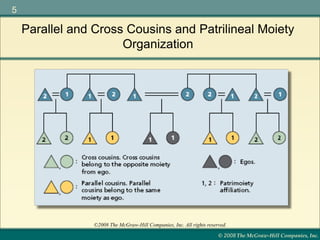
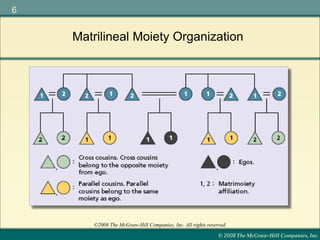
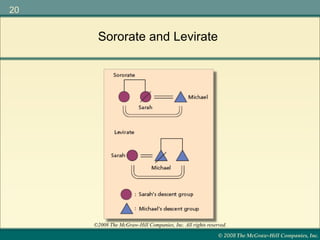
Marriage is defined differently across cultures and serves various purposes such as establishing legal parentage, giving spouses rights, and forming group alliances. Incest is universally taboo, though what constitutes incest varies. Explanations for the incest taboo include promoting genetic diversity through exogamy and avoiding disrupting family structures. Marriage customs such as bridewealth, dowry, and post-marital residence patterns influence divorce rates and kinship systems.