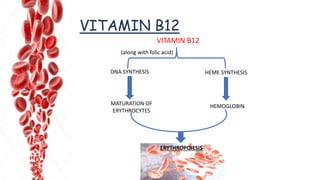
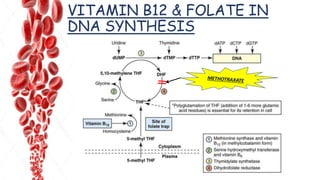
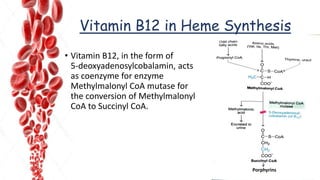
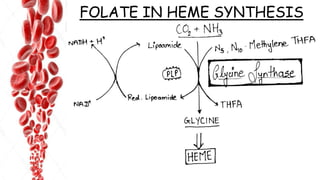
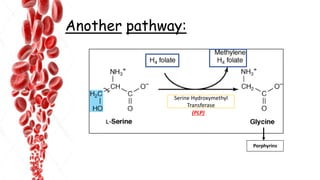
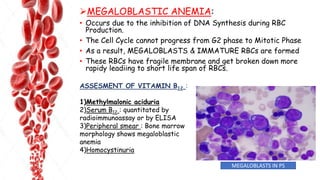
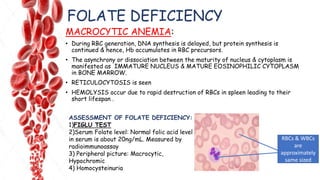
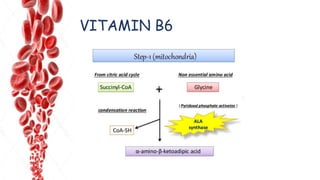
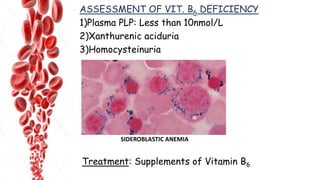
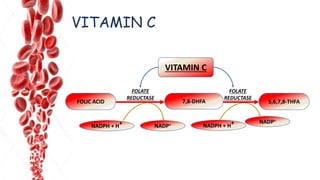
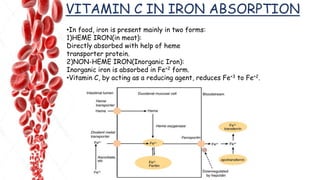
The document discusses hemopoietic vitamins essential for blood cell production, including the roles of vitamin B12, folic acid, and vitamin B6 in hemopoiesis and anemia treatment. It explains the consequences of deficiencies, such as pernicious anemia and megaloblastic anemia, their causes, and diagnostic methods. Additionally, it covers the importance of vitamin C in iron absorption and outlines dietary sources of these vitamins.