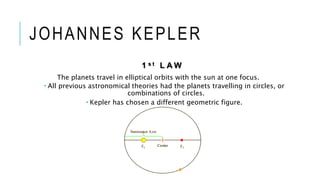
The document discusses the development of the heliocentric theory from Aristotle to Galileo. It began with Aristarchus proposing a heliocentric model over 2000 years ago, though the geocentric Ptolemaic system remained dominant. Nicolaus Copernicus later revived the heliocentric theory in the 16th century, providing a simplified mathematical model. Johannes Kepler further developed the theory through his laws of planetary motion. Galileo Galilei then provided strong observational evidence in favor of heliocentrism through his telescopic discoveries. The heliocentric theory fundamentally changed astronomical and scientific understanding.