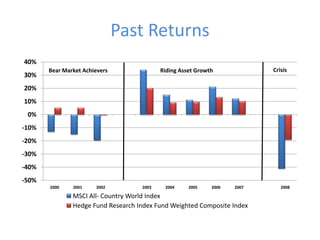
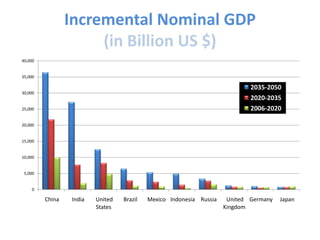
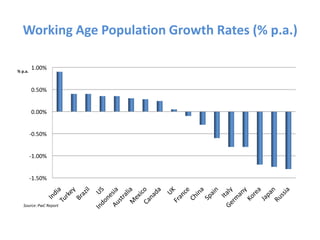
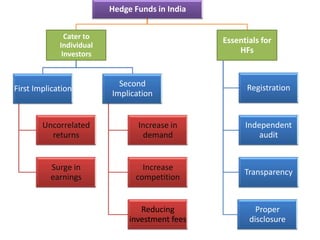
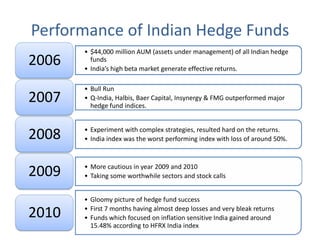
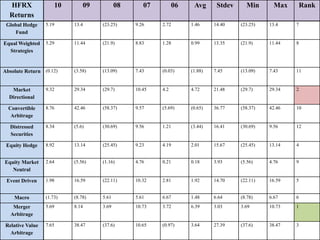
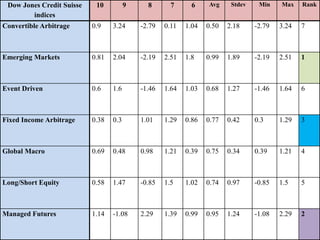
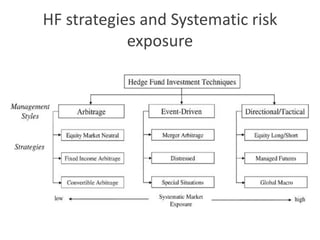
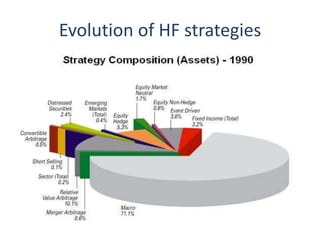
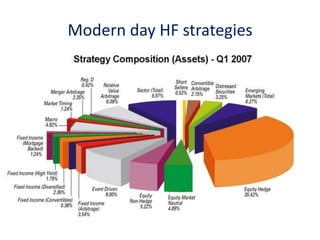
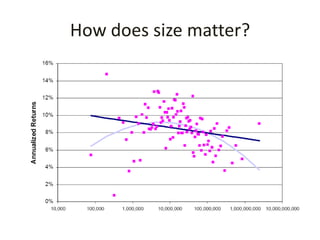
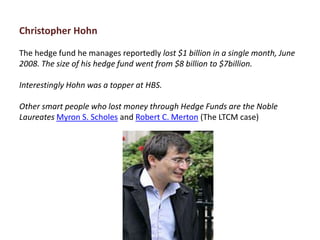
The document outlines the definition, strategies, and performance of hedge funds, emphasizing their objective of generating absolute returns with flexible investment approaches. It discusses the Indian hedge fund context, highlighting the attractiveness of India's market to investors and detailing regulatory frameworks governing hedge funds. Various hedge fund strategies are explored, showcasing how they navigate risks and volatility, along with notable historical performances and challenges faced by prominent hedge fund managers.